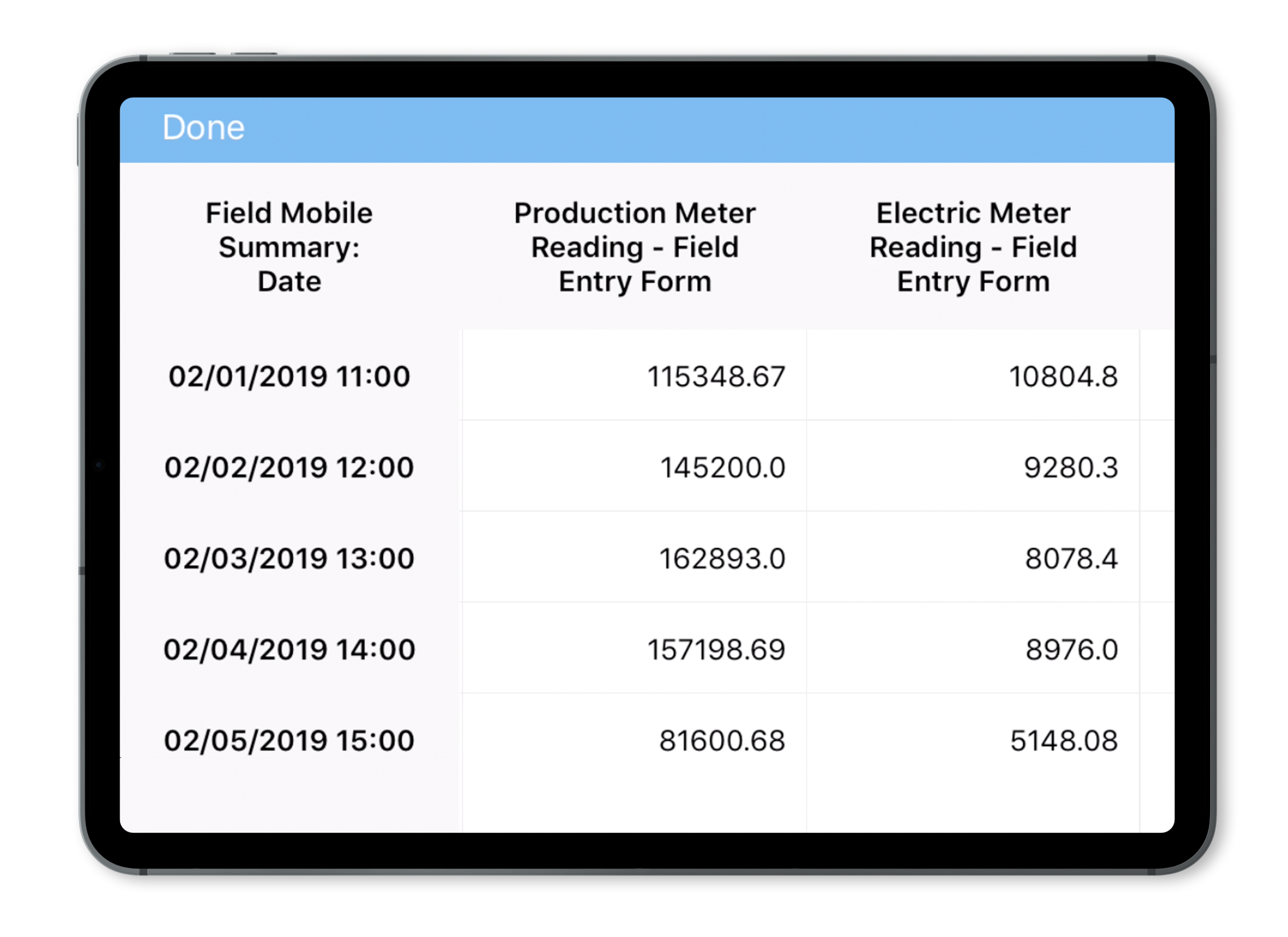
In 2025, there’s been a considerable increase in inquiries related to multitenancy and why it matters for EHS software, ESG Reporting, sustainability metrics, and more. Locus Technologies has been leading the market for two decades as the original multitenant EHS platform. During that time, we’ve watched countless single-tenant or on-prem competitors try to deflect when asked if they can deliver a multitenant solution. Considering the surge in interest in recent months, we are dusting off some of our earlier posts on the topic. This is one of those posts.
The announcements by several EHS software vendors this fall caught my attention. After offering their software on-premises for over a decade, suddenly many are discovering and planning to introduce multitenant Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) while promising to continue to maintain their current on-premises or single tenant offerings. In essence, they are introducing multitenancy as if it were a new version of their software. Anyone familiar with multitenancy knows this won’t work. Here’s why.
Most public announcements begin something like this: “In the next several years we plan to expand our software offerings to give customers the option to move from their current on-premises solution to the cloud.” However, is this even possible? What they consider the “cloud” may not be a true multitenant cloud. That train departed years ago, and most of the current EHS software vendors missed it. While multitenancy has been a game changer in the tech industry, many are uncertain of exactly what makes an application “multitenant” or why it matters.

There is a considerable degree of (intended) confusion in the EHS software space when it comes to the definition of a real cloud or better said, multitenancy. Companies that are considering SaaS solutions for EHS software hear all sorts of things from EHS software vendors hoping to tap into the momentum of cloud computing. Many go as far as saying “sure; we can do multitenant, single-tenant, whatever tenant you need!” –anything to win the job. These vendors do not understand the real cloud.
Multitenancy is a significant shift in computing and requires an all-new approach to the software architecture and the delivery model from the ground up. It is transformational, and customers who intend to buy the next generation of EHS software should spend the time to understand the differences. More importantly, multitenancy is a principle, not a software version or an upgrade. It is not an evolutionary step; instead, it is a revolution in the software delivery model, and it matters in the long run for the customer.
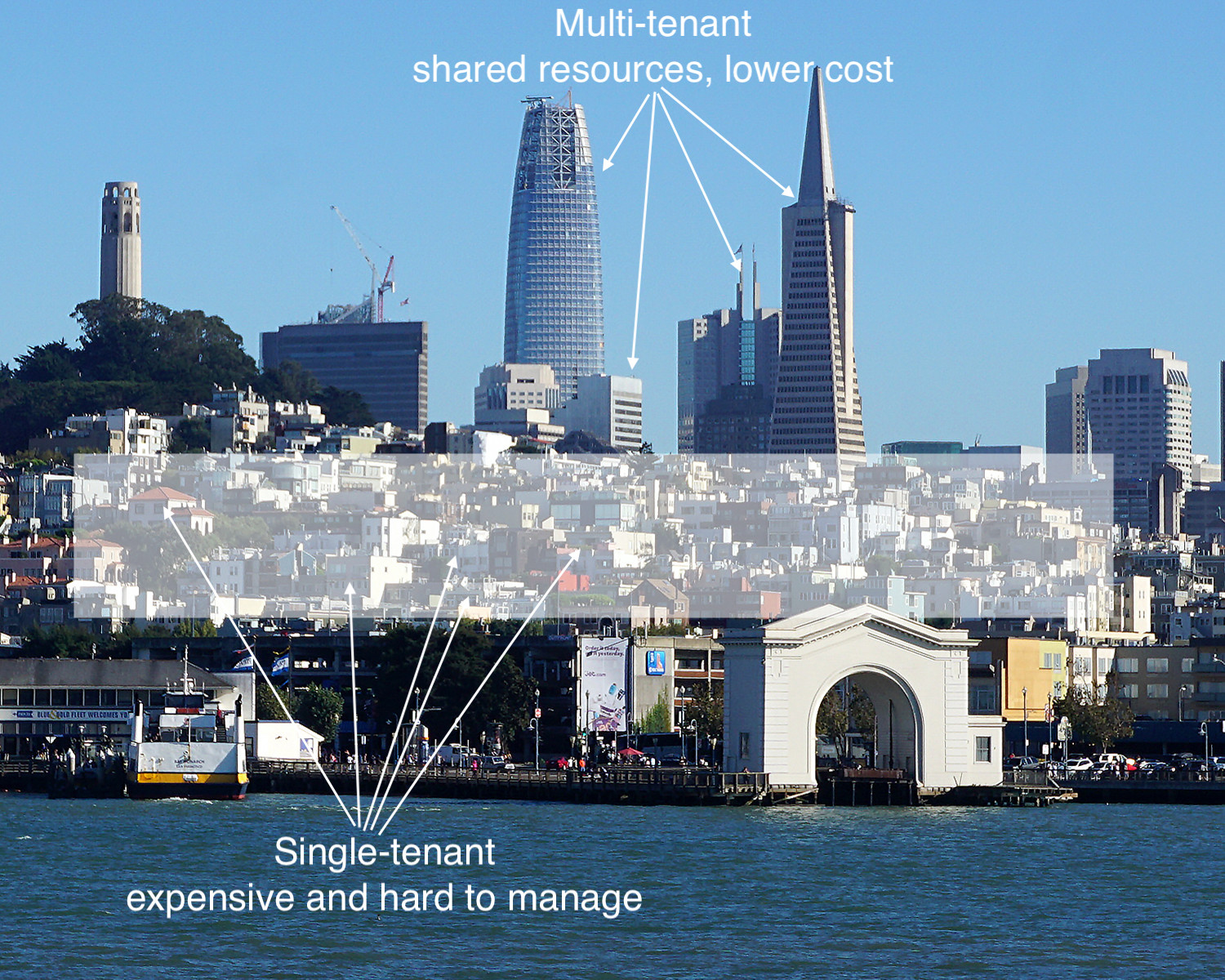
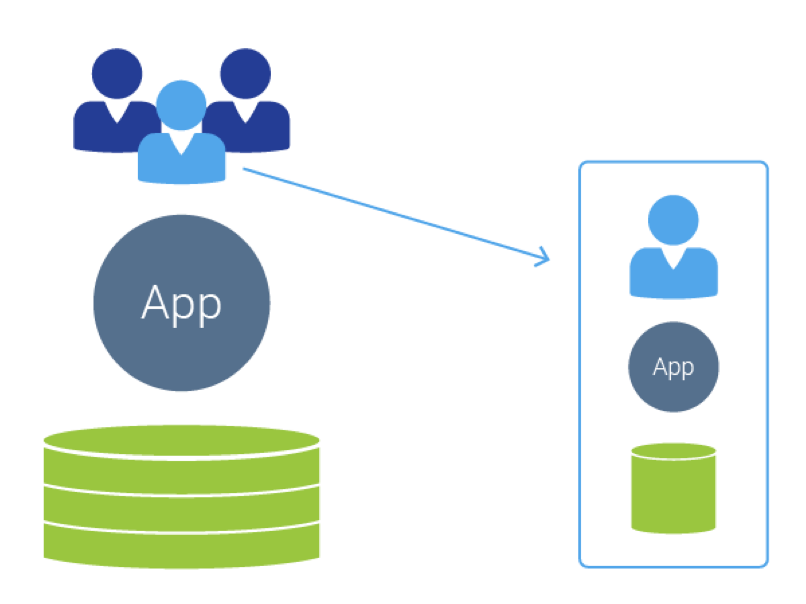
Figure 1: The single-tenant model cannot easily be switched or “upgraded” to multitenant. The software architecture does not allow for an easy switch the same way as a single-family home cannot be “remodeled” to become a multitenant high-rise. What differentiates a multitenant application architecture is its effectiveness in achieving the same goal in a scalable and sustainable fashion.
Can you imagine companies like eBay, Salesforce, Google, Workday, or Amazon supporting a “single-tenant” version of their offering side-by-side with their multi-tenant clouds? No, of course not. That would mean they had failed to decide on the fundamental strategy that would define their business, fuel their growth, and give customers the experience they’ve promised. I argue that any EHS software vendor who offers a single-tenant solution of any type, cannot be a serious contender in multitenant SaaS. Pick one; not both.
EHS software vendors with on-premise software applications or single-tenant web-enabled offerings are seduced by the seemingly low barriers to entry into the SaaS market with an architecture that leverages virtualization. This approach allows a software company to quickly offer subscription-based services of their legacy product to their initial customers. In the long run, however, this approach just won’t scale economically. A recent wave of ownership change of EHS software companies is the best indicator that sold companies became victims of their initial success. A SaaS provider who leverages virtualization puts the long-term viability of the business at risk as more efficient, true SaaS competitors come to dominate the market.
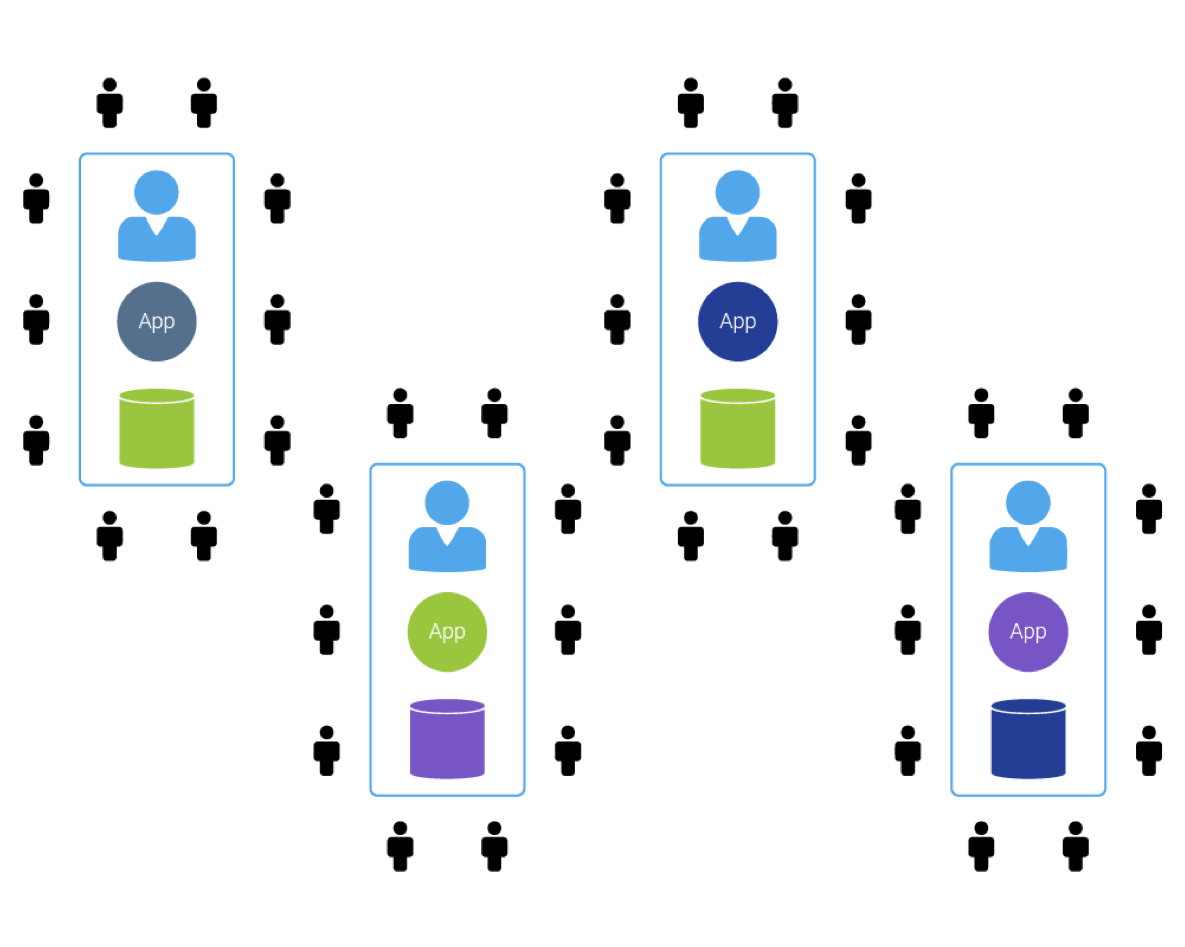
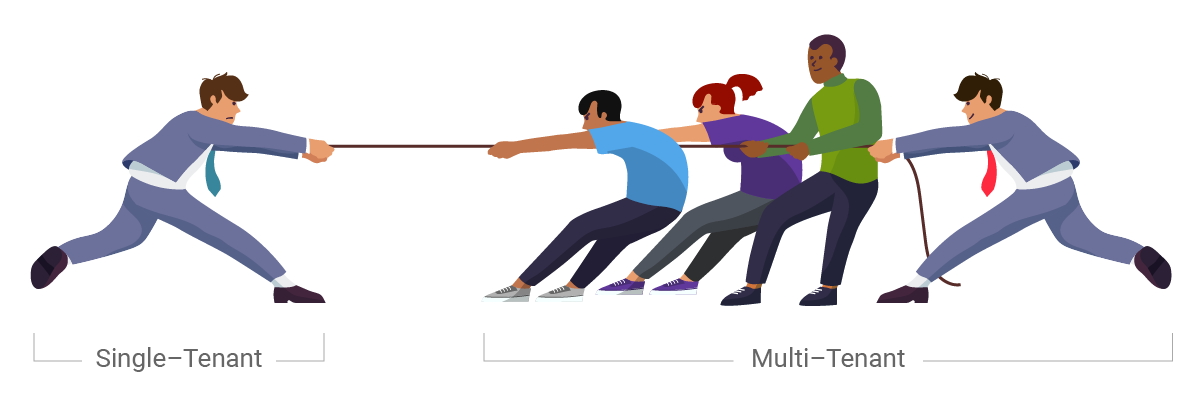
Figure 2: Single tenant requires many more vendor resources. The resource costs are eventually passed to customers. Each upgrade of the application will require each customer to upgrade independently and the ability to implement tenant management tools and tenant-specific customizations is significantly limited. The benefit of multitenancy is that instead of 100 copies of the operating system, 100 copies of the database, and 100 copies of apps, it has 1 OS, 1 database, and 1 app on the server with significantly less vendor resources required to manage it. And it is those savings that are passed to customers.
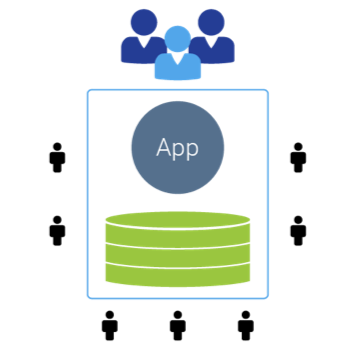
Figure 3: A multitenant model requires less resources and easier (and rolling) upgrades (i.e. no version numbers). Only one software instance and hardware stack for multiple tenants. All customers are always on the latest version of software. Locus Technologies figured this out in 1999, and it has become a key differentiator for us in the years since. Locus can scale up infinitely without adding proportional cost. Others cannot.
Figure 4: “Can’t we create a separate stack for just this one customer? I promise it’s just this one…” Even a single installation for one “special” customer breaks the multitenant model. Don’t do it.
I would also add that single-tenant (hybrid) cloud applications are worse than on-premises installments because they are fake clouds. In single tenancy, each customer has his or her independent database and instance of the software. These instances may reside on the same or different servers. In this model, a customer is, in fact, outsourcing maintenance of their application (software and hardware) to a vendor (or their consultant) that is not likely equipped to perform these tasks. No single vendor in the EHS software industry is large enough to undertake maintenance of the single-tenant infrastructure on behalf of their customers regardless of how inexpensive hardware or software virtualization may be. Even if they offer their hosting on Microsoft Azure Cloud or Amazon Web Services (AWS), they still cannot guarantee multitenancy as these solutions address only hardware challenges.
The Economist magazine described it as: “Those forerunners also promised a software revolution by hosting the software applications of companies. But they failed because they simply recreated each client’s complex and unwieldy data centre in their own basements, and never overcame the old problems of installation and integration with other software. With each new customer, the old ASPs had, in effect, to build another datacenter; there were few economies of scale.”
To improve their position in a shifting marketplace, on-premises EHS vendors have found a way to market their solutions as “cloud-based” when they are not backed by the fundamental principle of what that means. Considering the large investment that is associated with the purchase or licensing of EHS software, it is critical for customers to be able to discern a true cloud product from a fake one. But how can you spot a fake?
Just ask the EHS software vendor these four questions:
- Do you support both single-tenant and multi-tenant deployments of your software?
- Does your software have version numbers?
- Do you charge for upgrades?
- Can we install your software on our infrastructure?
If the answer to any of these questions is yes, the vendor is not committed to multitenant architecture, and you should not move to their “cloud.”
Multitenancy is the only proven SaaS delivery architecture that eliminates many of the problems created by the traditional software licensing and upgrade model where software is installed as a single-tenant application on a customer’s premises or at a customer’s or vendor’s data center. In contrast, in multitenancy, all customers access the same software on one or a set of linked servers.
Multitenancy requires a new architectural approach. Companies have to develop applications from the ground up for multitenancy. Once companies commit their limited financial resources to one architecture, it becomes nearly impossible for them to switch to the multitenancy model, no matter how many resources they have available. Moreover, for this reason, I am skeptical that many current vendors will be able to make a switch to multitenancy.
A vendor who is invested in on-premise, hosted, and hybrid models cannot commit to providing all the benefits of a true SaaS model due to conflicting revenue models. Their resources are going to be spread thin supporting multiple versions rather than driving innovation. Additionally, if the vendor makes the majority of their revenue selling on-premise software, it will be very difficult for them to fully commit to a true SaaS solution since the majority of their resources will be allocated to supporting the on-premise software.
And if they suddenly introduce a “multitenant” model (after selling an on-premises version for 10+ years) who in the world would want to migrate to that experimental cloud without putting the contract out to bid to explore a switch to a well-established and market-tested true multitenant provider? Even Google and Microsoft are playing a catch-up game with Amazon’s AWS when it comes to cloud hosting businesses. The first mover advantage when it comes to multitenancy is a huge advantage for any vendor.
In summary, an EHS software vendor can be either truly multitenant or not. If a vendor has installed their software on somebody’s else hardware and runs multiple instances of that software (even if the code base is the same) they are not and will never be true multitenant.
Figure 5: Where do you want your software to reside? In multitenant or single-tenant infrastructure? If multitenancy is attempted on old infrastructure or legacy application upgrade, watch out. After a vendor built the first few floors of that skyscraper, there is no easy way to replace the foundation. You will be lucky if they end up like the tower of Pisa or Millennium Tower in San Francisco. To keep the tower standing, they will have to do constant underpinning of the foundation and restrict access to the structure. And you, the customer, will pay for it. That is what many customers of single-tenant EHS vendors are facing today.
Therefore, when considering a SaaS solution, make sure that the vendor is a true SaaS vendor who is solely committed to the multitenant SaaS delivery model and has invested in a true multitenant platform. This is the only way to reap all the benefits that a SaaS model has to offer.