Using Prophet Modeling to look for Outliers in Groundwater Level Data
At Locus, we are constantly exploring innovative ways to visualize and analyze large datasets, empowering users to derive insights with ease.
At Locus, we are constantly exploring innovative ways to visualize and analyze large datasets, empowering users to derive insights with ease.
When looking for a GHG reporting program, there is one element that is typically overlooked. This short video gives us more insight.
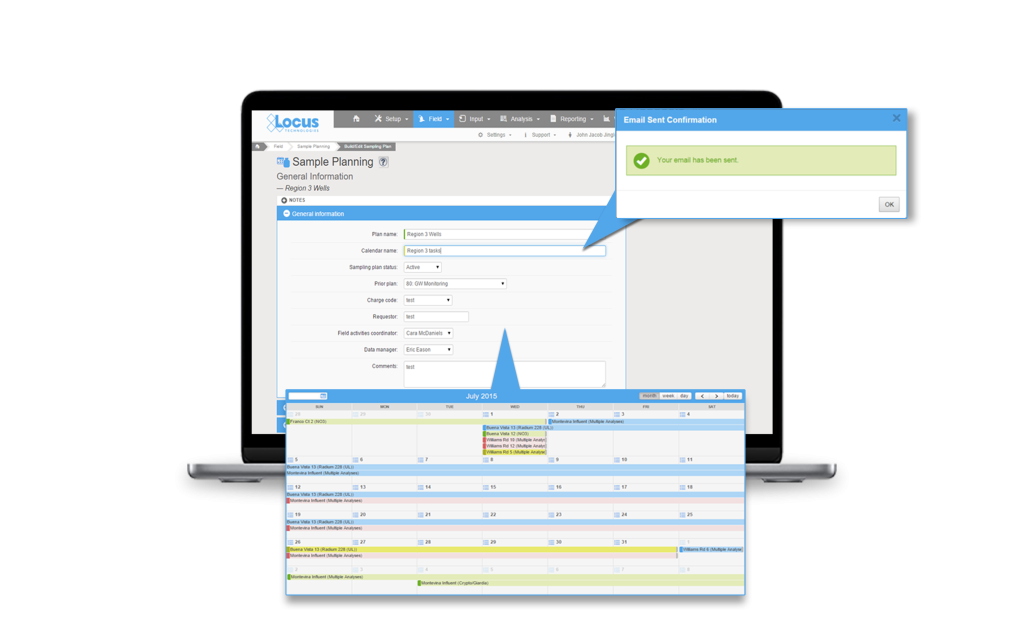
Locus Technologies’ customizable software makes scheduling and collecting routine water samples is made easy by using Locus Mobile and EIM.
There is a need for most water entities to centralize data, and more easily load, share, analyze, and report data. Locus Technologies’ customizable software makes scheduling and collecting routine water samples is made easy by using Locus Mobile and EIM. Below is a list of frequent challenges that customers have encountered during their water sampling process and how they can be solved using the right tools from Locus. or better communications.
Planning tools need to allow flexibility in terms of different sampling intervals and date ranges, different field and analytical parameters, and account for location grouping. Using a well-designed application can pull together all of this detailed information and can provide a summary view of the individual samples. A manager can easily view sample status, and whether the sample is complete, in process, or planned. A well-designed application can also generate the chain of custody (COC), and lab and sample shipping date information and labels per sample, which is a huge time saver. This type of sample tracking detail seemed to be very useful to many conference attendees to help ensure they are in regulatory compliance with required sampling frequencies. A key feature to look for is an application that is flexible enough that it can allow one-time, unplanned sample events such as water main breaks, customer complaints and schedule changes, and can handle complex multi-year routine sampling with ease. As a plus, it’s easy for you or your manager to know where you stand at any time.
Data entry errors and fixing bad data when it was transcribed from field notes to Excel or other programs is a persistent problem with the old way of doing things. Your company needs a better way to streamline the error prone data collection process. Many clients are interested in an alternative to the pencil/paper/clipboard method and had goals to move to tablet or smartphone for data collection. The universal wish list for mobile field applications included:
Everyone is aware that software updates all the time. Sometimes its security enhancements and sometime feature enhancements or bug fixes. A source of frustration is getting a software update and not knowing what was updated or how best to incorporate a new feature/enhancement into their established process. There was also concern for impact to an established routine with field crews that were used to the existing way of doing things. Even if a functionality improved the workflow, enhancements are only valuable to a user if they understand how to use them and how to incorporate them into their existing process.
Mobile applications, which appear very simple to the users, are in reality complex software and require careful integration with the receiving database for a range of complex use cases. This makes rolling out new mobile features challenging for both the developers and the users. Enhanced customer/developer communication along with a sandbox environment can go a long way towards solving some of the inherent issues with rapid innovations and updates associated with cloud and mobile software.

Software tools are available and can solve a lot of the common data management challenges, but know what you want, know the problem you are trying to solve and know it will take some time and effort, but the end result will significantly improve your business processes. Though these challenges are present when choosing a software, Locus Technologies has the experts to help you hurdle the challenges to find the solution that is best for your business.
Tracking your data is made easy within our software as a service (SaaS), Locus Platform (LP). Your company can take advantage of LP’s mobile-aware browser functions, giving you the capability to do all your fieldwork with your existing phones or tablets. When cellular connections are unavailable or unreliable, Locus also has a Mobile app which supports the offline capabilities you need to keep your workflow going.
Regardless of your mobile approach, each mobile form can be easily configured to capture the data you require in the field such as photos and the sampling results.
Whether in the office, or out in the field, Locus Technologies is with you every step of the way during the tracking process. Contact us to find your solution.
![]()
Today is GIS Day, a day started in 1999 to showcase the many uses of geographical information systems (GIS). Earlier Locus blog posts have explained how GIS and maps support visualization of objects in space and over time. This post covers a specific visualization method called data dashboards.
A data dashboard is a combination of charts, maps, text, and images that enables analysis of data and thereby promotes discovery of previously unknown relationships in the data. Companies and organizations use dashboards to develop insight into the overall status of a company or of a company division, process, or product line. Dashboards are also a common function in ‘business intelligence’ applications such as Microsoft Power BI and Tableau. A printed dashboard is static, but an online dashboard can be dynamic; in a dynamic dashboard, interacting with one item on the dashboard causes the other items to update. Taken together, the visualizations on a dynamic dashboard can help you find the story in your data.
One reason dashboards are so helpful is that they allow humans to partially ‘offload’ their thinking. Cognitive research has shown that human ‘working memory’ handles at most four items at a time. A good visualization, however, reduces the number of items to process in memory.
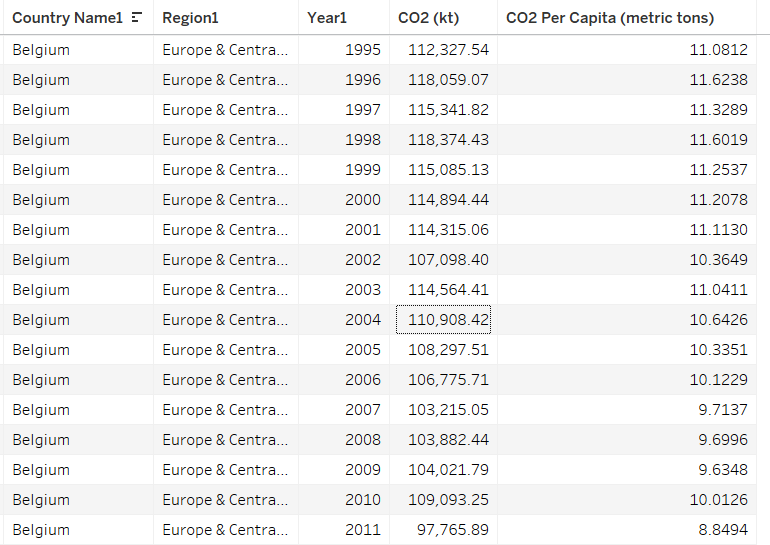
Consider a large table of carbon dioxide emissions by country for multiple years; it can be difficult to keep all the numbers in mind if you are trying to find trends.
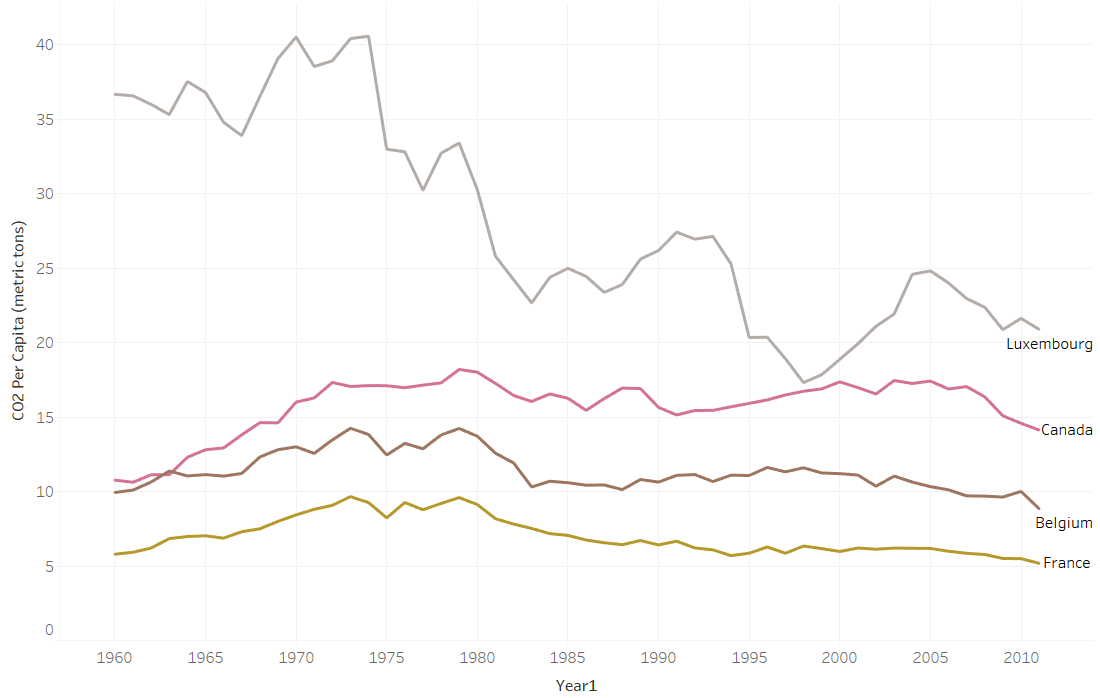
If you plot the data in a graph, however, each series of data in the chart becomes just one line on the graph. It is much easier to compare lines on the chart than to compare columns of numbers.
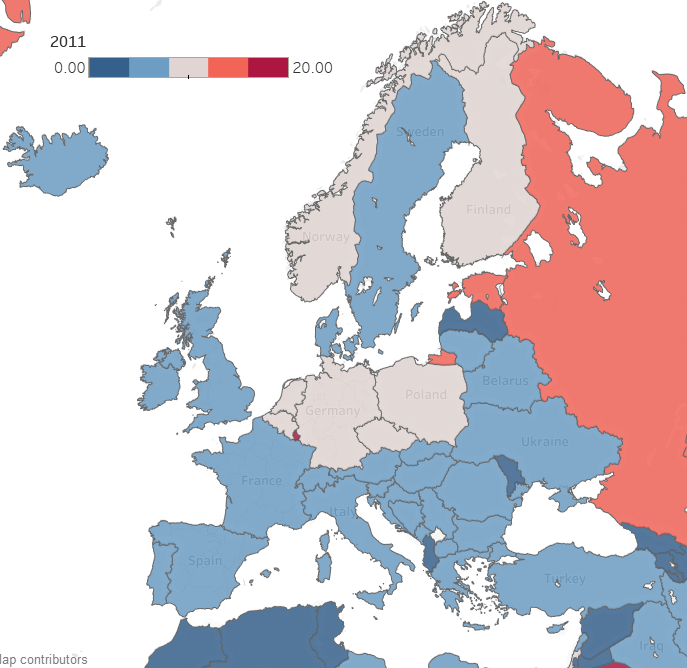
Now consider making a map with countries color coded by emissions. Again, for each country, the map reduces multiple numbers to a single color for that country on the map. You can compare country colors more easily than columns of numbers.
A dashboard that combines multiple visualizations further enhances data analysis. Imagine a dynamic dashboard showing you both the emissions chart and map described above. If you select a country on the map, the chart can highlight the line for that country, so you compare its emissions to other countries over time. Similarly, if you select a line on the chart for a specific country, the map can highlight the selected country to show how its emissions compare to nearby countries. This interactivity lets you drill into your data more effectively than using either the chart or the map by itself.
Here are three examples of effective dashboards that are available online:
Locus includes data dashboards in our applications. One example is the Site Metrics dashboard in EIM, Locus’s cloud-based, software-as-a-service application for environmental data management. The Site Metrics dashboard lets you perform roll-up queries across your portfolio of sites. A map on the dashboard shows all states with active sites. If you select one or more states, the dashboard updates the charts and tables on the right to show total sites, user logins, and record counts. Other dashboards can support showing sample locations of certain chemicals or counts of regulatory limit exceedances.
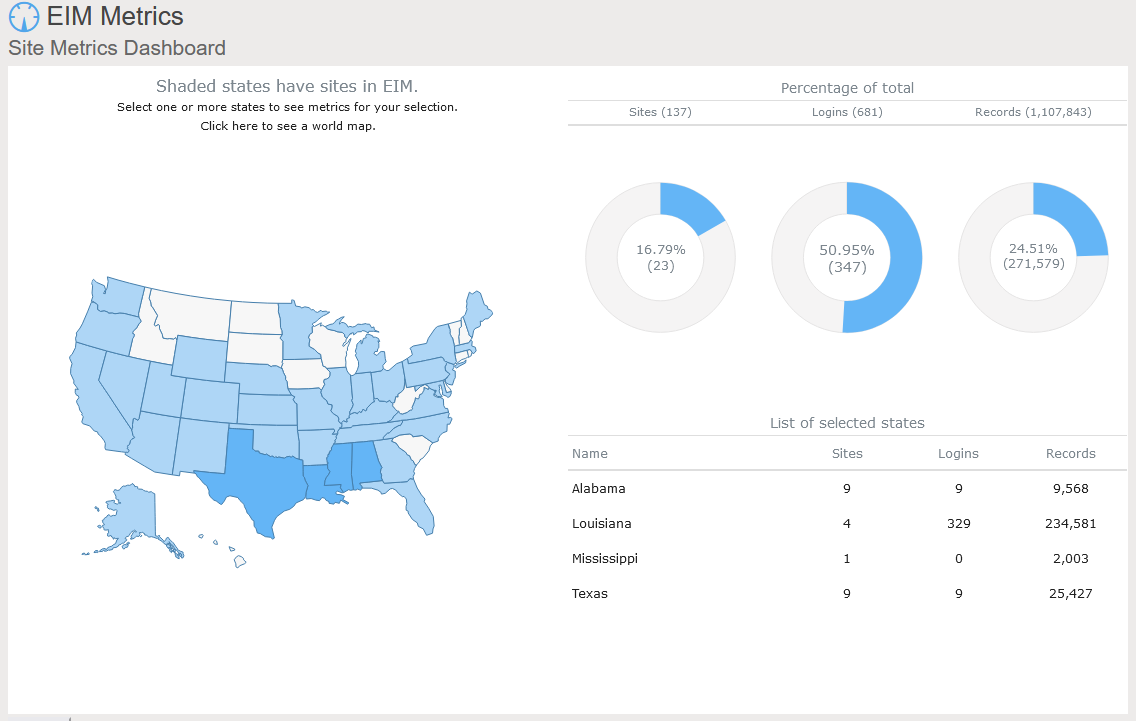
A further example comes from the Locus Environmental Social and Governance (ESG) application. ESG metrics are becoming increasingly important measures for an organization’s performance. Data dashboards can help companies quickly visualize trends in their ESG metrics using intuitive mapping tools.
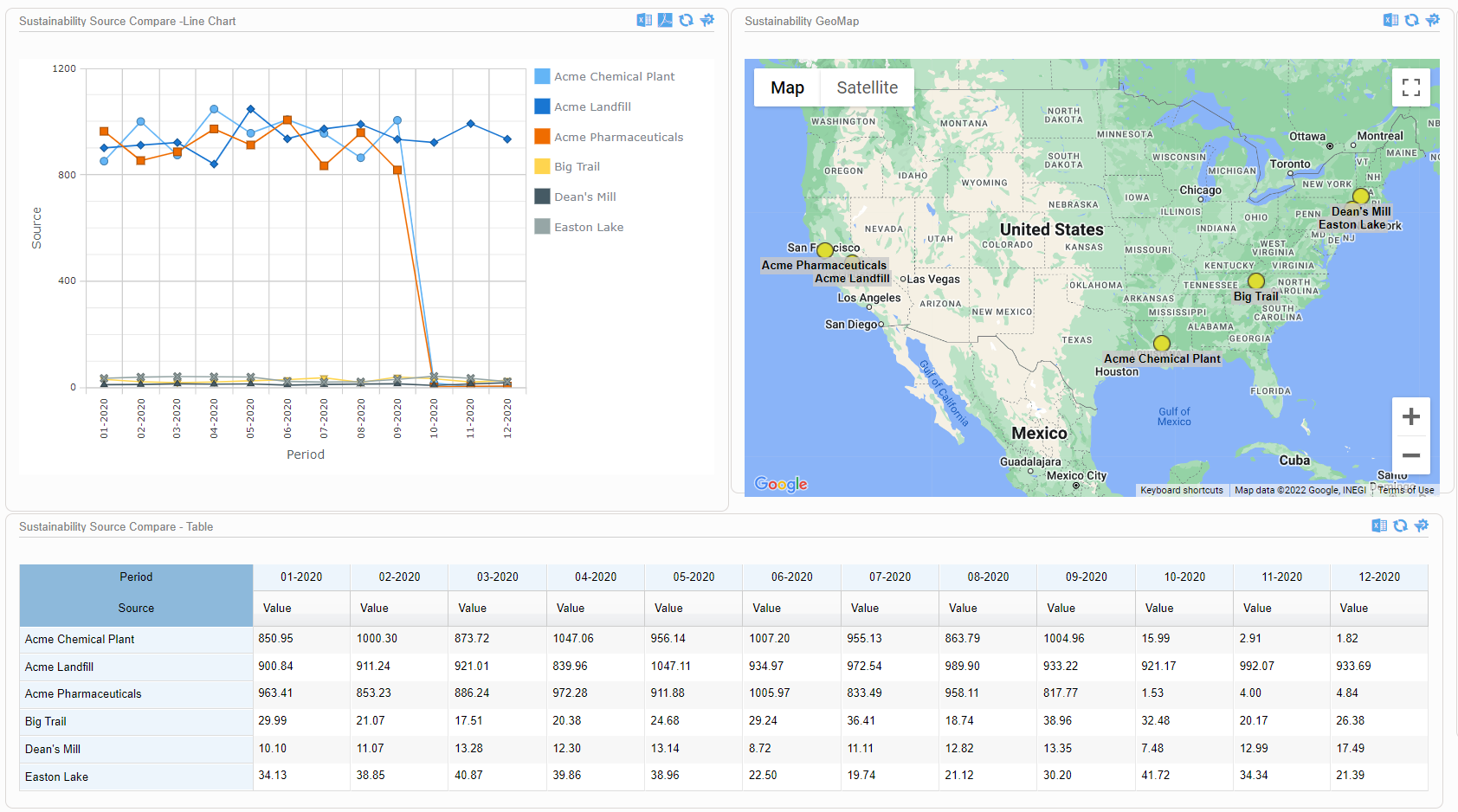
This dashboard illustrates both spatial and time trends and provides the raw data necessary for auditability and transparent decision making. Having these features on a single combined view provides users with instant access to the key inputs for ESG prioritization, planning, and project implementation.
As these examples from Locus show, data dashboards with integrated mapping are important tools for maximizing the value of your collected environmental and ESG data. For any dataset with a geographic component, it’s important to incorporate mapping elements in the outputs, to highlight trends and patterns that may not otherwise be visible in a chart or table. Modern software can combine these output formats in a way that tells the story shown by your data.
Locus GIS+ features all of the functionality you love in EIM’s classic Google Maps GIS for environmental management—integrated with the powerful cartography, interoperability, & smart-mapping features of Esri’s ArcGIS platform!
Learn more about Locus’ GIS solutions.
About the Author—Dr. Todd Pierce, Locus Technologies
Dr. Pierce manages a team of programmers tasked with development and implementation of Locus’ EIM application, which lets users manage their environmental data in the cloud using Software-as-a-Service technology. Dr. Pierce is also directly responsible for research and development of Locus’ GIS (geographic information systems) and visualization tools for mapping analytical and subsurface data. Dr. Pierce earned his GIS Professional (GISP) certification in 2010.
Today is GIS Day, a day started in 1999 to showcase the many uses of geographical information systems (GIS). Earlier blog posts by Locus Technologies for GIS day have shown how GIS supports cutting-edge visualization of objects in space and over time. This year’s post explains how GIS supports augmented reality.
Augmented reality (AR) is a technology that enhances how we experience the real world by overlaying your surroundings with computer-generated objects. It differs from virtual reality (VR) because in VR, everything you see is computer generated, but in AR, the majority of what you see is real – your experience of reality is enhanced (augmented) but not totally replaced.
You are probably familiar with one AR application already if you watch American football. The ‘virtual’ first down line that appears on field before each play is projected there by computer and is not really painted on the field. If you follow soccer (or football to the rest of the world), AR is used by a Video Assistant Referee (VAR) to objectively determine tight offsides decisions. Digital lines are drawn across the field to show whether or not attackers are illegally past the last defender or not. Another AR example is the popular game Pokémon Go that shows cute virtual creatures in your living room or your front yard.
To experience AR, you need something to project the non-real objects onto your view of the world. Many AR applications use mobile phones or other devices. An AR application uses the camera view to show you the world around you and then overlays virtual objects onto the view. Other devices such as head mounted displays, ‘smart glasses’, or even ‘bionic contact lenses’ can use AR, but have not been as popular as phones or other mobile devices. In contrast to AR, VR cannot be fully supported with just a mobile device and usually requires headsets to immerse you in a virtual world. Because of this need, AR is much less intrusive than VR is.
Locus has been exploring environmental uses of AR and GIS by adding AR to Locus Mobile, which is the Locus app for collecting field data, completing EHS audits, tracking waste containers, and completing other tasks requiring users to gather data out of the office. Locus Mobile now features an AR mode to assist users when taking field samples. When the user activates AR mode, the app uses the camera to show the user’s immediate area. The app then puts multiple virtual markers on the display corresponding to sampling points located in that direction. As the user moves or rotates the phone to change the viewing area, the markers change to reflect the locations in the user’s line of sight. Clicking a marker provides more information including the location name and the distance from the user.
Here is a sample image from Locus Mobile showing three nearby sampling locations along with information about past events or measurements at the locations. The three blue banners are the augmented reality displayed on top of the view of the nearby surroundings.

By using GIS and AR to assist users in finding sampling points, Locus Mobile makes field personnel more productive. Samplers can find field locations quickly and can easily pull up related information. Locus continues to explore using AR to expand the functionality of its environmental applications.
Locus GIS+ features all of the functionality you love in EIM’s classic Google Maps GIS for environmental management—integrated with the powerful cartography, interoperability, & smart-mapping features of Esri’s ArcGIS platform!
Learn more about Locus’ GIS solutions.
About the Author—Dr. Todd Pierce, Locus Technologies
Dr. Pierce manages a team of programmers tasked with development and implementation of Locus’ EIM application, which lets users manage their environmental data in the cloud using Software-as-a-Service technology. Dr. Pierce is also directly responsible for research and development of Locus’ GIS (geographic information systems) and visualization tools for mapping analytical and subsurface data. Dr. Pierce earned his GIS Professional (GISP) certification in 2010.
The Vapor Intrusion tools in Locus’ Environmental Information Management (EIM) software solve the problem of time-consuming monitoring, reporting, and mitigation by automating data assembly, calculations, and reporting.
Quickly and easily generate validated reports in approved formats, with all of the calculations completed according to your specific regulatory requirements. Companies can set up EIM for its investigation sites and realize immediate cost and time savings during each reporting period.

Today is GIS Day, a day started in 1999 to showcase the many uses of geographical information systems (GIS). Earlier Locus blog posts have shown how GIS supports cutting-edge visualization of objects in space and over time. This post is going to go “back to basics” and discuss what makes GIS unique and how environmental data analysis benefits from that uniqueness.
So, what makes GIS unique? It’s the ability of GIS to handle spatial relationships, which goes beyond just putting “dots on a map”. You are probably familiar with non-spatial relationships such as greater than, less than, or equal to, and you probably use them every day. For example, suppose you want to buy the latest gaming console (PS5, anyone?). You need to compare the price of the console to your bank account. If the console price is greater than your savings, then you cannot buy the console.
Or can you? With credit cards, you can pay later, so you go charge the console. At the time of the transaction, some software evaluates a non-spatial relationship and checks if the console price plus your current debt is less than your credit limit. If so, you can buy the console; if not, your purchase is denied.
The key point about this example is that spatial relations play no part. It doesn’t matter where you are located or where the game console is sold from. (OK, there may be things like state taxes and shipping, but that just contributes to the price.) Now, if you were trying to find all gaming consoles for sale within a certain distance of you, that is a spatial relationship. There are multiple types of spatial relationship, but the most common are inside, contains, crosses, overlaps, and within a distance of. Standard relational database software does not handle these sorts of relations, but GIS can.
As an illustration, let’s consider two current events: the 2020 US presidential election and the COVID-19 pandemic. With non-spatial relationships, you can answer various questions such as “did Biden get more votes than Clinton?” or “is the number of positive COVID tests increasing?”. But with spatial relations, you can answer more interesting questions such as “did areas with COVID hot spots vote more predominantly for Biden or Trump?”. For this question you must see if voters lie inside a COVID hot spot; a GIS can perform this analysis and then map the results. While many votes are still being counted, as of this blog post, it appears Trump performed better in COVID hot spots.
Let’s look at some example of spatial relations in environmental data. Assume you have a database of tritium sampling results in water, along with various map layers of natural and manmade features. What kind of spatial relationships can you explore with GIS?
To answer that, we’ll make some maps with the Locus GIS+ package in EIM, Locus’s cloud-based, software-as-a-service application for environmental data management. All maps shown here display wells with tritium samples, with the wells represented as colored circles. The color scale goes from blue through yellow to red, to indicate increasing tritium results.
Figure 1 shows an example of an inside spatial relationship. The map answers the question “what wells with tritium results are inside the Mortandad Canyon watershed?”. The watershed is highlighted in blue on the map, and you can easily see the wells inside the watershed.
Figure 2 shows wells with tritium results that are within a distance of a river. The map answers the question “what wells with tritium results are within 500 ft of the river?”. The river, highlighted in light blue, has a 500 ft buffer shown as a dotted blue line. The wells with tritium that lie within the buffer are shown on the map, so you can check if any high tritium results are close to the waterway.
Figure 3 shows another example of within a distance of. Here, the map answers the question “what wells with tritium results are within two miles of a middle school?”. The two-mile radius is shown as a shaded blue circle centered on the school. You can see the wells are confined to the area southeast of the school.
These three examples are just a small subset of what can be done with GIS and environmental data. Here are some other questions illustrating the kind of spatial analysis that GIS supports.
All these examples illustrate the power of GIS for analyzing spatial relationships, and these examples are just the beginning. GIS can also perform more sophisticated analyses that look at spatial relationships in different ways to answer questions such as:
Locus continues to bring new analysis tools to our Locus GIS+ system for environmental applications. These applications let you take advantage of the unique ability of GIS to analyze spatial relationships in your environmental data.
Acknowledgments: All the data in EIM used in the examples was obtained from the publicly available chemical datasets online at Intellus New Mexico.
Locus GIS+ features all of the functionality you love in EIM’s classic Google Maps GIS for environmental management—integrated with the powerful cartography, interoperability, & smart-mapping features of Esri’s ArcGIS platform!
Learn more about Locus’ GIS solutions.
About the Author—Dr. Todd Pierce, Locus Technologies
Dr. Pierce manages a team of programmers tasked with development and implementation of Locus’ EIM application, which lets users manage their environmental data in the cloud using Software-as-a-Service technology. Dr. Pierce is also directly responsible for research and development of Locus’ GIS (geographic information systems) and visualization tools for mapping analytical and subsurface data. Dr. Pierce earned his GIS Professional (GISP) certification in 2010.
Becomes Largest Real-time Database of Global PFAS Records from Nearly 40,000 Locations.
MOUNTAIN VIEW, Calif., April 9, 2025 —Locus Technologies, the leader in sustainability and Environmental Health and Safety (EHS) compliance software, announced that as of today, Locus clients have collectively contributed 3,000,000 validated Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) records to the company’s environmental database, making it the most extensive real-time, aggregated global analytical and geospatial PFAS information source. The records are secured in Locus’s sophisticated, multitenant SaaS database.
Locus’s expansive PFAS dataset includes all 430 chemicals identified in the US Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) PFAS inventory, collected from 38,553 global sites, predominantly in the United States. By combining advanced geographic information system (GIS) tools and artificial intelligence (AI)-driven analytics, Locus provides unmatched capabilities for identifying contamination sources, tracking environmental accumulations in water, soil, and living organisms, and visualizing critical “hot spots” for strategic remediation.
“This milestone underscores our commitment to advancing environmental safety through technology innovation,” said Neno Duplan, founder and CEO of Locus Technologies. “Our multitenant SaaS infrastructure uniquely positions Locus as the only platform capable of aggregating, analyzing, and reporting critical PFAS data in real-time. With three million records, we’ve reached an unprecedented capability for understanding and managing this global health threat.”
Locus Technologies’ multitenant SaaS platform enables individual organizations to securely manage and report their PFAS sampling data and compliance requirements while gaining broader insights from aggregated data. The company’s unique software architecture empowers clients to stay ahead of stringent regulatory frameworks, including emerging EU directives and global ESG reporting demands, while ensuring the absolute privacy of their proprietary information.
“Emerging research indicates the PFAS health crisis will be more significant than Asbestos, lead, and tobacco combined. Empowering organizations to effectively track and manage this data is imperative,” said Duplan. By leveraging the real-time analytical power of Locus, utilities, government agencies, and enterprises can proactively manage PFAS risks, streamline regulatory compliance, and safeguard public health and environmental ecosystems worldwide.
To learn more about Locus Technologies, please visit locustec.com.
About Locus Technologies
Locus Technologies, the global environmental, social, governance (ESG), sustainability, and EHS compliance software leader, empowers companies of every size and industry to be credible with ESG reporting. From 1997, Locus pioneered enterprise software-as-a-service (SaaS) for EHS compliance, water management, and ESG credible reporting. Locus apps and software solutions improve business performance by strengthening risk management and EHS for organizations across industries and government agencies. Organizations ranging from medium-sized businesses to Fortune 500 enterprises, such as Sempra, Corteva, Chevron, DuPont, Chemours, San Jose Water Company, The Port Authority of New York and New Jersey, Port of Seattle, and Los Alamos National Laboratory, have selected Locus. Locus is headquartered in Mountain View, California. For further information regarding Locus and its commitment to excellence in SaaS solutions, please visit http://www.locustec.com or email info@locustec.com.
SAN FRANCISCO, Calif., Jan. 16, 2024 — Locus Technologies, (Locus), the pioneer in water, Environmental, Health, and Safety (EHS) compliance and Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) software solutions, announces expansion of its water management SaaS platform to include management of produced water within the oil and gas industry. This cutting-edge solution, seamlessly integrated with Locus’ suite of applications, underscores the company’s unwavering commitment to driving sustainable practices while optimizing operational efficiency.
Locus has engineered a comprehensive application designed specifically for the efficient and sustainable management of produced water. This latest addition to Locus’s suite of water solutions aims to address the complex demands of the oil and gas industry while ensuring compliance, conservation, and operational excellence.
The new application is seamlessly interoperable with other Locus solutions catering to the oil and gas sector, such as ESG, air emissions, waste management, and water quality management. Locus software empowers organizations to make informed decisions, mitigate risks, and enhance overall efficiency across their operations by streamlining data integration and providing actionable insights.
Locus’ CEO, Neno Duplan, emphasized the company’s dedication to delivering comprehensive water management solutions while driving advancements in technology for the beneficial reuse of water beyond the realms of the oil and gas, and energy industries. “We remain focused on delivering comprehensive water management solutions to our customers while advancing technologies for the beneficial reuse of water inside and outside of the oil and gas industry, which holds the promise of further improving the sustainability of our customer’s operations,” stated Duplan.
With a proven track record in providing leading-edge EHS and ESG software solutions, Locus continues to spearhead advancements in compliance, sustainability, and corporate responsibility across diverse industries and geographies.
About Locus Technologies
Locus Technologies, the global environmental, social, governance (ESG), Sustainability, and EHS Compliance software leader, empowers companies of every size and industry to be credible with ESG reporting. From 1997 Locus Technologies pioneered enterprise software-as-a-service (SaaS) for EHS Compliance, water management, and ESG credible reporting. Locus apps and software solutions improve business performance by strengthening risk management and EHS for organizations across industries and government agencies. Organizations ranging from medium-sized businesses to Fortune 500 enterprises, such as Chevron, Sempra, Corteva, DuPont, Chemours, San Jose Water Company, The Port Authority of New York and New Jersey, Port of Seattle, Onto Innovations, and Los Alamos National Laboratory, have selected Locus.
Locus Technologies’ headquarters is in Mountain View, California.
For further information regarding Locus Technologies and its commitment to excellence in SaaS solutions, please visit www.locustec.com or email info@locustec.com.
MOUNTAIN VIEW, Calif., 14 February 2023 — Locus Technologies, the leading EHS Compliance, and ESG software provider, today announced that San Jose Water (SJW), an investor-owned public utility providing water service to a population of approximately one million people in the Santa Clara Valley, has expanded Locus’ environmental information management software to use Locus GIS+ for advanced GIS analysis.
SJW has been using Locus SaaS and mobile app since 2014 to manage its field data collection, water quality compliance, and regulatory reporting. SJW also uses Locus to track sewer discharges and well blow-offs.
“Our responsibility is to ensure our customers receive the highest quality drinking water from their taps. We monitor the quality and cleanliness of our water in terms of state and federal regulatory requirements. In 2021, our highly experienced staff collected more than 1,000 regulatory and non-regulatory samples from our distribution system and treatment plant, generating over 23,000 data points. To manage this data effectively, we used Locus’ cloud-based software. GIS mapping capabilities are essential for our environmental data analysis. Locus GIS+ will allow quick data visualization and is a quantum leap forward with advanced analysis tools that use Esri’s Smart Mapping technology,” said Suzanne DeLorenzo, the Director of Water Quality at San Jose Water.
“Locus’s mission is to help organizations, such as San Jose Water, to achieve their business goals by providing them the software tools to manage key data associated with water quality and compliance reporting,” said Neno Duplan, CEO of Locus. “With GIS+, SJW will have all the tools they need to perform a wide range of geospatial data analysis across their distribution system. Our water quality management cloud-based software, coupled with GIS+ and Locus Mobile for field data collection, provides our customers with a highly scalable and feature-rich application that gives water utilities strong analytical power and advanced GIS capabilities.”
Locus GIS+ is powered by Esri’s ArcGIS platform and offers various advanced features— including enhanced cartography, comprehensive spatial data analysis, and the ability to use the customer’s map data through integration with ArcGIS Online and Portal for ArcGIS.
ABOUT SAN JOSE WATER
Founded in 1866, San Jose Water is an investor-owned public utility and is one of the largest and most technically sophisticated urban water systems in the United States. Serving over one million people in the greater San Jose metropolitan area, San Jose Water also provides services to other utilities, including operations and maintenance, billing, and backflow testing. San Jose Water is owned by SJW Group, a publicly-traded company listed on the New York Stock Exchange under the symbol SJW. SJW Group also owns Connecticut Water Company in Connecticut; Maine Water Company in Maine; and SJWTX, Inc. (dba Canyon Lake Water Service Company) in Texas. To learn more about San Jose Water, visit www.sjwater.com.
299 Fairchild Drive
Mountain View, CA 94043
P: +1 (650) 960-1640
F: +1 (415) 360-5889
Locus Technologies provides cloud-based environmental software and mobile solutions for EHS, sustainability management, GHG reporting, water quality management, risk management, and analytical, geologic, and ecologic environmental data management.
