Top 10 Enhancements to Locus Environmental Software in 2019
Let’s look back on the most exciting new features and changes made in EIM, Locus’ environmental data management software, during 2019!
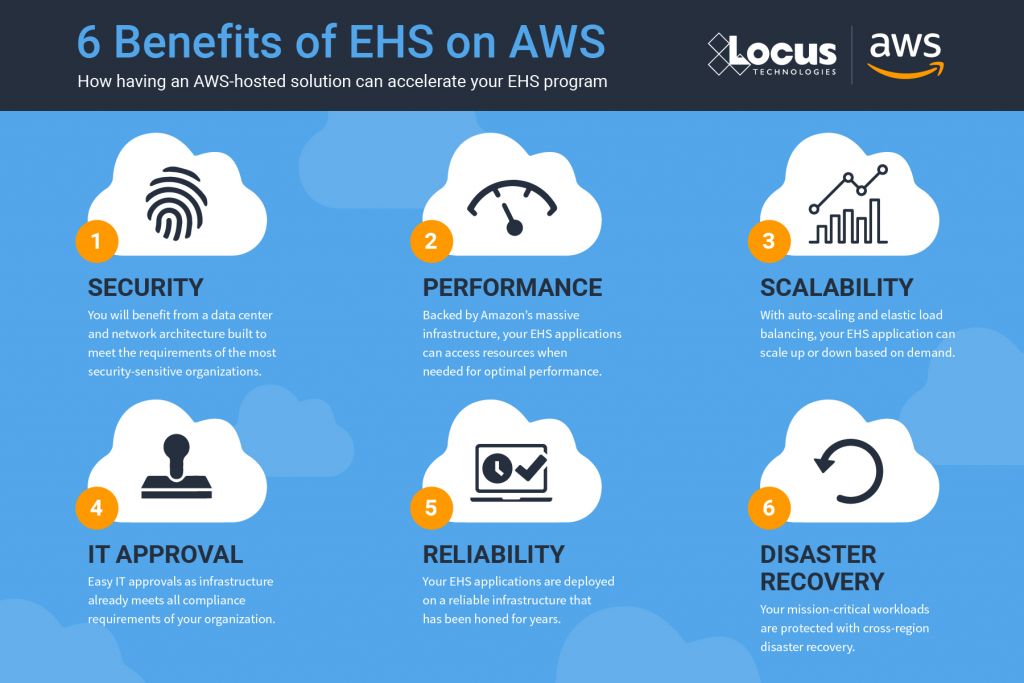
1. Migration to AWS Cloud
In August, Locus migrated EIM into the Amazon Web Services (AWS) cloud. EIM already had superior security, reliability, and performance in the Locus Cloud. The move to AWS improves on those metrics and allows Locus to leverage AWS specific tools that handle big data, blockchain, machine learning, and data analytics. Furthermore, AWS is scalable, which means EIM can better handle demand during peak usage periods. The move to AWS helps ensure that EIM remains the world’s leading water quality management software.
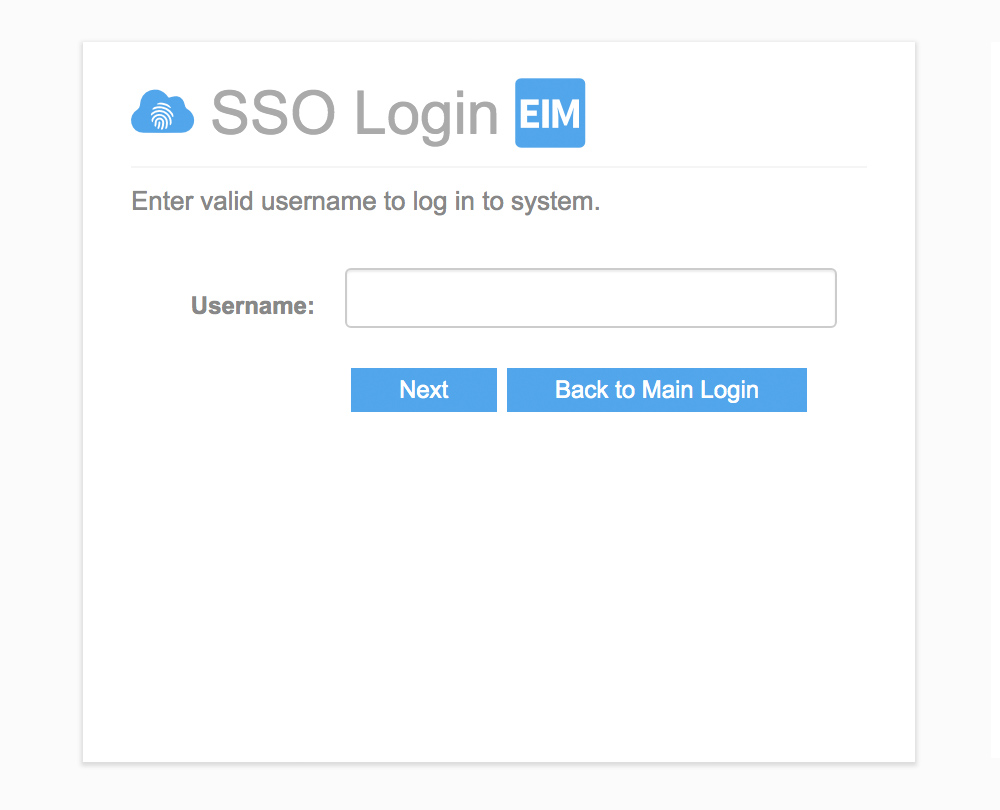
2. SSO Login
EIM now supports Single Sign-On (SSO), allowing users to access EIM using their corporate authentication provider. SSO is a popular security mechanism for many corporations. With SSO, one single login allows access to multiple applications, which simplifies username and password management and reduces the number of potential targets for malicious hacking of user credentials. Using SSO with EIM requires a one-time configuration to allow EIM to communicate with a customer’s SSO provider.
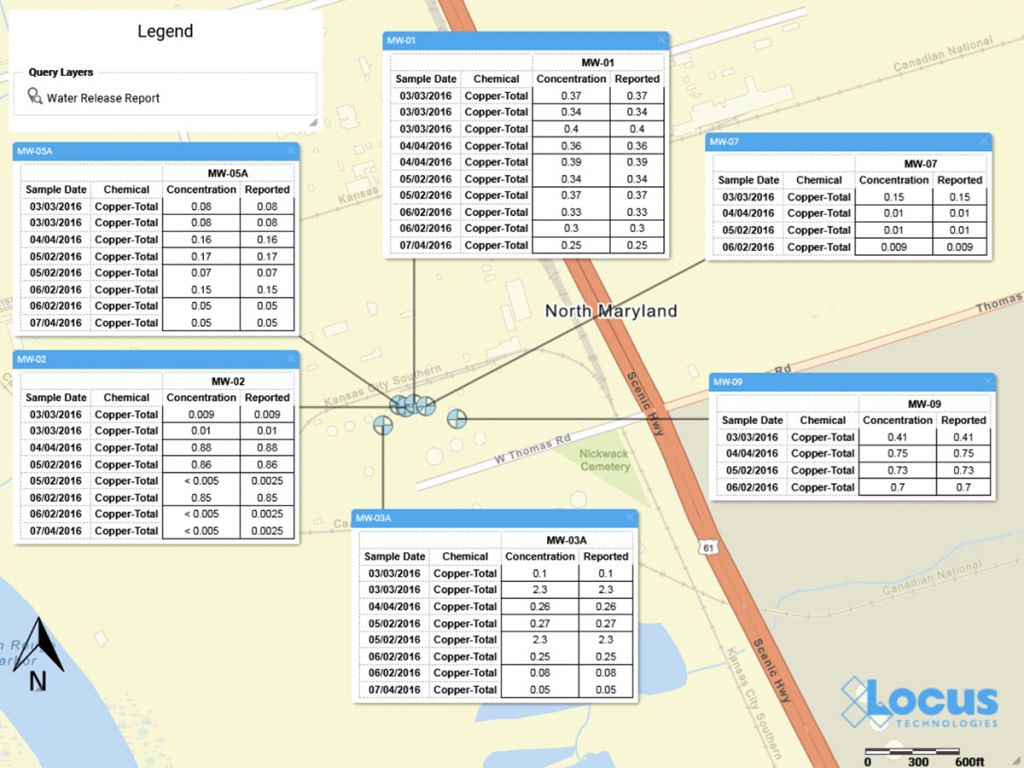
3. GIS+ Data Callouts
The Locus GIS+ solution now supports creating data callouts, which are location-specific crosstab reports listing analytical, groundwater, or field readings. A user first creates a data callout template using a drag-and-drop interface in the EIM enhanced formatted reports module. The template can include rules to control data formatting (for example, action limit exceedances can be shown in red text). When the user runs the template for a specific set of locations, EIM displays the callouts in the GIS+ as a set of draggable boxes. The user can finalize the callouts in the GIS+ print view and then send the resulting map to a printer or export the map to a PDF file.
4. EIM One
For customers who don’t require the full EIM package, Locus now offers EIM One, which gives the ability to customize EIM functionality. Every EIM One purchase comes with EIM core features: locations and samples; analytical and field results; EDD loading; basic data views; and action limit exceedance reports. The customer can then purchase add-on packages to get just the functionality desired–for example a customer with DMR requirements may purchase the Subsurface and Regulatory Reporting packages. EIM One provides customers with a range of pricing options to get the perfect fit for their data management needs.
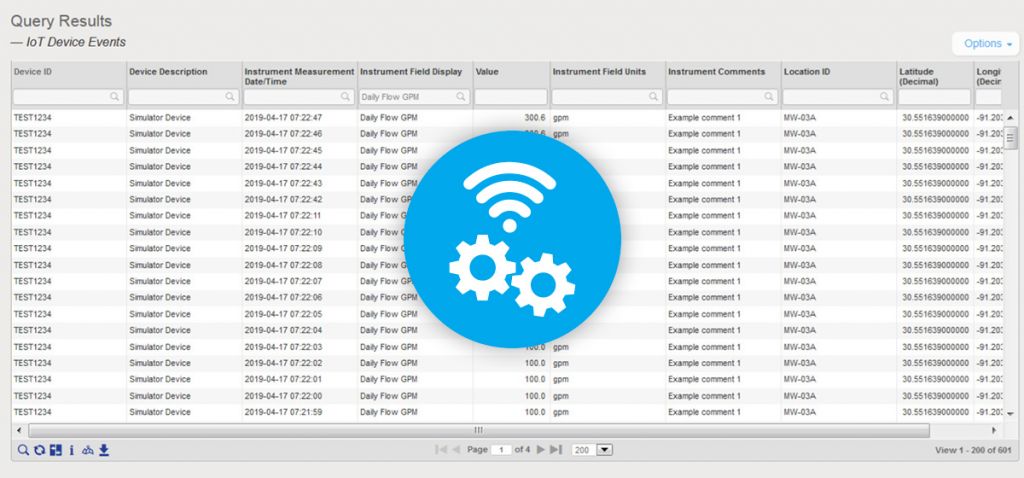
5. IoT data support
EIM can now be configured to accept data from IoT (internet of things) streaming devices. Locus must do a one-time connection between EIM and the customer’s IoT streaming application; the customer can then use EIM to define the devices and data fields to capture. EIM can accept data from multiple devices every second. Once the data values are in EIM, they can be exported using the Expert Query tool. From there, values can be shown on the GIS+ map if desired. The GIS+ Time Slider automation feature has also been updated to handle IoT data by allowing the time slider to use hours, minutes, and seconds as the time intervals.
6. CIWQS and NCDEQ exports
EIM currently supports several dozen regulatory agency export formats. In 2019, Locus added two more exports for CIWQS (California Integrated Water Quality System Project) and the NCDEQ (North Carolina Department of Environmental Quality). Locus continues to add more formats so customers can meet their reporting requirements.
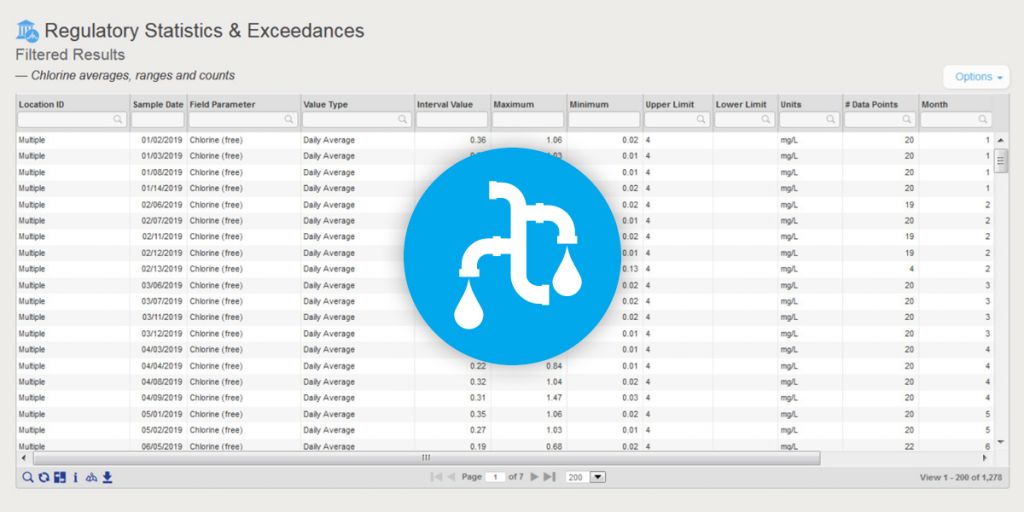
7. Improved Water Utility reporting
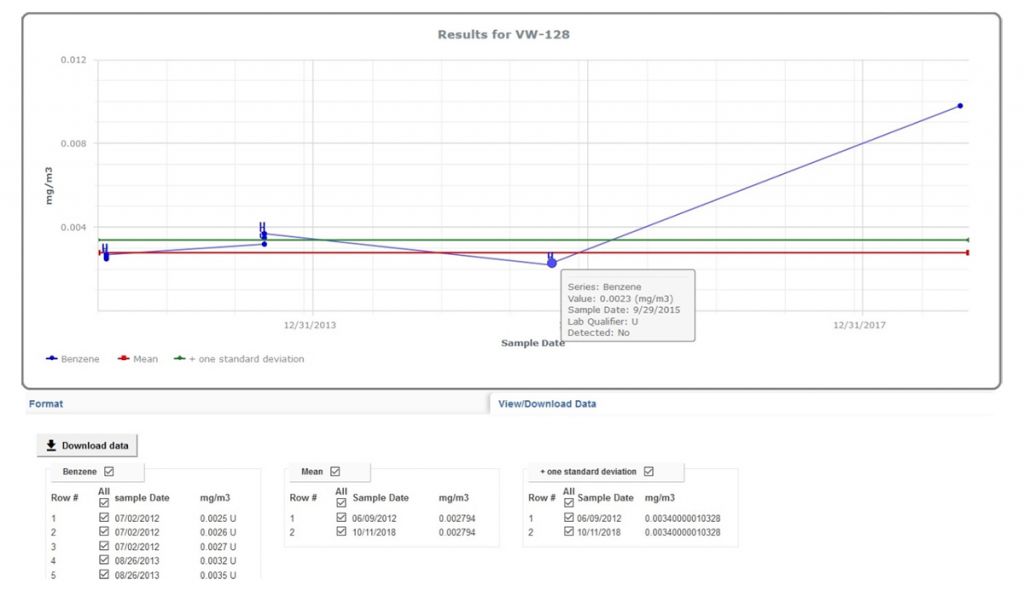
EIM is the world’s leading water quality management software, and has been used since 1999 by many Fortune 500 companies, water utilities, and the US Government. Locus added two key reports to EIM for Water in 2019 to further support water quality reporting. The first new report returns chlorine averages, ranges, and counts. The second new report supports the US EPA’s Lead and Copper rule and includes a charting option. Locus will continue to enhance EIM for Water by releasing the 2019 updates for the Consumer Confidence Report in January 2020.
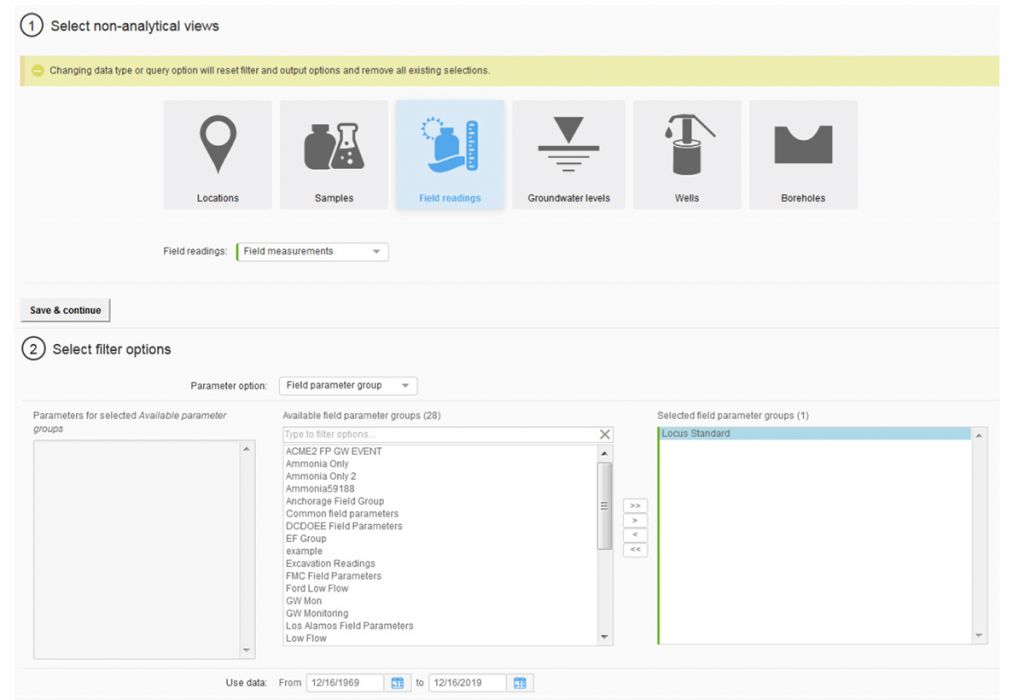
8. Improved Non-Analytical Views
Locus continues to upgrade and improve the EIM user interface and user experience. The most noticeable change in 2019 was the overhaul of the Non-analytical Views pages in EIM, which support data exports for locations, samples, field readings, groundwater levels, and subsurface information. Roughly 25 separate pages were combined into one page that supports all these data views. Users are directed through a series of filter selections that culminate in a grid of results. The new page improves usability and provides one centralized place for these data reports. Locus plans to upgrade the Analytical Views in the same way in 2020.
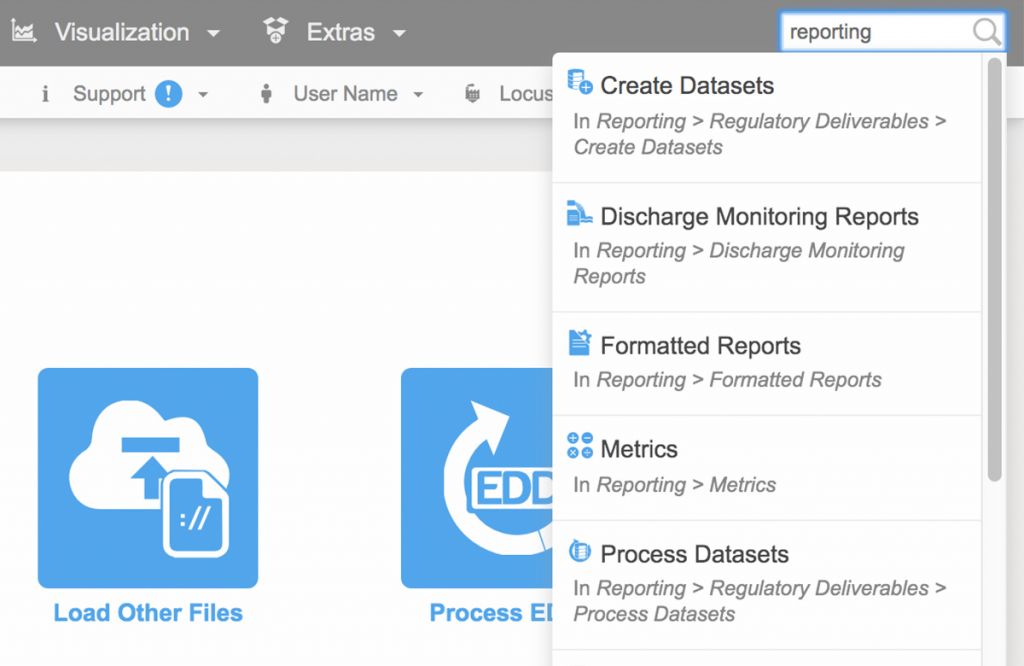
9. EIM search box
To help customers find the correct EIM menu function, Locus added a search box at the top right of EIM. The search box returns any menu items that match the user’s entered search term. In 2020, Locus will expand this search box to return matching help file documents and EDD error help, as well as searches for synonyms of menu items.
10. Historical data reporting in EDD loading
The EIM EDD loader now has a new “View history” option for viewing previously loaded data for the locations and parameters in the EDD. This function lets users put data in the EDD holding table into proper historical context. Users can check for any unexpected increases in parameter concentrations as well as new maximum values for a given location and parameter.
Locus Technologies goes all-in on AWS
SAN FRANCISCO, Calif., 23 July 2019 — Locus Technologies (Locus), the market leader in multi-tenant SaaS water quality, environmental compliance, and sustainability management, today announced that it is going all-in on Amazon Web Services, Inc. (AWS), moving its entire infrastructure to the world’s leading cloud. By moving its flagship product EIM (Environmental Information Management) to AWS this month, Locus will complete its transition to AWS. Locus previously moved its Locus Platform (LP) to AWS in 2018.
EIM is the world’s leading water quality management software used by many Fortune 500 companies, water utilities, and the US Government since 1999. Among its many features, EIM delivers real-time tools to ensure that water utilities deliver clean water to consumers’ taps and don’t discharge contaminated wastewater above allowable limits to groundwater or surface water bodies like streams, lakes, or oceans.
EIM generates big data, and with over 500 million analytical records at over 1.3 million locations worldwide, it is one of the largest centralized, multi-tenant water quality management SaaS systems in the world. With anticipated growth in double digits stemming from the addition of streaming data from sensors and many IoT monitoring devices, Locus needed to have a highly scalable architecture for its software hosting. The unmatched performance and scalability of AWS’s offerings are just the right match for powering Locus’ SaaS.
Because of the scope of its applications, Locus is expecting to leverage the breadth and depth of AWS’s services (including its database systems, serverless architecture, IoT streaming, blockchain, machine learning, and analytics) to automate and enhance the on-demand EHS compliance, sustainability, facility, water, energy, and GHG management tools that Locus’ software provides to its customers.
Running on AWS’s fault-tolerant and highly performant infrastructure will help support Locus’s everyday business, and will scale easily for peak periods, where reporting demand such as GHG calculation engine or significant emissions incidents like spills can skyrocket scalability demand.
By leveraging Amazon CloudFront, Amazon Virtual Private Cloud (Amazon VPC), Amazon Elastic Kubernetes Service (Amazon EKS) and AWS Lambda, Locus is migrating to a microservices architecture to create more than 150 microservices that independently scale workloads while reducing complexity in the cloud, thereby enhancing every element of the customer cloud experience. Locus built a data lake on Amazon Simple Storage Service (Amazon S3) and will leverage Amazon Redshift to analyze the vast amount of data it is storing in the cloud, delivering insights and predictive analytics that uncover chemicals trending patterns and predict future emissions releases at various locations.
Locus intends to leverage AWS IoT services and Amazon Managed Blockchain by building a new native integration to help businesses generate value from the millions of events generated by connected devices such as real-time environmental monitoring sensors and environmental treatment systems controls. AWS IoT is a set of cloud services that let connected devices easily and securely interact with cloud applications like EIM and Locus Platform and other devices. Locus IoT Cloud on AWS allows customers to experience real-time emissions monitoring and management across all their connected sensors and devices. And for customers who want to allow multiple parties to transact (e.g. GHG trading) without a trusted central authority, AWS provides a fully managed, scalable blockchain service. Amazon Managed Blockchain is a fully managed service makes it easy to setup, deploy, and manage scalable blockchain networks that Locus intends to use for emissions management and trading.
For example, a water utility company that maintains thousands of IoT-enabled sensors for water flow, pressure, pH, or other water quality measuring devices across their dispersed facilities and pipeline networks will be able to use Locus IoT on AWS to ingest and manage the data generated by those sensors and devices, and interpret it in real time. By combining water sensor data with regulatory databases, water utility companies will be able to automatically create an emergency shutdown if chemical or other exceedances or device faults are detected and as such, will be better prepared to serve their customers and environment.
By combining the powerful, actionable intelligence in EIM and rapid responsiveness through Locus Platform with the scalability and fast-query performance of AWS, customers will be able to analyze large datasets seamlessly on arrival in real time. This will allow Locus’ customers to explore information quickly, find insights, and take actions from a greater variety and volume of data—all without investing the significant time and resources required to administer a self-managed on-premises data warehouse.
“After 22 years in business, and after evaluating AWS for a year with our Locus Platform, we decided to switch and continue all our business on AWS. We are taking advantage of their extensive computing power, depth and breadth of services and expertise to develop an effective cloud infrastructure to support our growing business and goal of saving the planet Earth by providing and managing factual information on emissions management, all the while reducing operational costs of Locus’ customers,” said Neno Duplan CEO of Locus. “By operating on AWS, we can scale and innovate quickly to provide new features and improvements to our services – such as blockchain-based emissions management – and deliver exceptional scalability for our enterprise customers. With AWS, we don’t have to focus on the undifferentiated heavy lifting of managing our infrastructure, and can concentrate instead on developing and improving apps and services.”
“By organizing and analyzing environmental, sustainability, and water quality information in the cloud, Locus is helping organizations to understand the impact of climate change on drinking water,” said Mike Clayville, Vice President, Worldwide Commercial Sales at AWS. “AWS’s unmatched portfolio of cloud services, proven operational expertise, and unmatched reliability will help Locus to further automate environmental compliance for companies ranging from local water utilities to multinational manufacturing corporations, to federal government research agencies. ”By choosing to go all-in on AWS, Locus is able to innovate and expand globally, developing new solutions that will leverage comprehensive analytics and machine learning services to gain deeper insights and forecast sustainability metrics that will help deliver clean drinking water to consumers around the world.”
Is PFAS Contamination in US Drinking Water Supply the Next Crisis?
In most cities in the US, drinking water quality conforms with the norms of the Safe Drinking Water Act, which requires EPA to set Maximum Contaminant Levels (MCL) for potential pollutants. Besides, the EPA’s Consumer Confidence Rule (CCR) of 1998 requires most public water suppliers to provide consumer confidence reports, also known as annual water quality reports, to their customers.
PFAS stands for “perfluoroalkyl and polyfluoroalkyl substances,” with the most important thing to know that this large group of synthetic chemicals includes perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA) and perfluorooctane sulfonate (PFOS).
Not Regulated by EPA
When it comes to drinking water from the tap in the US, the phrase that fits concerning PFOA and PFOS is “caveat emptor” (buyer beware). The EPA has not regulated these chemicals. There are no federal regulations for PFOA and PFOS in drinking water in the US.
In May 2016, the EPA established a drinking water “health advisory” of 70 parts per trillion (ppt) for the combined concentrations of PFOA and PFOS. While that was a start, there’s a big difference between a health advisory and a regulation that has teeth. Moreover, many scientists consider 70 ppt too high a limit. Reportedly, the EPA is considering turning its 70 ppt health advisory into regulation.
Meanwhile, some states have stepped up to the plate to protect their residents and visitors better. In April 2019, for instance, the New Jersey Department of Environmental Protection (DEP) proposed maximum contamination levels (MCLs) of 14 ppt for PFOA and 13 ppt for PFOS in the state’s drinking water.
As a water consumer, you should be aware of this crisis, as it has the potential to affect both your health and wealth.
What are PFOA and PFOS?
This toxic couple has contaminated the drinking water supply in areas surrounding some industrial sites and military bases. They’re the most studied of the PFAS group because they’re the ones that have been produced in the most significant quantities in the United States, according to the US Environmental Protection Agency (EPA).
PFOA and PFOS, which repel water and stains of various types, have been used as coatings on fabrics and leather and in the production of stain-repellent carpeting and are found in firefighting foams — which have been used extensively on US military bases for decades — among other products. Moreover, some related polyfluoroalkyl compounds can be transformed into these chemicals in the environment, per the National Institutes of Health (NIH), with the Environmental Working Group (EWG) stating that some perfluorinated chemicals not only break down into PFOA in the environment but also can do so in the human body.
While PFOA and PFOS are no longer made in the US, that hardly matters in our global economy. Both are still produced internationally, which means they end up in our country via imports of consumer goods such as carpet, apparel, textiles, and paper and packaging.
Why all the concern about PFOA and PFOS?
These chemicals — dubbed “forever chemicals” because they’re persistent in the environment and the human body — have been linked to cancer, thyroid disease, weakened the immune system and liver function, low infant birth weight, and other health problems, according to many sources.
And this is what the EPA says: “There is evidence that exposure to PFAS can lead to adverse health outcomes in humans. If humans, or animals, ingest PFAS…the PFAS are absorbed and can accumulate in the body. PFAS stay in the human body for long periods. As a result, as people get exposed to PFAS from different sources over time, the level of PFAS in their bodies may increase to the point where they suffer from adverse health effects.”
EHS Digital Transformation: Managing Drinking Water Quality Data and Compliance: CCR in the Cloud
In most industrialized cities around the world, drinking water is readily available and safe. Safeguarding groundwater (aquifers), streams, rivers, reservoirs, and lakes is crucial to continue delivering clean water on the tap. So is testing and validated water quality data. There are several aspects of drinking water quality that is of concern in the United States, including Cryptosporidium, disinfection by-products, lead, perchlorates, and pharmaceutical substances.

Recent headlines about water quality issues in cities like Flint, Pittsburgh, Asheville, or Rome and Cape Town are motivating consumers to ask more questions about their water quality. Albuquerque’s groundwater is becoming seriously depleted; Fresno’s groundwater is highly susceptible to contamination; In Atlanta, Chicago, Detroit, Houston, Los Angeles, New Orleans, Newark, Philadelphia, Phoenix, San Diego and Washington, D.C., source water is threatened by runoff and industrial or sewage contamination; Water supplies in Baltimore, Fresno, Los Angeles, New Orleans, San Diego, and several other cities are vulnerable to agricultural pollution containing nitrogen, pesticides or sediment.

Locus Technologies IoT Monitoring. Connected at all times.
In most cities in the US, drinking water quality is in conformity with the norms of the Safe Drinking Water Act, which requires EPA to set Maximum Contaminant Levels (MCL) for potential pollutants. In addition, the EPA’s Consumer Confidence Report (CCR) Rule of 1998 requires most public water suppliers to provide consumer confidence reports, also known as annual water quality reports, to their customers. Each year by July 1 anyone connected to a public water system should receive in the mail an annual water quality report that tells where water in a specific locality comes from and what’s in it. Locus EIM automates this reporting and allows utilities to be transparent by publishing CCR online in real time so that consumers have access to their CCR at all times. Consumers can also find out about these local reports on a map provided by EPA.
Utilities must maintain good water quality records and manage them in a secure database with built-in alerts for any outliers so that responsible water quality managers can react quickly when there is exceedance of MCL or another regulatory limit.
Learn more about our water solutions.
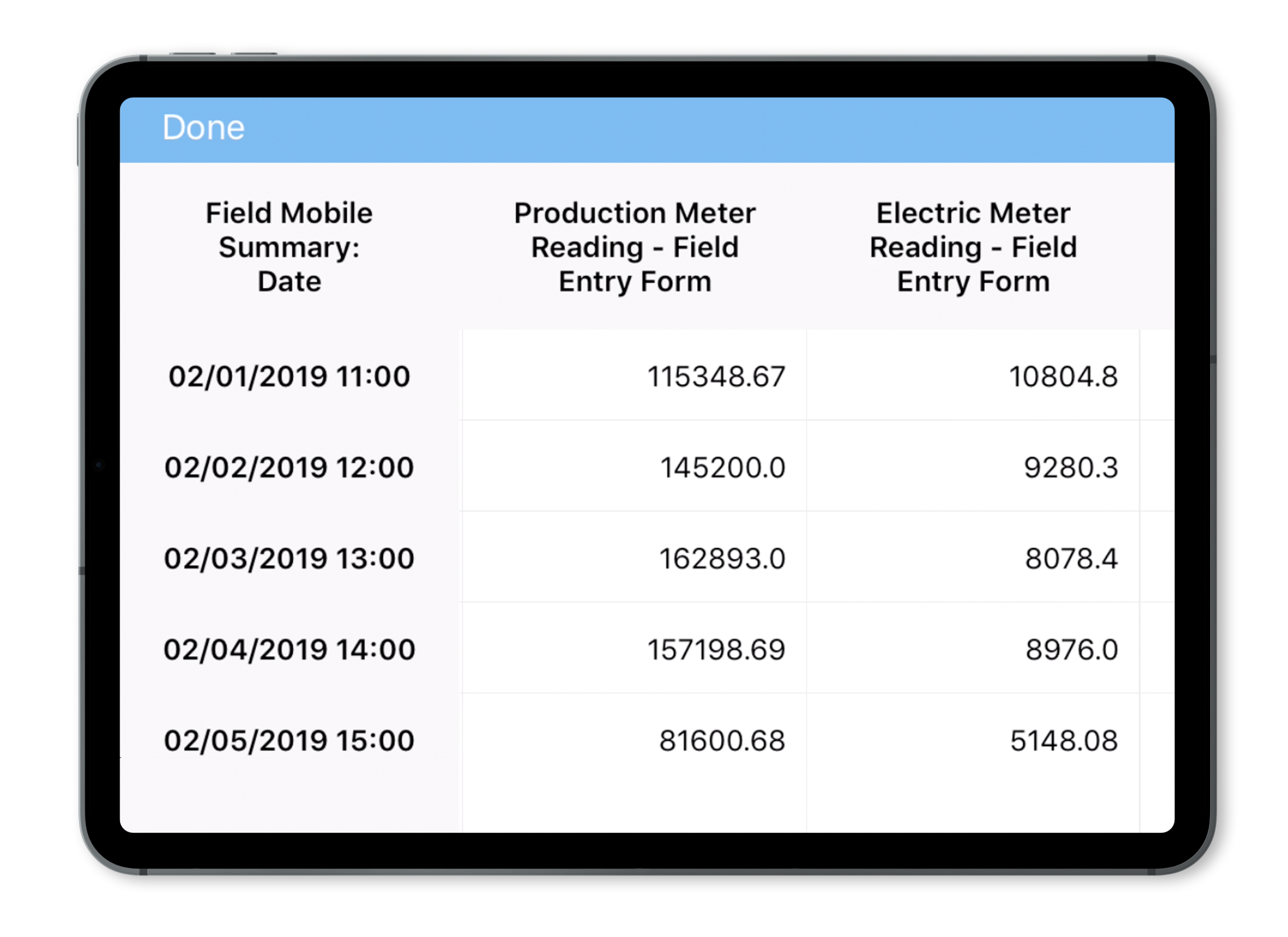
A better way to manage all those ops readings
Manage all those ops readings without spreadsheets or paper forms
I am constantly reminded by the number of calls we receive, that no matter how robust a SCADA and HMI system is, there is always a requirement for in-field O&M verification and documentation. It’s almost universal, and spans a myriad of industries, large and small, the need to monitor and record thousands of periodic (daily/per shift/weekly, etc.) routine readings/recordings at a prescribed frequency often recorded on pen to paper field forms. The same processes sometimes use “template” spreadsheets for data collection that are then emailed/placed on shared file servers or otherwise sent to some central location for review and post processing. These processes are antiquated and subject to data quality and record keeping challenges.
It’s time for an upgrade!
Why simple form builders are not a good software solution for ops data
Electronic forms are great for collecting data and almost every business entity has built such forms in spreadsheets, word processing or simple databases to collect the information. In addition, there is a software category of form builders and they can certainly build forms. The question becomes is it a good fit so solve your business process issues?
Most customers have more sophisticated needs than simply collecting information on one or more custom forms – they want to do something with all the information collected far beyond what simple form builder tools can provide. Even customers with sophisticated spreadsheet forms, can’t manage them as they multiply exponentially or their Excel gurus retire.
Here are some examples of where you may require software tools beyond a simple form builder:
- Collecting equipment readings on each shift at multiple locations and report the data to centralized management, who review the data, look for trends/ issues.
- Verifying and validating data at the point of data entry to eliminate data entry errors.
- Automatically visualizing (charts or tables) information in near real time to make operations decisions.
- Sharing the information with others.
- Scheduling activities related to periodic or infrequent data collection events.
- Receiving notifications when actions are due.
- Automatically creating regulatory reports in prescribed formats.
- Creating complex work flows and audited approval processes.
- Creating intelligent forms with calculations based on past data or other criteria
Forms with Benefits
Locus Platform is a configurable platform with standard applications that are easy to configure to customers unique requirements. One of its many strengths is its powerful form builder capable of creating simple or complex forms with simple or sophisticated logic. So for customers looking to move from paper and spreadsheet templates, it’s an excellent option to consider, especially if you require more than a simple “fill in the blank” form for transmittal using mobile devices. Best of all, the data are securely stored in a database structure for reporting and alternative business uses and analyses, compared to the almost impossible management of hundreds of spreadsheets or paper forms.
Here are some examples where sophisticated forms are integrated with a flexible database:
- Water Utilities – Tracking chlorination and aerobic digestion processes with daily inputs/outputs with a monthly summary and chart, and tracking well production across well fields.
- Water Utilities – Tracking periodic sewer discharges and water samples for permit compliance.
- Agriculture – Monitoring food processing equipment for compliance with optimum equipment operating parameters for air permits.
- Pharmaceutical/Chemical Manufacturing Facilities- Tracking EHS daily, weekly, monthly, etc. investigations and in-house audits.
- Universities – tracking chemical inventories.
- Facility Engineering – Documenting O&M activities for groundwater treatment systems.
- Electric Utilities – Monitoring water/energy/gas usage from old style meters for sustainability reporting with data entry validation.
- Refineries and Terminals – Collecting O&M, usage and wastewater data.
If you still rely on paper forms and template spreadsheets and are ready to streamline your process and enhance the value of your data, give us a call and we can show you a range of options that will retire the paper forms for good!
Locus announces EIM One — a new way to streamline environmental data management for projects of all sizes and needs
MOUNTAIN VIEW, Calif., 12 March 2019 — Locus Technologies, (Locus), the industry leader in EHS, sustainability, and environmental compliance management software, is pleased to announce EIM One is available today, enabling a range of affordable solutions to automate laboratory analytical testing, analytical data workflow process, and meet environmental information management and EHS compliance needs.
“EIM has been a market leader since its introduction in 1999, and has a long history meeting the environmental compliance needs at a wide range of complex, technically challenging sites and enterprise deployments. However, some projects need a simpler, focused solution to manage analytical data for small sites or drinking water utilities. It’s for these projects that EIM One was created. EIM One can be deployed on hours’ notice and used for routine data collection needs often handled by spreadsheets or paper forms,” said Wes Hawthorne, President of Locus.
With today’s current push towards digital transformation, many consultants, small firms, water utilities, and others are ready to finally move away from ad hoc data management approaches and adopt a more robust and formal software solution. However, it is important that the solution be configurable, scalable and right-sized for their needs today and be able to expand as their needs and businesses change.
EIM One takes advantage of Locus’ 20-year history of EHS software in the cloud and includes all the essentials for environmental and analytical data management in a modular and scalable package. This means customers can start with the essentials and add functionality when and if they need it. This approach allows Locus to offer a range of attractive pricing options. With the essential EIM One configuration, customers will be loading analytical laboratory data and producing reports in record time and taking advantage of market tested SaaS-based database design, configurability, security, and accessibility.
“EIM One is a great place to start if you’re new to digital transformation. We are excited to release EIM One and finally give customers the options they have been asking for and provide just the essentials they need so they can confidently start to digitally transform their older data management approaches at very affordable pricing” said Neno Duplan, Founder and CEO at Locus. “Today’s customer wants choice above all else, and EIM One gives them the options, including mobile, in a modern configurable SaaS solution.”
Tips for choosing a GIS application for your environmental database
You can turbocharge your water data management by including a geographical information system (GIS) in your toolkit! Your data analysis efficiency also gets a huge boost if your data management system includes a GIS system “out of the box” because you won’t have to manually transfer data to your GIS. All your data is seamlessly available in both systems.
Not all GIS packages are created equal, though. Here are some tips to consider when looking at mapping applications for your environmental data:
1) Confirm that integration is built-in and thorough
Mapping is easy when properly integrated with your environmental database. You should not need extra filters or add-on programs to visualize your data. Look for built-in availability of features, such as “click to map”, that take the guesswork and frustration out of mapping for meaningful results.
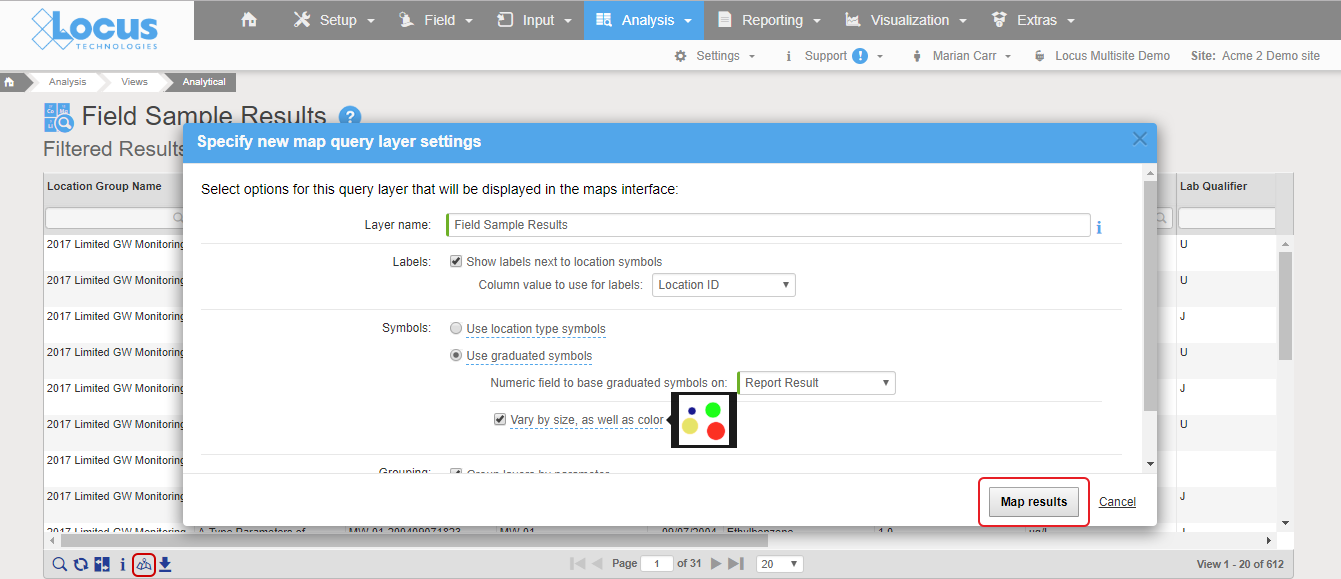
Good integration means mapping is as easy as clicking a “show on map” button. In Locus EIM, you can run a data query and click “Show results on map” icon, change the default settings if desired, and instantly launch a detailed map with a range of query layers to review all chemicals at the locations of interest.
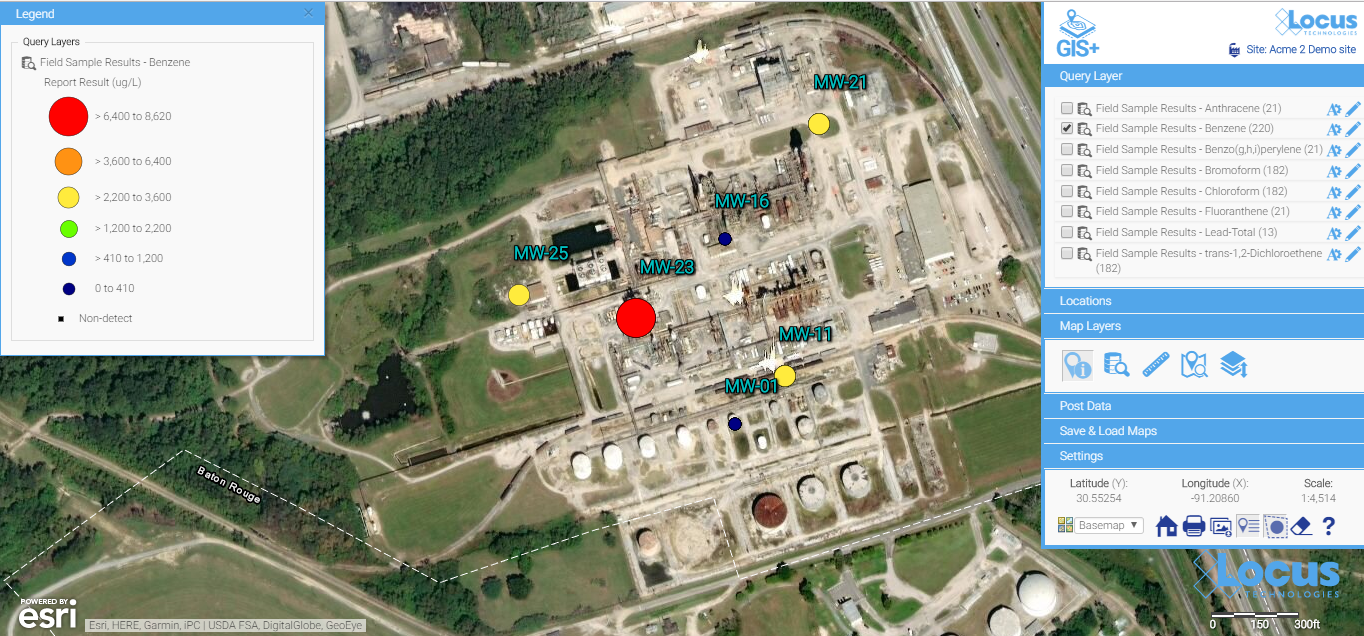
All the query results are presented as query layers, so you can review the results in detail. This map was created with the easy “show results on map” functionality, which anyone can use with no training.
2) Check for formatting customization options
Look for easy editing tools to change the label colors, sizes, fonts, positioning, and symbols. Some map backgrounds make the default label styles hard to read and diminish the utility of the map, or if you’re displaying a large quantity of data, you’ll almost certainly need to tweak some display options to make these labels more readable.
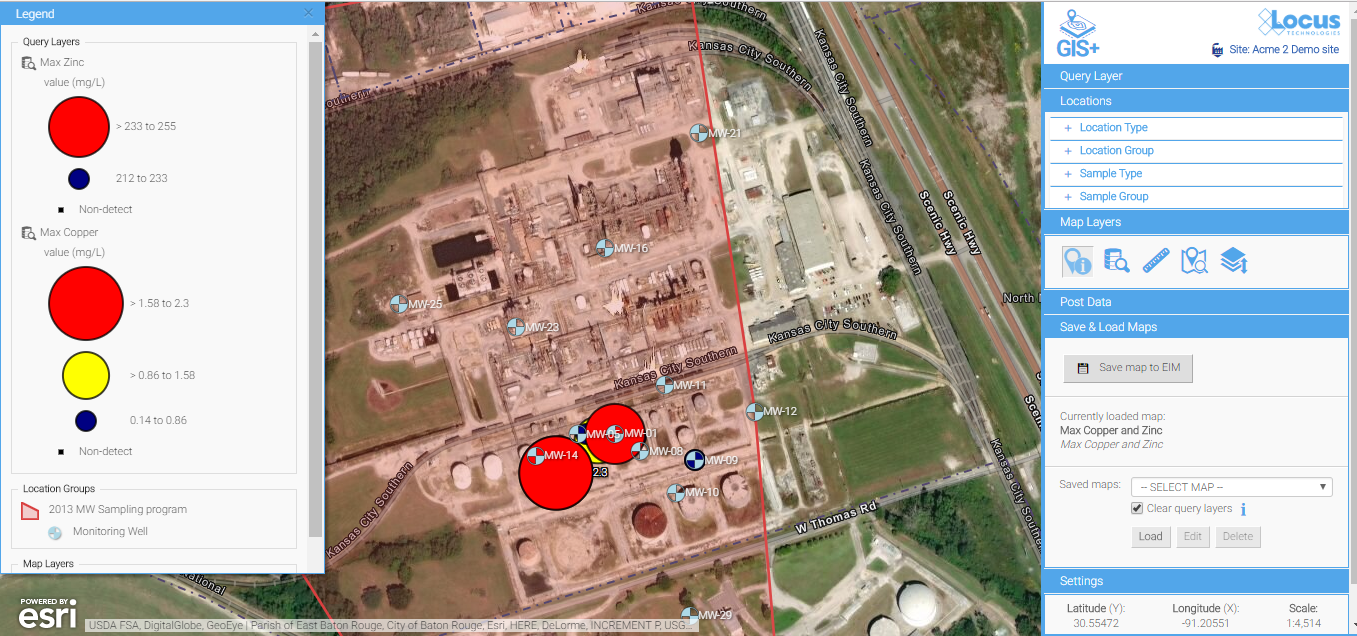
Default label styles are legible on this background, but they are a bit hard to read.
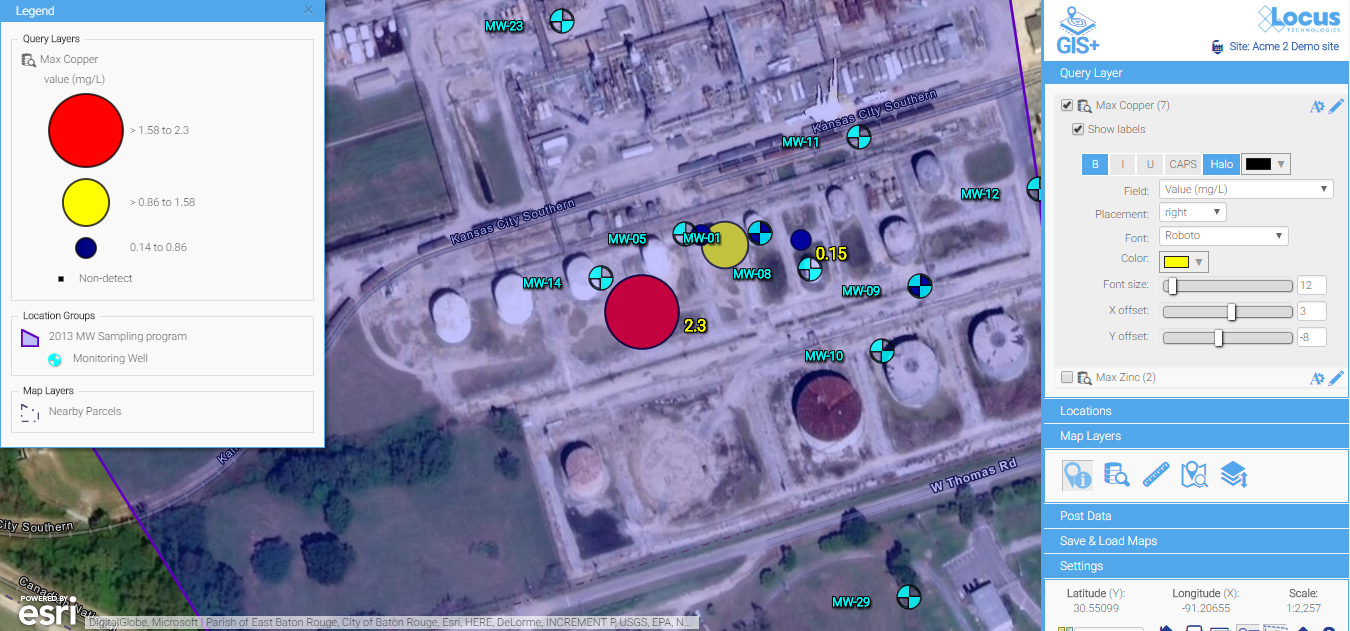
A few simple updates to the font color, font sizes, label offset, and background color make for much easier reading. Changes are made via easy-to-use menus and are instantly updated on the map, so you have total control to make a perfectly labeled map.
3) Look for built-in contouring for quick assessment of the extent of the spatial impact
Contours can be a great way to visually interpret the movement of contaminants in groundwater and is a powerful visualization tool. In the example below, you can clearly see the direction the plume is heading and the source of the problem. An integrated GIS with a contouring engine lets you go straight from a data query to a contour map—without export to external contouring or mapping packages. This is great for quick assessments for your project team.
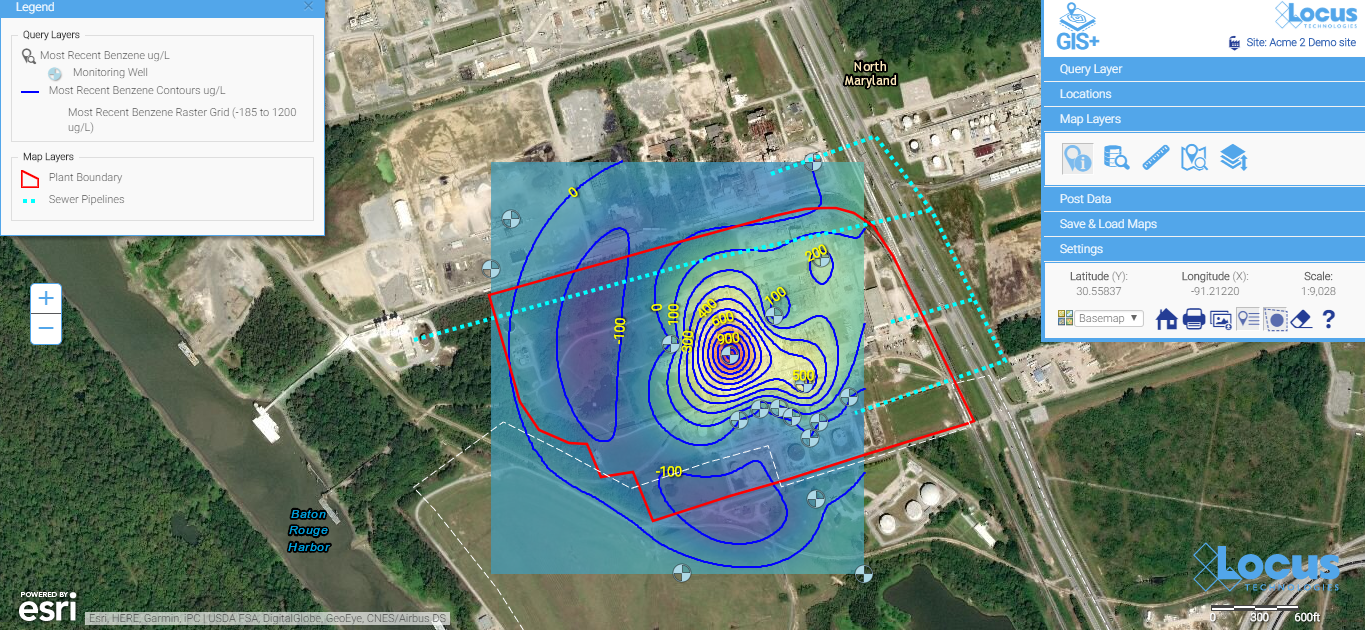
Contour maps make it easy to visualize the source and extent of the plumes. They can be easily created with environmental database management systems that include basic contouring functionality.
4) Look for something easy to use that doesn’t require staff with specialized mapping knowledge
Many companies use sophisticated and expensive mapping software for their needs. But the people running those systems are highly trained and often don’t have easy access to your environmental data. For routine data review and analysis, simple is better. Save the expensive, stand-alone GIS for wall-sized maps and complex regulatory reports.
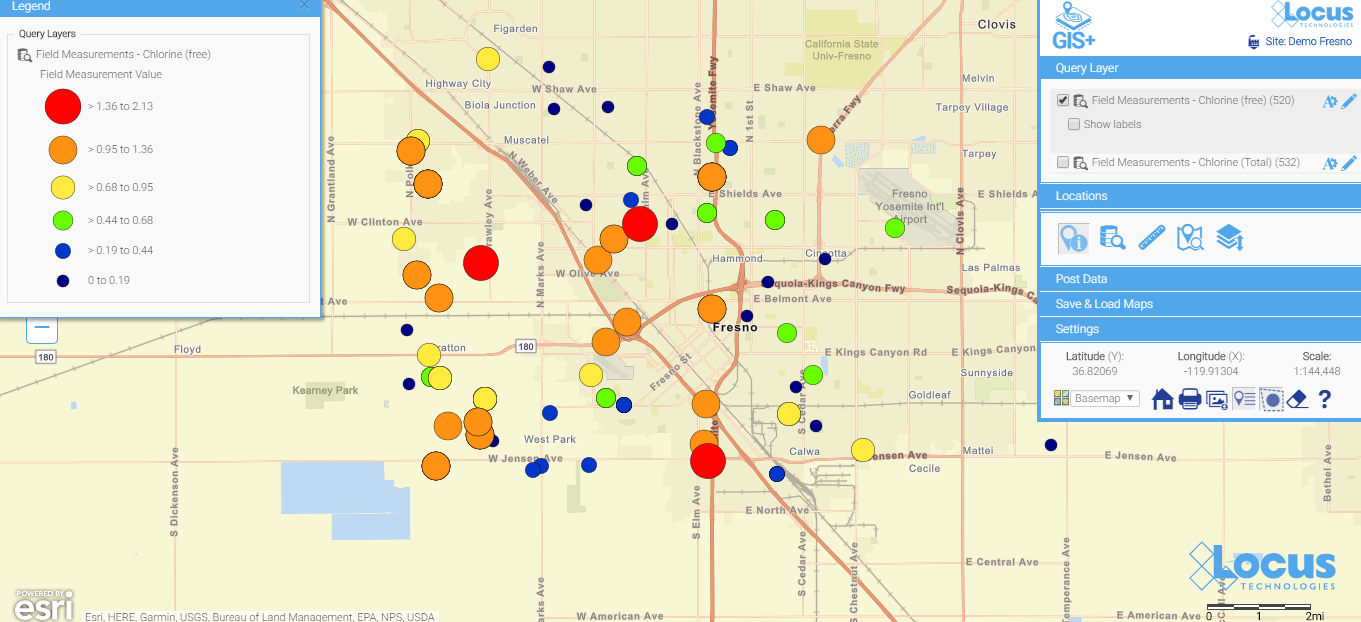
Here is a simple map (which is saved, so anyone can run it) showing today’s chlorine data in a water distribution system. You don’t have to wait for the GIS department to create a map when you use a GIS that’s integrated with your environmental database system. When data are updated daily from field readings, these maps can be incredibly helpful for operational personnel.
 See your data in new ways with Locus GIS for environmental management.
See your data in new ways with Locus GIS for environmental management.Locus offers integrated GIS/environmental data management solutions for organizations in many industries.
Find out more >
Taking the next steps
After viewing some of the many visualization possibilities in this blog, the next step is make some maps happen!
- Make sure your environmental data system has integrated mapping options.
- Make sure your sampling/evaluation/monitoring locations have a consistent set of coordinates. If you have a mixed bag of coordinate systems, you will need to standardize. Otherwise, your maps will not be meaningful. Here are some options to try, as well as some good resource sites:
- https://epsg.io/ (transformations)
- http://www.earthpoint.us/Convert.aspx (transformations)
- Start with a few easy maps—and build from there.
Happy mapping!
Shape of Water: Cape Town running out of drinking water
The city cut daily water use limits first to 87 liters and then 50 in a bid to avert shutting off supplies.
The city had set a 50-liter daily limit and had told citizens “Day Zero” was approaching when people would have to queue at standpipes.
But water-saving efforts in the South African city have seen the day pushed back from April to 27 August. Seasonal rains should mean that date is now averted, the city said. The shortages follow three years of low rainfall. The city had resorted to increasingly drastic measures to clamp down on water usage, including “naming and shaming” the 100 addresses using the most water and fining residents who failed to comply with the 50 liters (13 gallons) limit per person.
By comparison, the average California consumer uses some 322 liters (85 gallons) of water per day. Water use in California was highest in the summer months of June through September, where it averaged 412 liters per person per day. By comparison, during the cooler and wetter months of January through March of 2016, average per capita water use was only 242 liters per person per day.
Although the risk that piped water supplies will be shut off this year has receded, politicians and environmentalists warn that the water crisis is there to stay in Cape Town, as year-on-year rainfall levels dwindle.
Rethinking Urban Water Management

Improved wastewater distribution and treatment technologies have largely eradicated once-common waterborne diseases.
Water supply and distribution were ranked as the fourth greatest engineering achievement of the 20th century by the National Academy of Engineering (NAE), and rightfully so.
Developments in water management have drastically improved public health and safety. In the early 1900s, for example, dysentery and diarrhea, both waterborne diseases, were the third largest cause of death in the United States (Wulf, 2000).
Currently, incidences of waterborne diseases in the United States are minimal, thanks in large measure to improved water distribution and treatment technologies. Additionally, cities are now less susceptible to flooding due to the development and implementation of storm drain systems. The current paradigm in urban water management entails a centralized drinking water plant, connected to individual households through an underground network of pipes, and a sewer that carries the wastewater to a centralized treatment plant for further discharge into a natural water stream. This system has permitted significant progress in our society.
Our clean water supply and sanitation systems may be endangered
NAE also says that providing access to clean water is the fifth greatest challenge that we will face this century. Despite all its positive qualities, the urban water management paradigm has some serious limitations that are likely to get worse in the future due to increasing urban population, expansion of paved areas, scarcity of water, and climate change:
- Reliance on large quantities of water
Centralized systems depend heavily on large quantities of water— an already scarce resource that will likely become even more so, with increasing population and climate change. Population growth also requires increasing the capacity of the water treatment plants and expanding the already-complex network of water lines. - More runoff
Fast-growing cities mean larger paved areas and, therefore, higher runoff during rain events. Runoff, which carries pollutants from the street surface, is difficult and expensive to contain and treat. Many cities— including some cities here in the San Francisco Bay Area— discharge their storm water runoff directly to the sea, with minimal treatment. If you live in the San Francisco Bay area, you may have noticed blue signs posted next to storm drains, which read “Drains to the Bay”. Runoff is expected to become an even bigger issue due to the variability in rainfall caused by climate change. - Expensive operation and maintenance
Extensive underground pipe networks for drinking and wastewater are expensive to operate and maintain. They make urban planning more difficult because pipe locations are not always known, and multiple independent agencies and companies run pipes and cables underground. Furthermore, the lead poisoning in Flint, Michigan, shows us that poorly maintained old pipes can present a serious public health issue. - Leaky pipes
An estimated 10 – 40% of the global urban water supply is lost due to leaky pipes, which are difficult and costly to repair (Larsen et al., 2016).. - Lost nutrients
Centralized water systems are not particularly efficient in recovering the nutrients that wastewater offers (i.e., nitrogen and phosphorous).
In search of a more sustainable solution

Centralized treatment plants have vastly improved public health, but perhaps a more decentralized urban water management system would address some of their shortcomings.
Across the country and the world, innovative teams have proposed and implemented multiple improvements and alternatives to the current urban water management paradigm. But there is still no widely-accepted solution to the current and future challenges in urban water management.
A real, sustainable solution would involve a combination of measures adapted to local needs. One promising approach to replace or supplement our current systems is to decentralize the management of urban water. This means treating the wastewater close to the source in small-scale treatment systems, instead of transporting it through a complex network of pipes to a centralized treatment plant. Decentralization offers a series of advantages— such as less reliance on pipes, easier coverage expansion in rapidly growing cities, lower variability in the loading of the treatment systems, and efficient utilization of the wastewater as a resource.
Decentralized systems, for example, offer the opportunity to separate blackwater (urine, faeces, flushwater), brownwater (faeces and flushwater), and greywater (water from washing food, clothes, and dishware, and from bathing)— which would be very complicated in a centralized system, due to the need to install separate pipelines for each.
Separating these sources makes wastewater treatment more efficient, as each of them require different extents of treatment. It also opens the possibility of water reuse. For example, greywater can easily be treated at a local scale and reused, therefore saving water and energy. Source separation also provides the opportunity to recover nutrients from human waste more efficiently. Urine, for example, contains a high concentration of nitrogen, which is lost as nitrogen gas in most centralized treatment plants. By separating the urine in a decentralized system, nitrogen could be recovered.
Nevertheless, decentralized systems have their own challenges. These include the complexity of operating, maintaining, and inspecting a network of treatment systems; the development of reliable and robust small-scale systems; and public acceptance. Decentralized urban water management is still in its early development, but it’s an idea that certainly deserves further consideration.
Why now?
Historically, major innovations in urban water management have been triggered by crises: the overpopulation of Ancient Rome led to the development of large scale water distribution systems; the cholera and typhoid fever outbreaks in Europe led to the development of disinfection; and the severe pollution of water stream led to development and implementation of wastewater treatment (Sedlak, 2014). With increasing world population, rapid urbanization, climate change, and a growing scarcity of resources, our current urban water management systems will be under increasingly significant stress. It is crucial to our health, our safety, and the overall well-being of our society that we anticipate the challenges and start innovating now.
—
References
Hansen, R. D. (n.d.). Water and Wastewater Systems in Imperial Rome. [online] <Accessed 16 December 2016>
Larsen, T. A., Hoffmann, S., Lüthi, C., Truffer, B., Maurer, M. (2016). Emerging solutions to the water challenges of an urbanizing world. Science, 352 (6288), pp. 928-933.
National Academy of Engineering. (2008). Grand Challenges for Engineering. National Academy of Science.
San Francisco Public Utilities Commission. (n.d.). Only Drain Down the Rain. [online] <Accessed on 16 December 2016>
Sedlak, D. (2014). Water 4.0: The Past, Present, and Future of the World’s Most Vital Resource. Yale University Press.
Tilley, E., Ulrich, L., Lüthi, C., Reymond, P., Schertenleib, R., Zurbrügg C. (2014). Compendium of Sanitation Systems and Technologies, 2nd Revised Edition. Swiss Federal Institute of Aquatic Science and Technology (Eawag), Dübendorf.
Wulf, W. A. (2000). Great Achievements and Grand Challenges. The Bridge, 30 (3&4), pp. 5-10.
—
Still looking for the right EHS software to revolutionize your environmental and compliance initiatives? Book a demo with us today!

About guest blogger— Victor Huanambal, Locus Technologies
Victor Huanambal has been working at Locus for close to two years as an environmental engineer. He graduated from the University of California, Berkeley, in 2014.
At Locus, he is mostly involved in projects related to groundwater remediation, environmental compliance, and greenhouse gases verification.
Locus Technologies » Industries » Water Utilities » Page 5
Locus Technologies
299 Fairchild Drive
Mountain View, CA 94043
P: +1 (650) 960-1640
F: +1 (415) 360-5889
Locus Technologies provides cloud-based environmental software and mobile solutions for EHS, sustainability management, GHG reporting, water quality management, risk management, and analytical, geologic, and ecologic environmental data management.