12 ways commercial SaaS can save your complex environmental data (part 3/4)
 Continued from Part 2
Continued from Part 2
6) Simultaneous usage is better supported by databases
Microsoft Support confirms that it is possible to share an Excel workbook. Two or more individuals can indeed access the same spreadsheet simultaneously. Edits are even possible:
You can create a shared workbook and place it on a network location where several people can edit the contents simultaneously… As the owner of the shared workbook, you can manage it by controlling user access to the shared workbook and resolving conflicting changes. When all changes have been incorporated, you can stop sharing the workbook.
Sharing a spreadsheet may work in a small office or facility with a couple of users, but it certainly is not a viable option when more users need to access, view, and generate reports. This is a task for which databases are far better suited.
On any given day, for example, Locus EIM supports hundreds of simultaneous users. Some may be inputting form data, while others are loading and checking laboratory EDDs, and still others are creating reports and graphs and viewing data on maps and in tables. Many of these are very data-intensive processes—yet Locus EIM handles them seamlessly.
Being able to handle such simultaneous activity is inherent in the designs of relational databases. In contrast, the ability to share an Excel workbook is not a native feature of such software and, as such, is unlikely to meet the needs of most organizations (especially as they evolve and grow).
 7) Processing speed, capacity, and scalability is better with databases
7) Processing speed, capacity, and scalability is better with databases
Compared to spreadsheets, databases are the hands-down winners with respect to processing speed and the numbers of records they can store. Higher-end databases can store hundreds of millions of records. In contrast, spreadsheets with hundreds of thousands of records can bog down and become difficult to manage.
An underappreciated, yet the critical difference is that while you’re using a spreadsheet, the entire file is stored in a computer’s random access memory (RAM). In contrast, when using a database, only the dataset that you are currently working with is loaded into RAM.
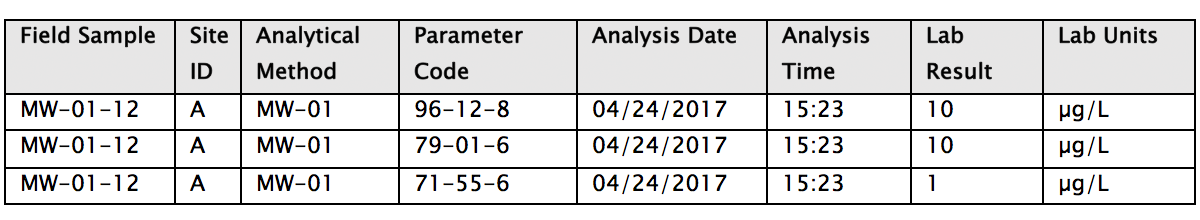
To illustrate just how fast a powerful database can be, I sent a query to EIM at our secure facility on the opposite coast, asking how many “benzene” records were in one of our larger laboratory results table (N > 4,500,000). Sitting at a desk here in the hinterlands of Vermont, the result (“number of records = 64773”) came back in less than a second. I did not even have time to call in the cows for their afternoon milking.
Because they are both faster and can store more, databases scale far better than spreadsheets. As such, they can meet both your current and future requirements, no matter how fast the information you are required to store grows over time.
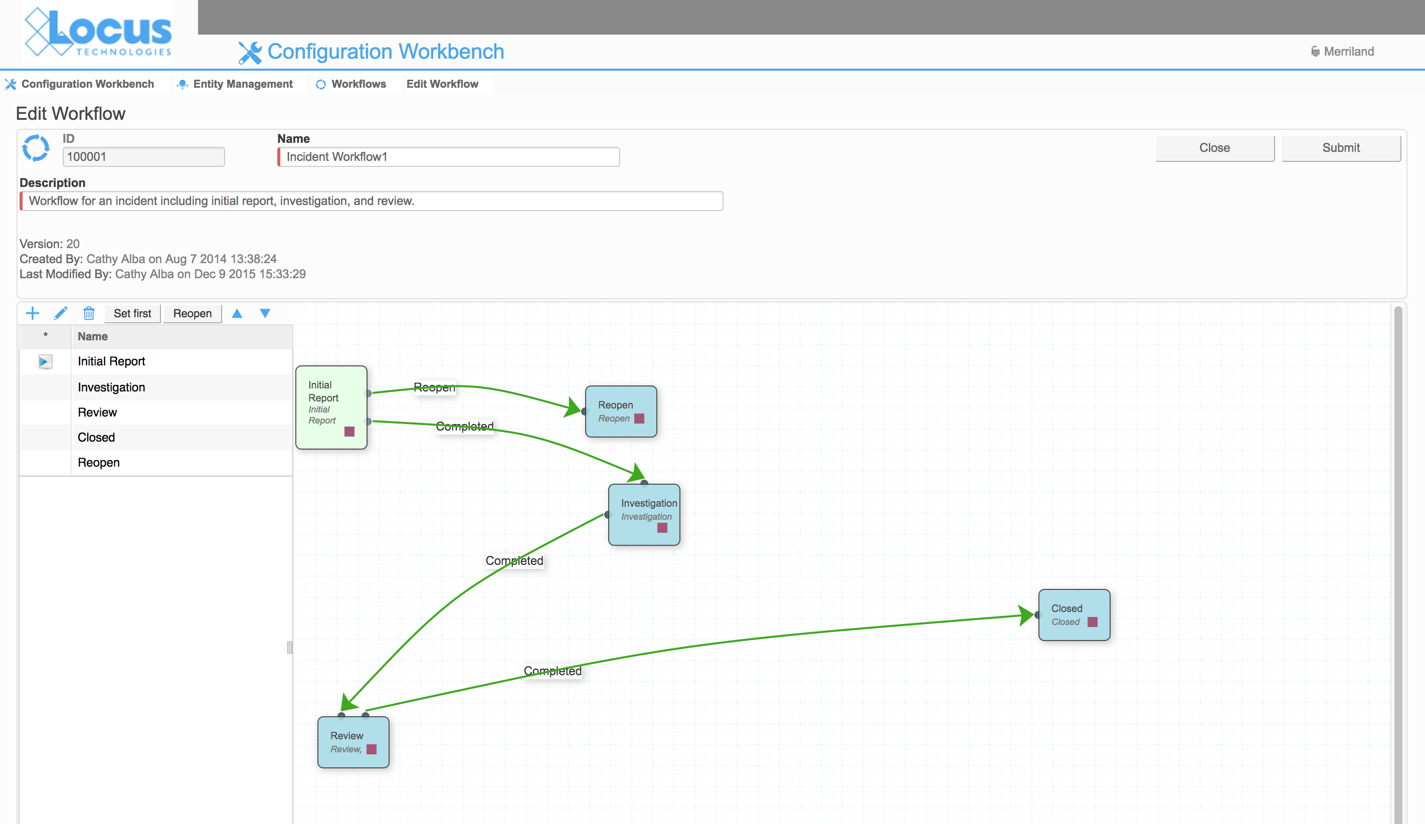
 8) Databases support creating and following complex workflows
8) Databases support creating and following complex workflows
In contrast to spreadsheets, databases support the creation of formal workflows. Let’s consider one example from EIM—its cradle-to-grave sample planning, collection, and tracking process.
Using EIM’s Sample Planning module, you can:
- Identify one-time or recurring samples and analyses that need to be collected
- Transfer information on these planned samples and analyses to Locus Mobile
- Collect field data
- Upload field data to EIM (where it is stored in various tables)
- Generate chains of custody and sample bottle labels (after which the samples are sent to the lab for analysis)
- (Days or weeks later, labs upload their findings to EIM’s holding table, where they are automatically matched with the previously uploaded field information)
- Receive notifications that the lab results are now available (additional notifications can be sent if any results are found to exceed a regulatory limit)
- Track the status of the samples throughout this process with forms that can tell you the status of each planned sample, including whether any results are late or missing
- Generate relevant reports, maps and charts for internal use or for submittal to the appropriate agency
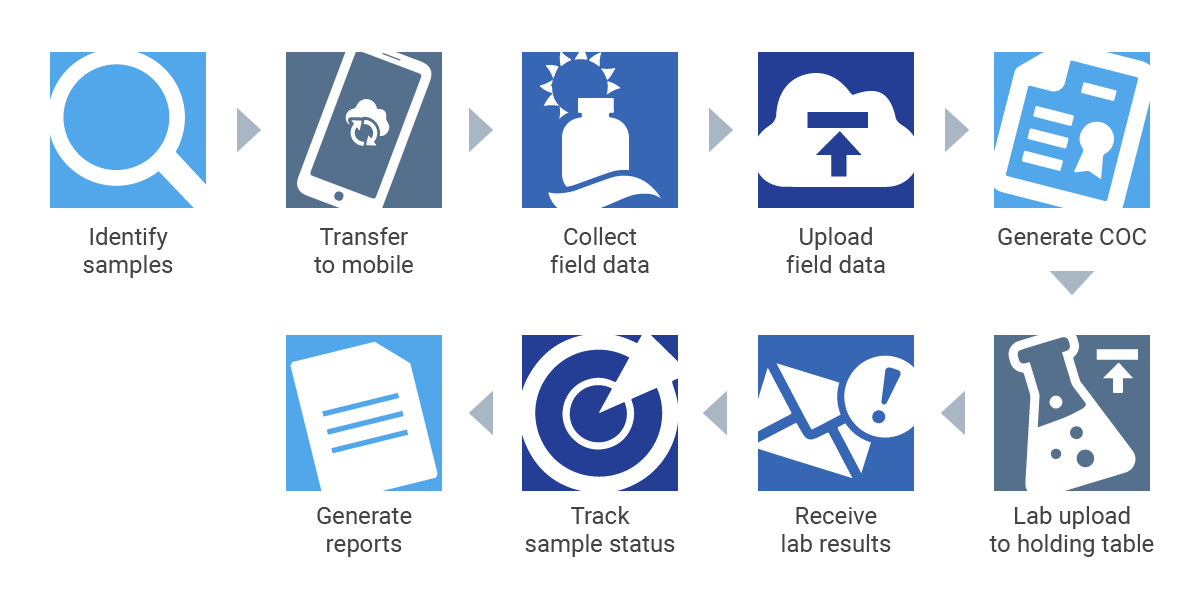
You simply could not build such a comprehensive and sophisticated workflow in Excel. Notice we mentioned maps. Building complex workflows is yet another area where advanced, integrated database management systems shine, especially as they can automatically create GIS-based maps of the results from data housed in the database—without the need (or expense) for ancillary software.
 9) Databases provide more security than spreadsheets
9) Databases provide more security than spreadsheets
Microsoft identifies the following security features available in Excel:
User-level data protection
You can remove critical or private data from view by hiding columns and rows of data, and then protect the whole worksheet to control user access to the hidden data. In addition to protecting a worksheet and its elements, you can also lock and unlock cells in a worksheet to prevent other users from unintentionally modifying essential data.
File-level security
At the file level, you can use encryption to prevent unauthorized users from seeing the data. You can also require password entry to open a workbook, or you can secure a workbook by employing a digital signature.
Restricted access to data
You can specify user-based permissions to access the data, or set read-only rights that prevent other users who may be able to view the data from making changes to it.
Perusing the web for postings comparing the features of databases to spreadsheets, you’ll find plenty of accusations that spreadsheets lack security and control features. Clearly, Microsoft’s description of the security features available in Excel shows that this isn’t the case. However, these security features may not be as robust as Microsoft claims, and they may prove difficult for the average user to implement.
As Martin Cacace of BoundState Software explains, “Although Excel allows you to protect data with a password and Windows-based permissions, it is extremely delicate and requires a deep understanding of Excel.” Some of these features won’t work if you have people using different operating systems or if you need access from other computers. Even a password protected Excel file is not really secure; there are tools on the Internet that anyone can use to unlock a protected Excel file without knowing the password.”
Databases offer far more control than spreadsheets over who can access and make changes to data. As an example, Locus EIM users must have a unique username and password. Users can be assigned to multiple privilege levels, ranging from “administrator” to “guest”. Customers that require a more fine-grained approach can use “roles” to assign permissions to specific modules, activities, or functionality to users. Password security is typically robustly designed in commercial databases, and can be configured to require complex passwords, session expiry, and password expirations to match customer IT requirements, something Excel would find challenging. Locus EIM also tracks all users and makes that information available to database admins to provide yet another layer of security for the system.
 10) Databases are better at preventing data loss and data corruption
10) Databases are better at preventing data loss and data corruption
Because of the general lack of controls that exist in most spreadsheets, it is far easier for a user to wreak havoc on them. One of the most dreaded developments that can occur is associated with the “Sort” function. A user may choose to sort on one or more columns, but not all—resulting in the values in the missed columns not matching up with those in the sorted ones. Nightmares like this are easily preventable (or are simply not possible) in databases.
Another advantage of database management systems is their ability to create audit trails, which preserve the original values in separate tables when changes are made to records. In the event that a user wants to undo some changes (including deletions) that he or she has made to a table, a data administrator can retrieve and restore the original state of the modified or deleted records. Also importantly, the circumstances of these changes are fully tracked (who, what, when, where), which is a minimum requirement for any quality assurance process.
Lastly, Excel stores the entire spreadsheet in memory, so if there is a system crash, you will lose everything you have entered or edited since your last save. In contrast, each operation you perform in a database is saved as you complete it. Moreover, most databases have daily backups, and in some cases, maintain an up-to-date copy of the data on a secondary device. Additionally, data is typically backed up in multiple geographic locations to provide even more recovery options in a disaster situation. Any good commercial database vendor will be happy to share their disaster recovery process because securing and maintaining your data is their most important job. In short, you can rest assured that your valuable data—often gathered over many years at a high cost—will not be lost if it is stored in a DBMS like Locus EIM.

Make sure to read the entire series to find out about 12 reasons commercial SaaS databases excel at managing complex environmental data!
About the author—Gregory Buckle, PhD, Locus Technologies
 Dr. Buckle has more than 30 years of experience in the environmental field, most of which have been devoted to the design, development, and implementation of environmental database management systems. When he joined Locus in 1999, he was responsible for building and deploying Locus’ cloud-based EIM software. He was also instrumental in customizing EIM for the water utility industry and developing EIM’s powerful Sample Planning and Data Validation modules. The latest iteration of the Sample Planning module that Dr. Buckle built is currently being used by Los Alamos National Laboratory and San Jose Water Company to plan and schedule thousands of samples per year.
Dr. Buckle has more than 30 years of experience in the environmental field, most of which have been devoted to the design, development, and implementation of environmental database management systems. When he joined Locus in 1999, he was responsible for building and deploying Locus’ cloud-based EIM software. He was also instrumental in customizing EIM for the water utility industry and developing EIM’s powerful Sample Planning and Data Validation modules. The latest iteration of the Sample Planning module that Dr. Buckle built is currently being used by Los Alamos National Laboratory and San Jose Water Company to plan and schedule thousands of samples per year.
About the author—Marian Carr, Locus Technologies
 Ms. Carr is responsible for managing overall customer solution deployments and customer relationships with Locus’ government accounts. Her career at Locus includes heading the product development team of the award-winning cloud-based environmental ePortal solution as well as maintaining and growing key customer accounts with Locus’ Fortune 100 enterprise deployments. In addition, Ms. Carr was instrumental in driving the growth and adoption of the Locus EIM platform with key federal and water organizations.
Ms. Carr is responsible for managing overall customer solution deployments and customer relationships with Locus’ government accounts. Her career at Locus includes heading the product development team of the award-winning cloud-based environmental ePortal solution as well as maintaining and growing key customer accounts with Locus’ Fortune 100 enterprise deployments. In addition, Ms. Carr was instrumental in driving the growth and adoption of the Locus EIM platform with key federal and water organizations.

 2) Data quality is better with databases
2) Data quality is better with databases 3) It’s easier to prevent data duplication and redundancy when your data resides in your database
3) It’s easier to prevent data duplication and redundancy when your data resides in your database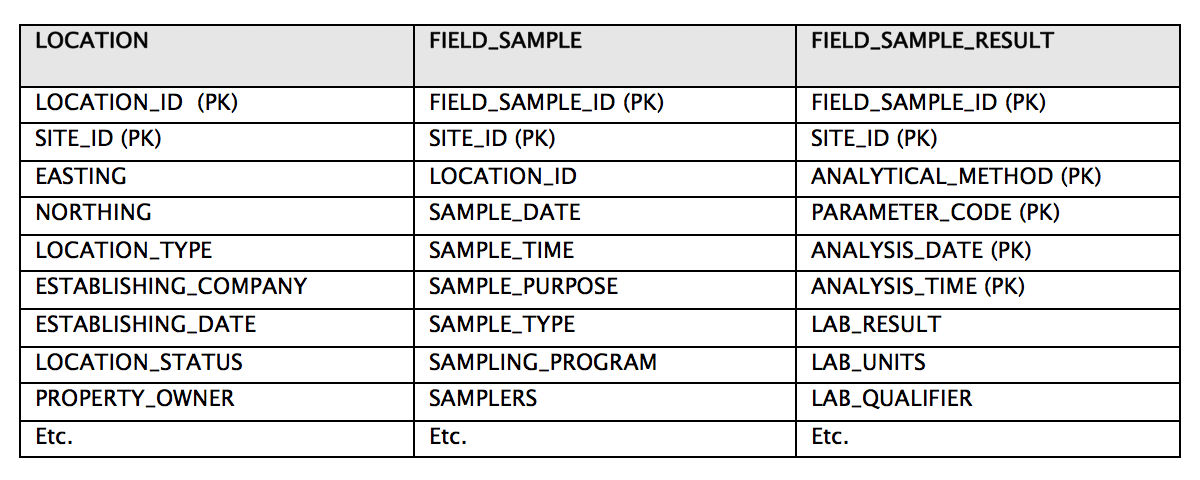
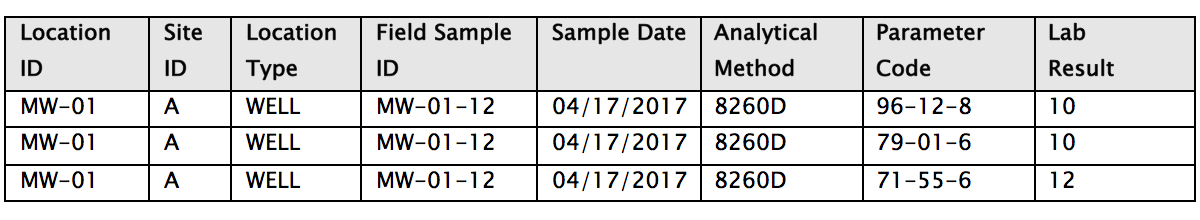
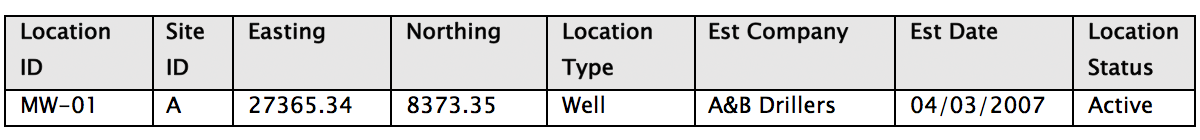
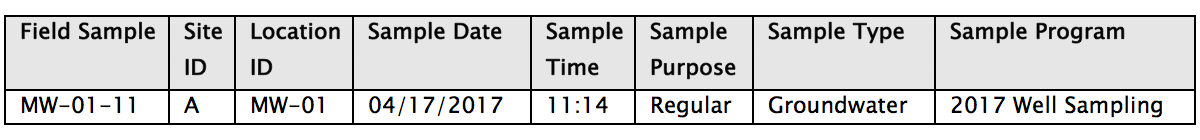
 4) Entity relationships are more manageable in databases
4) Entity relationships are more manageable in databases 5) Data reporting and integration is faster and easier with databases
5) Data reporting and integration is faster and easier with databases
 If you use spreadsheets to manage your environmental information, how do you get data into it?
If you use spreadsheets to manage your environmental information, how do you get data into it?