The recent year of lockdowns pushed many daily activities into the virtual world. Work, school, commerce, the arts, and even medicine have moved online and into the cloud. As a result, considerably more resources and information are now available from an internet browser or from an application on a handheld device. To navigate through all this content and make sense of it, you need the ability to quickly search and get results that are most relevant to your needs.
You can think of the web as a big database in the cloud. Traditionally, database searches were done using a precise syntax with a standard set of keywords and rules, and it can be hard for non-specialists to perform such searches without learning programming languages. Instead, you want to search in as natural a matter as possible. For example, if you want to find pizza shops with 15 miles of your house that offer delivery, you don’t want to write some fancy statement like “return pizza_shop_name where (distance to pizza shop from my house < 15 miles) and (offers_delivery is true). You just want to type “what pizza shops within 15 miles of my house offer delivery?” How can this be done?

Enter the search engine. While online search engines appeared as early as 1990, it wasn’t until Yahoo! Search appeared in 1995 that their usage became widespread. Other engines such as Magellan, Lycos, Infoseek, Ask Jeeves, and Excite soon followed, though not all of them survived. In 1998, Google hit the internet, and it is now the most dominant engine in use. Other popular engines today are Bing, Baidu, and DuckDuckGo.
Current search engines compare your search terms to proprietary indexes of web page and their content. Algorithms are used to determine the most relevant parts of the search terms and how the results are ranked on the page. Your search success depends on what search terms you enter (and what terms you don’t enter). For example, it is better to search on ‘pizza nearby delivery’ than ‘what pizza shops that deliver are near my house’, as the first search uses less terms and thus more effectively narrows the results.
Search engines also support the use of symbols (such as hyphens, colons, quote marks) and commands (such as ‘related’, ‘site’, or ‘link’) that support advanced searches for finding exact word matches, excluding certain results, or limiting your search to certain sites. To expand on the pizza example, support you wanted to search for nearby pizza shops, but you don’t want to include Nogud Pizza Joints because they always put pineapple on your pizza. You would need to enter ‘pizza nearby delivery -nogud’. In some ways, with the need to know special syntax, searching is back where it was in the old database days!
Search engines are also a key part of ‘digital personal assistants’, or programs that not only perform searches but also perform simple tasks. An assistant on your phone might call the closest pizza shop so you can place an order, or perhaps even login to your loyalty app and place the order for you. There is a dizzying array of such assistants used within various devices and applications, and they all seem to have soothing names such as Siri, Alexa, Erica, and Bixby. Many of these assistants support voice activation, which just reinforces the need for natural searches. You don’t want to have to say “pizza nearby delivery minus nogud”! You just want to say “call the nearest pizza shop that does delivery, but don’t call Nogud Pizza”.
Search engine and digital personal assistant developers are working towards supporting such “natural” requests by implementing “natural language processing”. Using natural language processing, you can use full sentences with common words instead of having to remember keywords or symbols. It’s like having a conversation as opposed to doing programming. Natural language is more intuitive and can help users with poor search strategies to have more successful searches.
Furthermore, some engines and assistants have artificial intelligence (AI) built in to help guide the user if the search is not clear or if the results need further refinement. What if the closest pizza shop that does delivery is closed? Or what if a slightly farther pizza place is running a two-for-one special on your favorite pizza? The built-in AI could suggest choices to you based on your search parameters combined with your past pizza purchasing history, which would be available based on your phone call or credit charge history.
Searching in Locus EIM
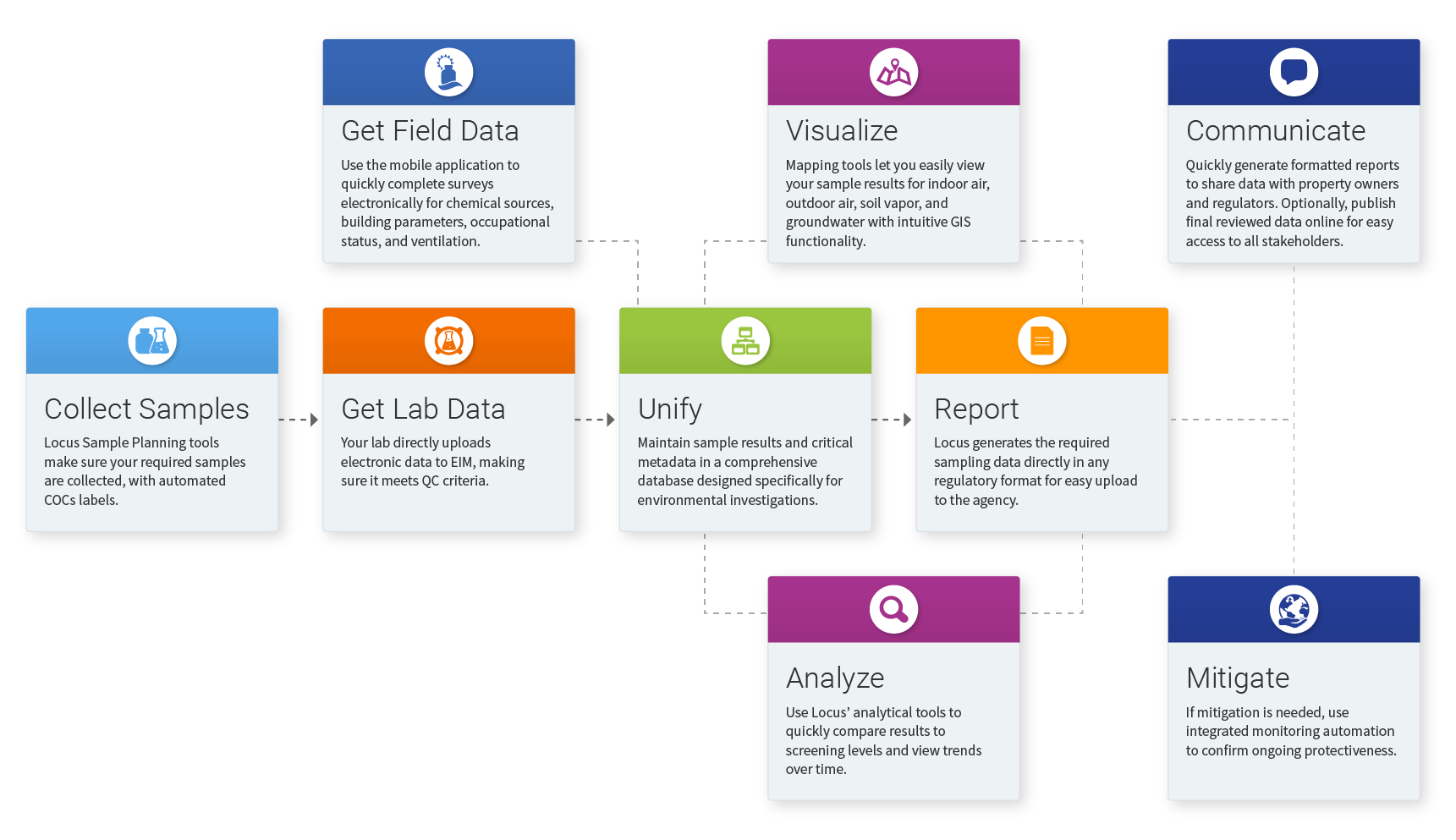
The Locus team recently expanded the functionality of the EIM (Environmental Information Management) search bar to support different types of data searches. If a search term fits several search types, all are returned for the user to review.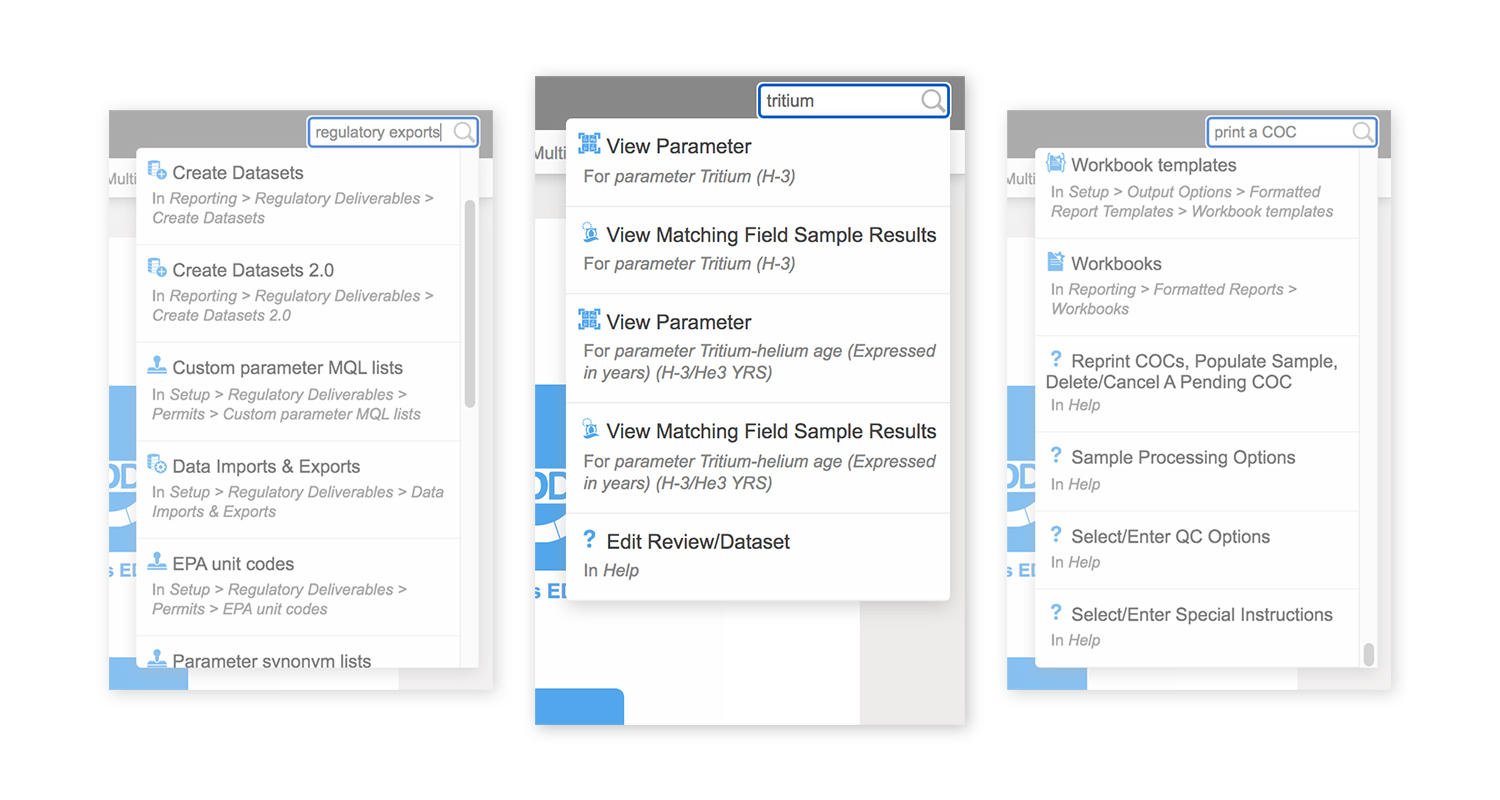
- Functionality searches: entering a word that appears in a menu or function name will return any matching menu items and functions. For example, searching for ‘regulatory exports’ returns several menu items for creating, managing, and exporting regulatory datasets.
- Help searches: entering a word or phrase that appears in the EIM help files will return any matching help pages. For example, ‘print a COC’ returns help pages with that exact phrase.
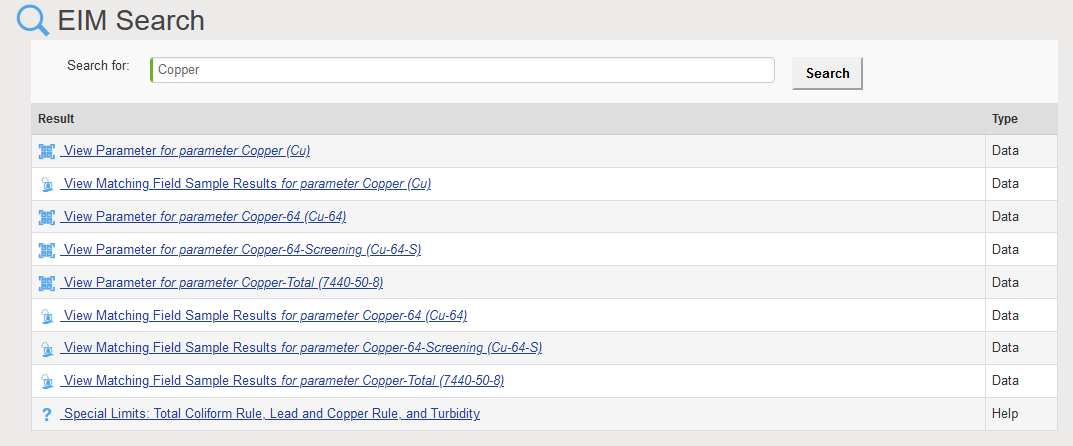
- Data searches: entering a location, parameter, field parameter, or field sample will return any matching data records linked with that entity. For example, searching for the parameter ‘tritium’ returns linked pages showing parameter information and all field sample results for that parameter. Searching for the location ‘MW-1’ returns linked pages showing all field samples, groundwater levels, field measurements, and field sample results at the location.
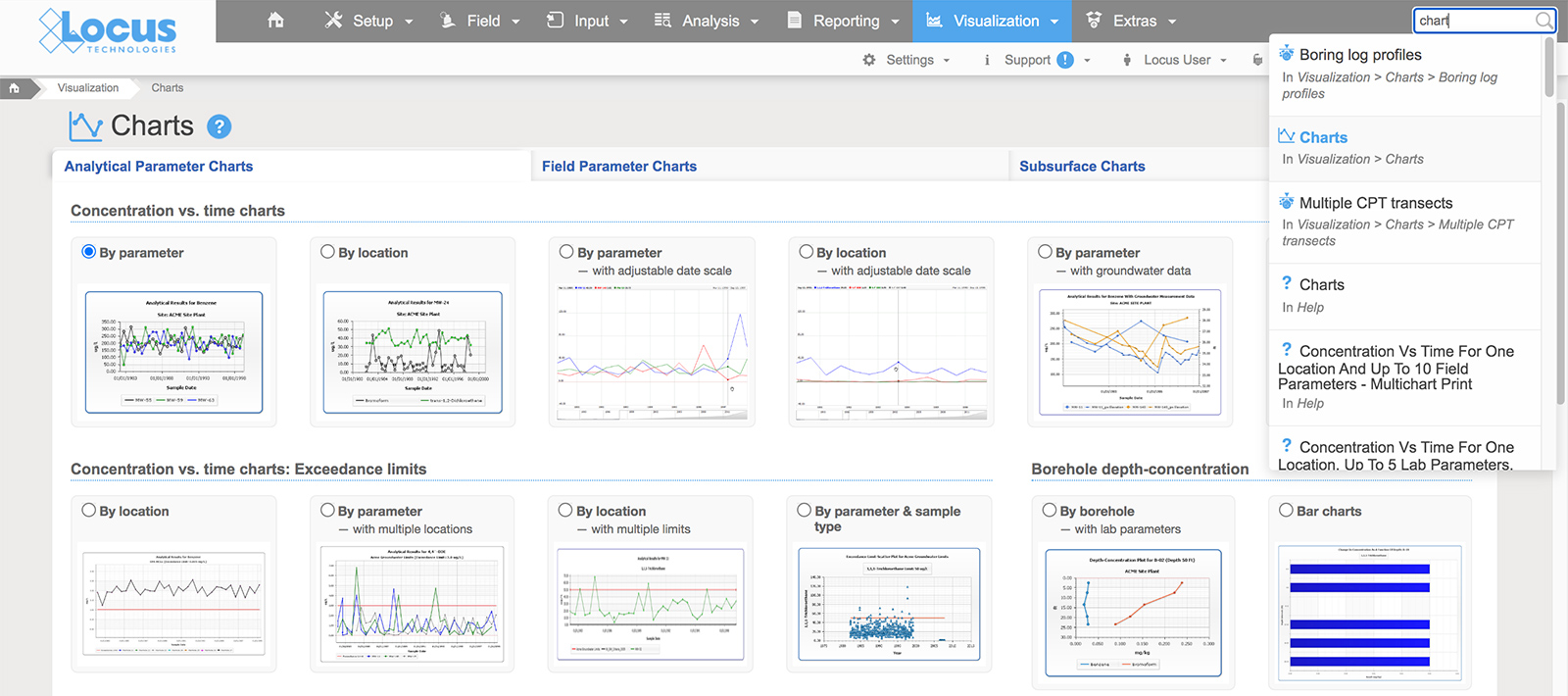
EIM lets the user perform successful searches through various methods. In all searches, the user does not need to specify if the search term is a menu item, help page, or data entity such as parameter or location. Rather, the search bar determines the most relevant results based on the data currently in EIM. Furthermore, the search bar remembers what users searched for before, and then ranks the results based on that history. If a user always goes to a page of groundwater levels when searching for location ‘MW-1’, then that page will be returned first in the list of results. Also, the EIM search bar supports common synonyms. For example, searches for ‘plot’, ‘chart’, and ‘graph’ all return results for EIM’s charting package.
By implementing the assistance methods described above, Locus is working to make searching as easy as possible. As part of that effort, Locus is working to add natural language processing into EIM searches. The goal is to let users conduct searches such as ‘what wells at my site have benzene exceedances’ or perform tasks such as ‘make a chart of benzene results’ without having to know special commands or query languages.’
How would this be done? Let’s set aside for now the issues of speech recognition – sadly, you won’t be talking to EIM soon! Assume your search query is ‘what is the maximum lead result for well 1A?’
- First, EIM extracts key terms and modifiers (this is called entity recognition). EIM would extract ‘maximum’, ‘lead’, ‘result’, ‘well’, and ‘1A’, while ignoring connecting words such as ‘the’ or ‘for’.
- Then, EIM categorizes these terms. EIM would be ‘trained’ via AI to know ‘lead’ is mostly used in environmental data as a noun for the chemical parameter, and not a verb. ‘Result’ refers to a lab result, and ‘well’ is a standard sampling location type.
- EIM then runs a simple query and gets the maximum lead result for location 1A.
- Finally, EIM puts the answer into a sentence (‘The maximum lead result at location 1A is 300 mg/L on 1/1/2020’) with any other information deemed useful, such as the units and the date.
A similar process could be done for tasks such as ‘make a chart of xylene results’. In this case, however, there is too much ambiguity to proceed, so EIM would need to return queries for additional clarifications to help guide the user to the desired result. Should the chart show all dates, or just a certain date range? How are non-detects handled? Which locations should be shown on the chart? What if the database stores separate results for o-Xylene, m,p-Xylene, plus Xylene (total)? Once all questions were answered, EIM could generate a chart and return it to the user.
Natural language is the key to helping users construct effective searches for data, whether in EIM, on a phone, or in the internet. Locus continues to improve EIM by bringing natural language processing to the EIM search engine.
About the Author—Dr. Todd Pierce, Locus Technologies
Dr. Pierce manages a team of programmers tasked with development and implementation of Locus’ EIM application, which lets users manage their environmental data in the cloud using Software-as-a-Service technology. Dr. Pierce is also directly responsible for research and development of Locus’ GIS (geographic information systems) and visualization tools for mapping analytical and subsurface data. Dr. Pierce earned his GIS Professional (GISP) certification in 2010.





 Anyone who has worked to align standards and frameworks, corral internal champions around disclosure requirements, and marry quantitative performance data with narratives on management approach, knows that this is no easy feat.
Anyone who has worked to align standards and frameworks, corral internal champions around disclosure requirements, and marry quantitative performance data with narratives on management approach, knows that this is no easy feat.