Artificial Intelligence and EHS Compliance Revisited, Part 3: Multitenancy and AI
Key Benefits of Multitenant Cloud Architecture for EHS SaaS
This article was originally published in 2019, and it has been updated to reflect the realities of AI for EHS in 2025.
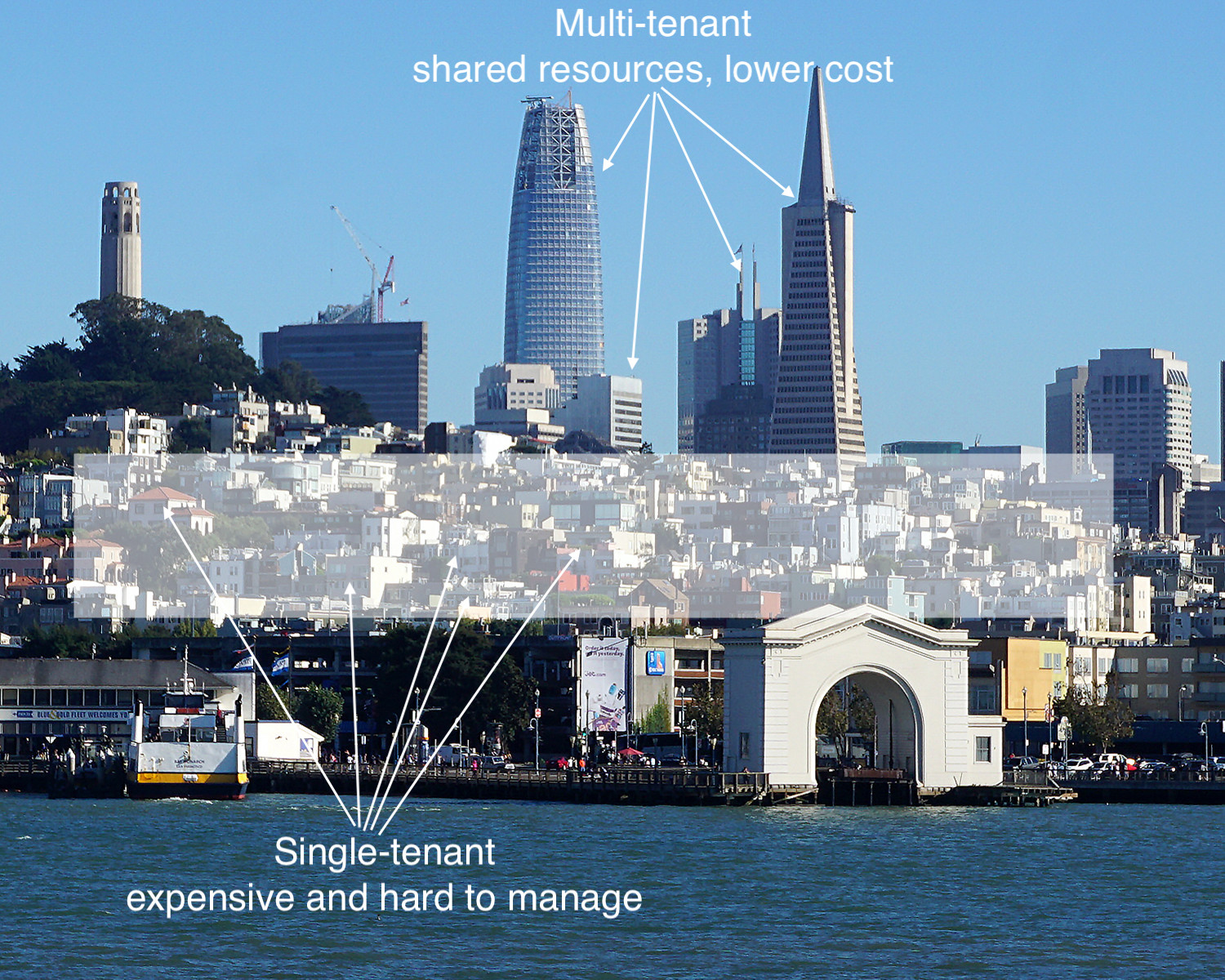
Multitenancy offers distinct benefits over traditional, single-tenant software hosting. A multitenant SaaS provider’s resources are focused on maintaining a single, current version of the application, rather than having its resources diluted in an attempt to support multiple software versions for its customers. If a provider is not using multitenancy, it may be hosting or supporting thousands of single-tenant customer implementations. By doing so, a provider cannot aggregate information across customers and extract knowledge from large data sets as every customer may be housed on a different server and possibly a different version of software. For these reasons, it is almost impossible and prohibitively expensive to deliver modern artificial intelligence (AI) tools via single tenancy.
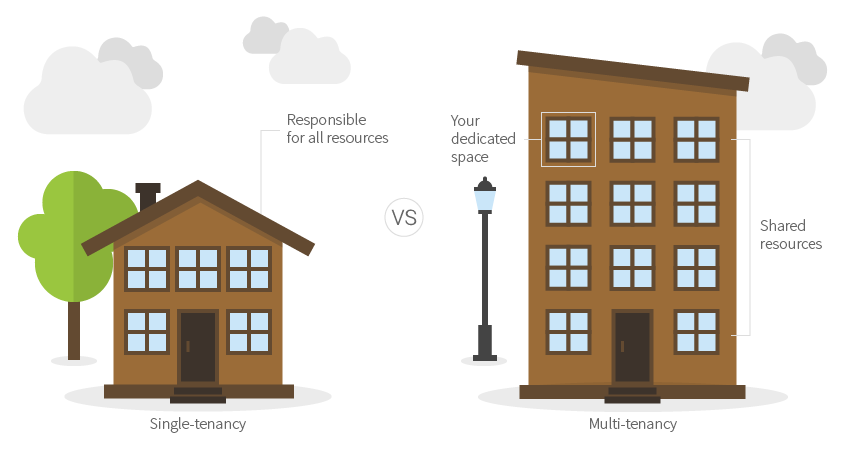
Multitenancy has other advantages as well. Because every customer is on the same version of the software and the same instance, machine-learning (a prerequisite for AI) can happen more quickly as large datasets are constantly fed into one system. A multitenant SaaS vendor can integrate and deploy new AI features more quickly, more frequently, and to all customers at once. Lastly, a single software version creates more of a sense of community among users and facilitates the customers’ ability to share their lessons learned with one another (if they chose to do that). Most of today’s vendors in the EHS&S software space cannot offer AI, sustain their businesses, and grow unless they are a true multitenant SaaS provider.
Leveraging AI for EHS Compliance, ESG Reporting, and More
Almost 30 years after the publication of our paper on the hazardous data explosion, SaaS technologies combined with other advancements in big data processing are rising to the challenge of successful processing, analyzing, and interpreting large quantities of environmental and sustainability data. It is finally time to stop saying that AI is a promising technology of the future. It’s here.
Gone are the days when EHS software was just a database. There are two factors that are fueling the adoption of AI technologies for EHS compliance and water quality management. First, there is Big Data and all the burdens and opportunities that come with it. Second, there is the move to true multitenant SaaS solutions, which enables the intake and dissection of data from multiple digital sources (streaming data) from multiple customers, all in real-time.
AI has entered the mainstream with the backing and advocacy of companies like Microsoft, IBM, Google, and Salesforce, who are heavily investing in the technology and generating lots of buzz. It is remarkable to observe how quickly AI is proliferating in so many verticals. Think back to this old CBS’s 60 Minutes segment and compare that to how most of us leverage AI tools on a daily basis now.
For our purposes, let’s look at where AI is likely to be applied in the EHS space. The mission-critical problem for EHS enterprise software companies is finding solutions that both enhance compliance and reduce manual labor and costs. This is where AI will play a major role. So far, companies have largely focused on aggregating their data in a record system(s); they have done little to interpret that data without human interaction. To address the ever-changing growth in environmental regulations, companies have been throwing people at the problem, but that is not sustainable.
AI and natural language processing (NLP) systems have matured enough to read through the legalese of regulations, couple them with company’s monitoring and emissions data, and generate suggestions for actions based on relevant regulations and data. Take, for example; a CEMS installed at many plants to monitor air emissions in real-time. Alternatively, a drinking water supply system monitoring for water quality. In each of these systems, there are too many transactions taking place to monitor manually to ascertain which ones are compliant and which ones are not. It is an onerous task to figure out every exceedance on a case-by-case basis. Intelligent databases with a built-in AI layer can interpret data on arrival and signal when emissions exceed prescribed limits or when other things go wrong. The main driver behind applying AI to EHS compliance is to lower costs and increase the quality of EHS compliance, data management, and interpretation, and ultimately, to avoid all fines for exceedances.
For example, a large water utility company has to wade through thousands of analytical results to look for outliers of a few dozen chemicals they are required to monitor for compliance. Some of these may be false positives, but that still leaves some results to be investigated for outliers. Each of those investigations can take time. However, if a software algorithm has access to analytical results and can determine that the problem rests with a test in the lab, that problem can be solved quickly, almost without human interaction. That is powerful.
Combing through data and doing this by hand or via spreadsheet could take days and create a colossal waste of time and uncertainty. Hundreds of billable hours can be wasted with no guaranteed result. Using AI-driven SaaS software to determine what outliers need investigation allows compliance managers, engineers, and chemists to focus their expertise on just these cases and thus avoid wasting their time on the remaining ones that the AI engine indicates need no further examination.
Predictive analytics based on Big Data and AI will also make customer data (legacy and new) work harder for customers than any team(s) of consultants. A good analogy that came to me after watching that old 60 minutes story is that the same way the clinical center in North Carolina used AI to improve cancer treatment for their patients, engineers and geologists can improve on selecting the site remedy that will be optimized for given site conditions and will lead to a faster and less expensive cleanup with minimum long-term monitoring requirements.
Another example where AI will add value is in the area of enterprise carbon management. SaaS software is capable of integrating data from multiple sources, analyzing and aggregating it. This aggregated information can then be distributed to a company’s divisions or regulatory agencies for final reporting and validation/verification, all in real-time. This approach can save companies lots of time and resources. Companies will be able to access information from thousands of emission sources across the states, provinces, and even countries where their plants are located. Because each plant is likely to have its own set of regulatory drivers and reporting requirements, these would have to be incorporated into the calculation and reporting engine. After data from each plant is uploaded to a central processing facility, the information would be translated into a “common language,” the correct calculation formulae and reporting requirements applied, and the results then returned to each division in a format suitable for reporting internally and externally.
Blockchain for EHS: Looking ahead
Blockchain can further augment the power of AI for EHS monitoring and compliance. Blockchain’s decentralized approach coupled with AI will bring another revolution to EHS compliance and water monitoring.
Parts one, two, and four of this blog series complete the overview of Big Data, IoT, AI, and multitenancy. We look forward to feedback on our ideas and are interested in hearing where others see the future of AI in EHS software – contact us for more discussion or ideas!

 Version Island
Version Island Off the Grid
Off the Grid Sunsetting (Decommissioning)
Sunsetting (Decommissioning) Serene Security
Serene Security Making Plans
Making Plans