Climate change is about to upend the corporate world. Companies that fail to address their impacts on the environment are likely to face a backlash as their lack of effort will not sit well with the public, particularly as climatic changes become ever more severe and prominent. Firms need to react quickly if they want to be “on the right side of history.” The reinstatement and enforcement of canceled or ignored regulations and new standards in many countries will force more firms to report their emissions. But what reporting standards should they use? And how will they compile and aggregate their emissions data to provide credible and verifiable accounts of their activities?
Figure 1: Companies brace themselves for new ESG regulations
These are timely questions to address with the expected renewed focus on the Paris Agreement accords as the United States re-engages with the rest of the world. One place to start is with better carbon-emissions data. Today, few companies even know how much greenhouse gas they or their suppliers emit, making it difficult for them to assess their products or operations’ full environmental impact. Where data does exist, it is often self-reported, inconsistent, or too out of date to be useful. Efforts are underway to fix this, mostly coming from an unexpected source–the push to incorporate environmental, social, and governance (ESG) reporting in evaluating companies’ creditworthiness by financial institutions. Many shareholders and professional investors now believe that investors who are not considering possible impacts related to climate change could be exposing themselves to serious risk.
While climate-related issues are a key component of the E in ESG reporting, it encompasses much more and is measured by various means. Some examples are GHG emissions, water use, generated waste, land usage, and so forth, both in a firm’s direct operations and along its supply chain. In this paper, I intend to focus on the problems and issues associated with such measurements.
Post Covid-19 Economy
In the post-Covid economy, many investors will want to align their investment strategy with accepted science. Many companies, countries, cities, and politicians have pledged to have net zero emissions before 2050 or some other year in the distant future (when those making the proclamation most likely will not be alive). However, to better manage and account for climate change risk and help keep global warming from rising to dangerous levels, investors are increasingly asking whether their portfolios are climate-change friendly in the short term. Pledges where a company hopes to be in 2030, 2040, or 2050 mean little to them.
Far from turning investors away from ESG investing, the pandemic has heightened interest in sustainable portfolios. I expect ESG scores will become as important to investors as financial performance indicators in the coming decade. According to several research analysts, at least $3 trillion of institutional assets now track ESG scores, and the share is rising quickly.
To stay relevant and attractive to investors, companies will urgently need to step up their efforts to minimize their impacts on the climate. Climate change is already causing both severe physical damage and harmful effects on the biosphere. Pushed by mainly younger voters, governments around the world are introducing ever-tougher regulations. Many expect the U.S. to do the same now that Biden has taken office.
ESG Scores as Important as Financial Performance
In the developed economies of North America, Asia, and Europe, there is a movement among some politicians, corporate executives, and investors to shift away from measuring corporations based solely on their financial performance. They want to incorporate climate change as another catalyst — a shift that would involve assessing which firms are “dirtier” than others. This effort’s success will depend on firms providing accurate and verifiable data on their emissions and related discharges.
Data from Morningstar, a research investment firm, show that in the first nine months of 2020, climate-aware funds attracted almost 30 percent of all investments in sustainable fund inflows.
In 2019, this proportion was just 15 percent. Climate change has never been so prominent in the minds of the financial community. But while awareness of climate change issues is rising within financial institutions, interest and concern in the U.S. have been suppressed in recent years by the very regulatory agencies that are supposed to be managing it. But more on that subject later.

Figure 2: Climate change risks are real.
To attract capital, many companies will have to adjust their reporting to this new reality. Voluntary reporting of relevant key performance indicators (KPIs) will not be enough as governments develop more and better standards. “Markets need high-quality, comparable information from companies to enable informed capital-allocation decisions in the face of climate-related risk,” said Mary Schapiro, a former U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) chairwoman. we can predict where we will be 20 or so years from now, we need to know where we are today. Only reliable, verifiable, and normalized data across industries can tell us that.
How To Measure Companies’ Sustainability Performance?
Measuring companies’ performance relative to climate change or sustainability is a challenge even with a set of agreed-upon standards. However, no such meaningful and accepted standards exist, let alone reporting rules or data interchange specifications. Some measures are slowly emerging, such as carbon emissions equivalents, energy consumption per something, water consumption, and type and quality of discharges. More effort is needed to standardize reporting and compare climate risk for companies in different industries. Besides the lack of standards, there is also a lack of unified enterprise software tools to make the reporting job easier.

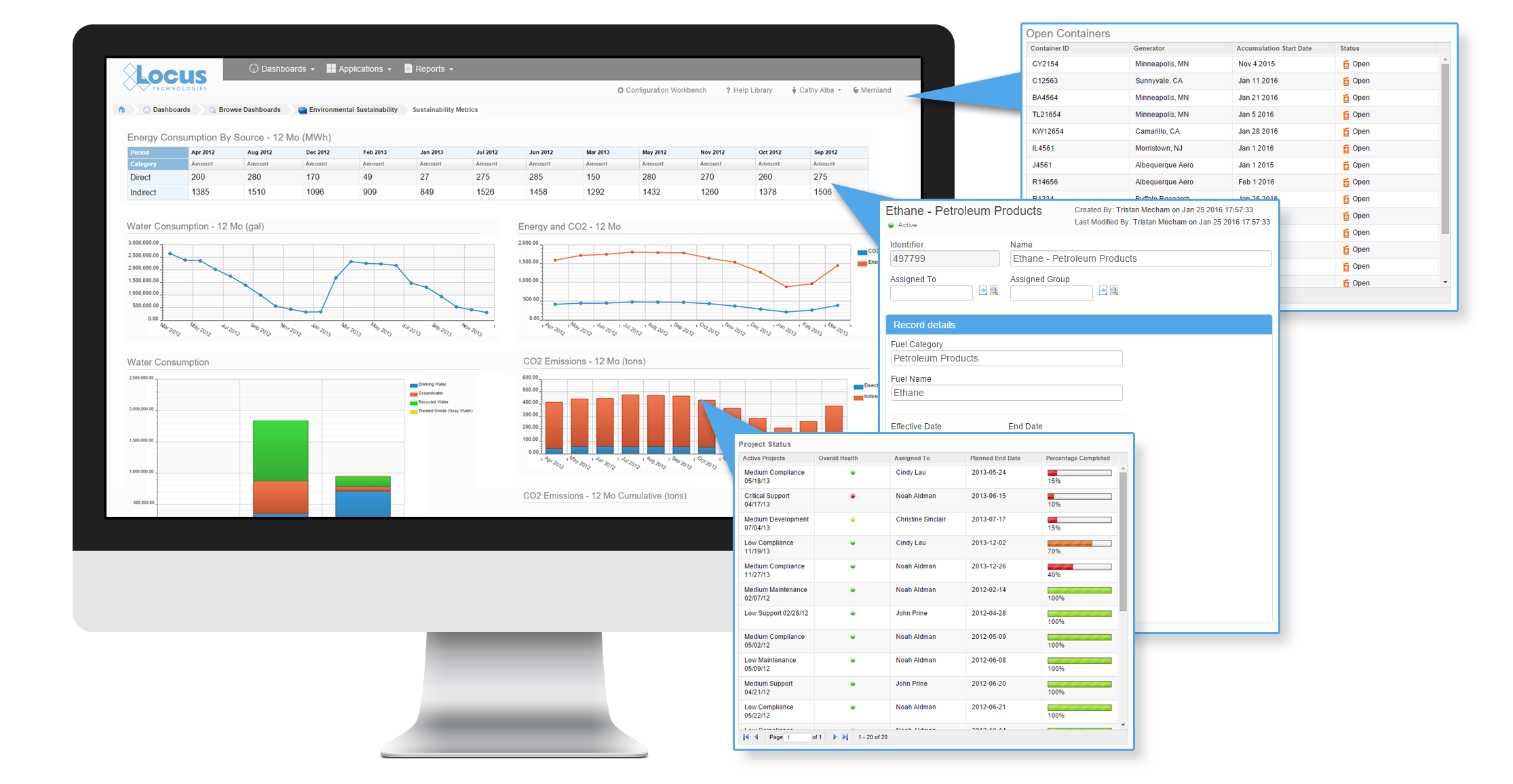
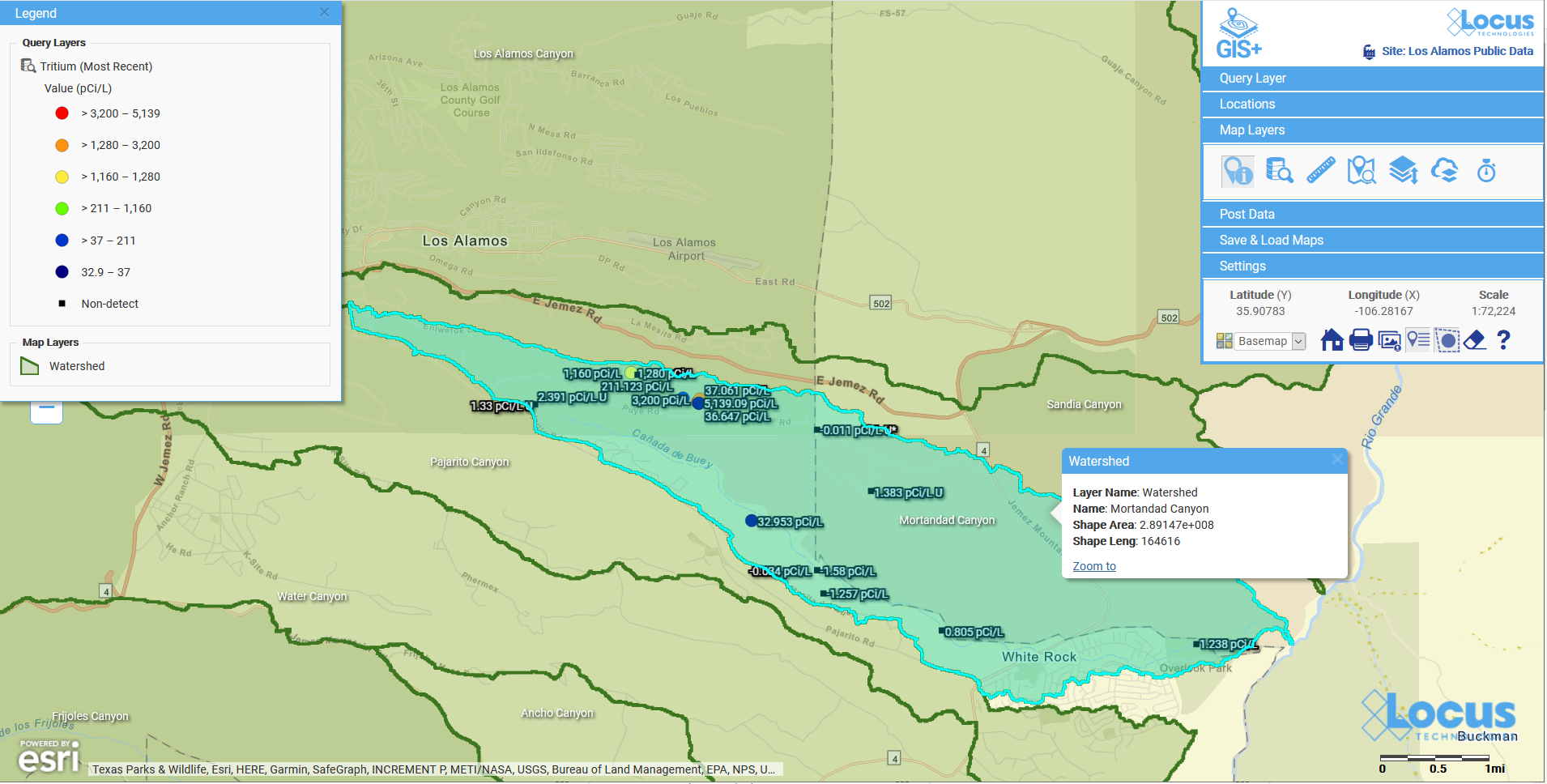
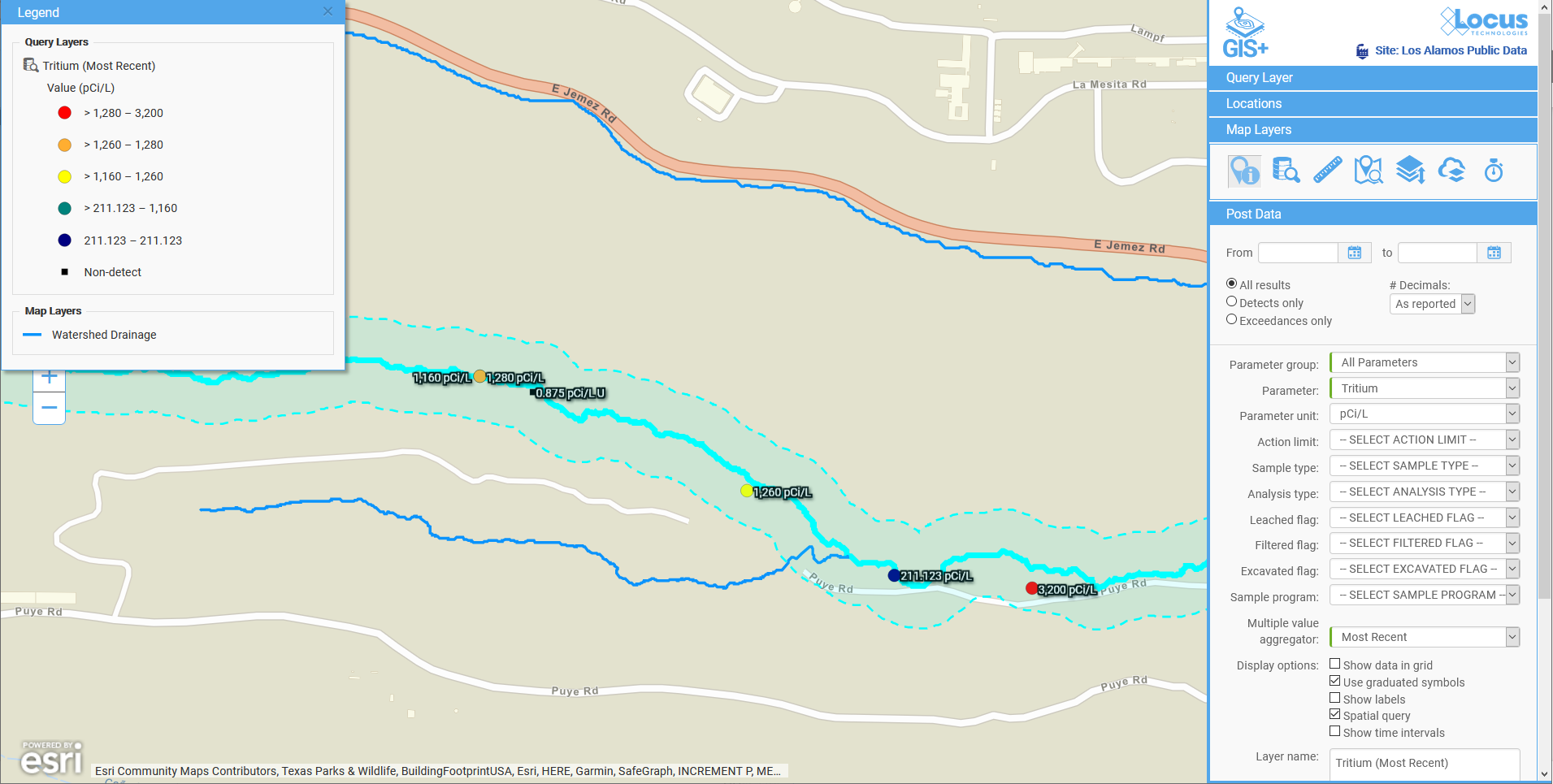
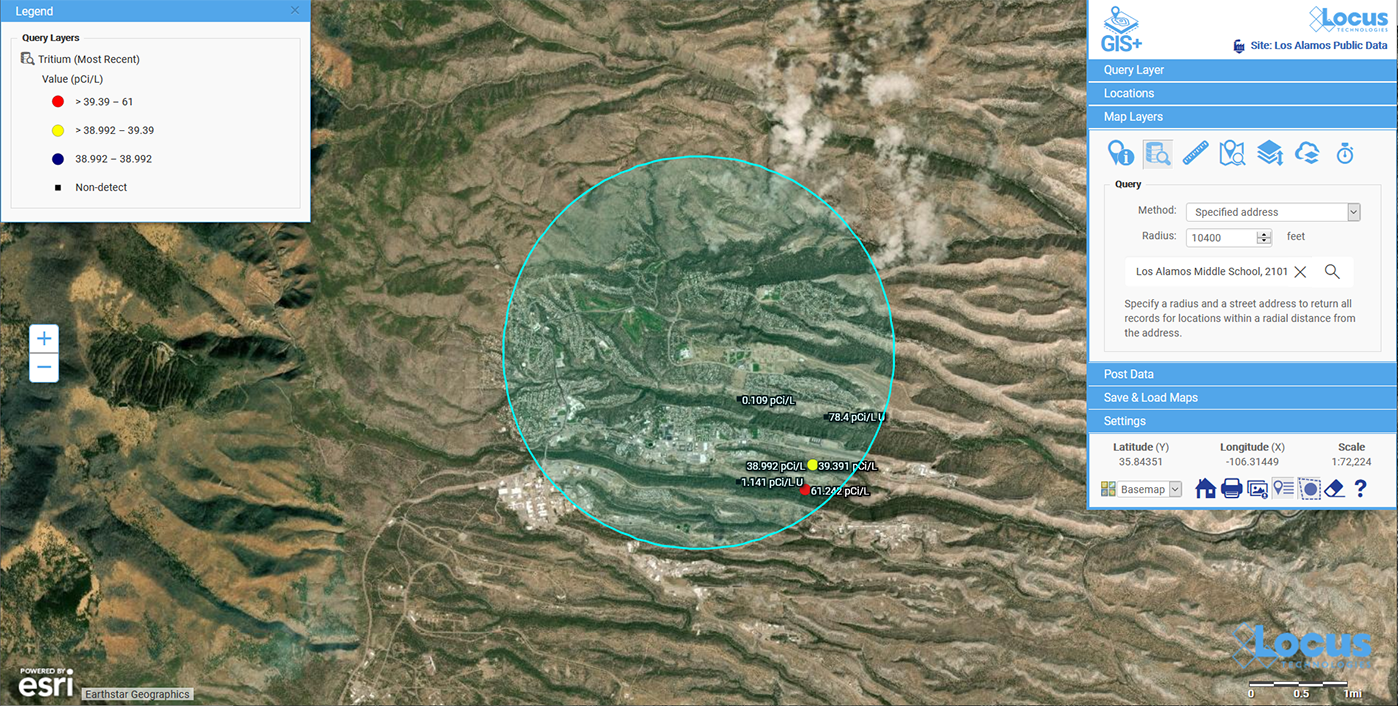
Figure 3: Energy consumption reading, real-time upload and reporting to Locus Platform
In the absence of such standards and guidance, I expect some investors to place their bets on the least polluting steel manufacturing company or the traditional car manufacturer that has invested the most in electric vehicles. Or they may invest in companies that have set ambitious (future years) emissions targets, i.e., committing to become carbon neutral by some year in the distant future. While an improvement, all of these do not provide a clear picture of the risk associated with an investment. Who will be around 20 to 30 years from now to hold companies, individuals, or politicians accountable for “future-looking statements and predictions” that they are making today? Certainly not the people making those announcements. Moreover, at that time, a new generation will be focused on solving their own unimaginable or unpredictable problems today.
Since President Nixon’s 1974 State of the Union — where he made energy independence a national goal — a bipartisan procession of presidents has regularly made similar declaration calls to reduce America’s dependence on foreign oil. None of them was correct when or how the country would reach that noble goal, and nobody ever held them accountable for their failures. I expect the same will happen with today’s predictions on carbon neutrality by so many CEOs.
ESG Standards
One of the most problematic ESG reporting issues is that there are no globally enforced reporting and compliance standards for ESG and other sustainability information. For financial reporting, at least, there are standards in the form of Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP) and International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS).
Nowhere is corporate “book-cooking” more on show than in firms’ sustainability reports. Today, 58 percent of companies in America’s S&P 500 index publish one, up from 37 percent in 2011, according to Datamaran, a software provider. Among the photos of pollution-free blue skies, blooming red flowers, and smiling children of all races, firms sneak in such ESG data as their carbon footprint, waste generation, and water usage. As expected, all charts showing these data trend downwards, like an inverse hockey stick. But the information in the sustainability reports differs wildly from firm to firm, making it impossible to draw comparisons based on their ESG data. Unlike financial data that are audited and include the familiar balance sheet, income statements, and cash flows, there is nothing similar on the ESG side. This situation arises from the absence of widely adopted standards for ESG reporting. The most obvious sign of this mess is that, unlike financial statements, ESG scores assigned by different rating firms poorly correlate with each other, rendering their ratings useless for smart investors.
With the U.S. EPA missing in action over the last four years, five voluntary ESG standards have come to dominate the scene. The Global Reporting Initiative (GRI) focuses on metrics that show firms’ impact on society and the planet. The Dow Jones Sustainability Indices (DJSI), launched in 1999, are a family of indices evaluating the sustainability performance of thousands of companies trading publicly. By contrast, the Sustainability Accounting Standards Board (SASB) includes only ESG factors that have a material effect on a firm’s performance. The Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures (TCFD) and the Carbon Disclosure Project (CDP) is chiefly concerned with climate change. They specifically focus on companies’ exposure to climate change’s physical effects and potential regulations to curb carbon emissions. There are still other regulatory standards worth mentioning: AB32, the California Global Warming Solutions Act of 2006, and the EU emissions trading system (EU ETS) that is a cornerstone of the EU’s policy to combat climate change and is its essential tool for cost-effectively reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
GRI is the most popular of the voluntary standards, in part because it is the oldest, founded in 1997. It has been embraced by about 6,000 firms worldwide. However, all these standards are based on voluntary reporting and have no teeth. Absent real climate change regulations and standards, many financial institutions promote one of these standards.
To further complicate matters, the number of ESG standards in the world has grown from around 700 in 2009 to more than 1,700 in 2019. That includes more than 360 different ESG accounting standards set primarily by various financial institutions or rating agencies. To say the situation is chaotic is an understatement. Last September, the World Economic Forum (WEF) announced a new set of ESG metrics for firms to report, making the current state of affairs even more confusing. These new metrics have received the backing of four large accounting firms. The Davos agenda for 2021 is: “How corporate leaders can apply ESG tools to help overcome global challenges.” Let’s hope they make some progress between their martinis and skiing.
The WEF stressed that this is not yet another new standard but a collection of useful measures picked from other standards. The intention, they claim, is to simplify ESG reporting, not to add to the confusion. But that is exactly what this mixture of standards does.
The IFRS Foundation, a global financial-accounting standard-setter, is considering its ESG standard. Moreover, the EU is planning rules that will force big companies to disclose more ESG information; as of the beginning of 2021, it is still thinking about which measures to use.
These efforts fuel demand for normalized ESG ratings and a uniform set of reporting standards. The goal is to create a single score from disparate non-financial indicators, such as a firm’s carbon emissions. The proliferation of standards hinders comparability. Simplification is needed. Many complain that voluntary reporting lets companies cherry-pick positive results by taking reporting numbers out of context.
Some have pushed for an ESG equivalent to the GAAP used in financial reporting. But these took years to agree on, and there are still sizable differences between the U.S. and the EU in applying them. Before regulators can establish any accounting-like standards, they must first base them on pure science and scientific calculations. Many such standards already exist in various U.S. EPA environmental compliance reporting requirements such as the Clean Water Act, Clean Air Act, or California AB32 for greenhouse gas emissions.
Instead of aggregating many voluntary reporting standards developed by non-scientists, lawmakers should aggregate the existing reporting requirements that have been developed by federal and state agencies under existing programs over the last 50+ years. A unified reporting schema and associated enterprise, cloud-based software to aggregate it should be the ultimate objective. We do not need to create yet more regulations to institute climate change regulations. What we need to do instead is synchronize, unify, and coordinate existing rules. Almost every current environmental law already has built-in components that relate to climate change. For example, many voluntary reporting programs like GRI or CDP require companies to track waste or water consumption and discharges or air emissions. And all of these are already regulated by EPA.
Voluntary standards reporting requirements lack the rigor and comprehensiveness of waste management requirements developed under the EPA RCRA program, water quality management under the EPA Clean Water Act, or air emissions management under the Clean Air Act. Why duplicate efforts if they do not bring added value? The EPA’s cradle-to-grave hazardous waste management system, for example, provides the critical foundation needed to keep America’s land and people safe from hazardous materials. Added reporting on waste under GRI or CDP brings no additional value. The Resource Conservation and Recovery Act (RCRA) passed in 1976 to set up a framework for properly managing hazardous waste is far superior to any voluntary reporting programs of recent years.
Likewise, Title V of the 1990 Clean Air Act Amendments requires all major sources and some minor air pollution sources to obtain an operating permit. A Title V permit grants a source permission to operate. The permit includes all air pollution requirements that apply to the source, including emissions limits and monitoring, record keeping, and reporting requirements. It also requires that the source report its compliance status concerning permit conditions to the permitting authority. None of the voluntary programs has similar requirements.
How are Firms Rated on their Climate Change by Financial Analysts?
Many would-be investors are confused because there is no standard terminology for describing and defining sustainability and other ESG reporting components. The resulting variability in the quality, quantity, and relevance of disclosures prevents investors and stakeholders from getting the information they need. Rating firms use teams of analysts, AI-driven software algorithms, and scattered data from companies to collect and massage ESG information. They then convert this information into a single score. And how is this score used? Some customers of these rating firms seek to gain an investment edge; others want their money to benefit society and themselves. But the ratings are not yet ready for the critical role they are being asked to play.
A recent report by the Governmental Accountability Office (GAO) in July 2020 emphasized that ESG disclosures and reporting are not always clear or helpful for decision making. If reported information is not useful for decision making, we must ask, what purpose does it serve in its current state?
As government regulations on heavy polluters and heavy emissions emitters get stricter and companies see their business models under threat, it only makes good financial sense to implement a system that aggregates all their emissions data (to air, water, or soil) and present it to regulators and investors in an organized, transparent, credible, and defensible way.
Just as the Sarbanes-Oxley (SOX) Act of 2002 provided unexpected drivers for reporting the environmental liability on the balance sheet of publicly traded companies, ESG reporting drivers may help standardize EHS reporting.
U.S. EPA: Missing in Action
The U.S. conversation about protecting the environment began in the 1960s. Rachel Carson had published her attack on the indiscriminate use of pesticides, Silent Spring, in 1962. Concern about air and water pollution had spread in the wake of disasters. An offshore oil rig in California fouled beaches with millions of gallons of spilled oil. Near Cleveland, Ohio, the Cuyahoga River, choking with chemical contaminants, had spontaneously burst into flames. Astronauts had begun photographing the Earth from space, heightening awareness that the Earth’s resources are finite.
In early 1970, due to heightened public concerns about deteriorating city air, natural areas littered with debris, and water supplies, and navigating bodies of water and beaches contaminated with dangerous chemicals, President Richard Nixon sent Congress a plan to consolidate many environmental responsibilities of the federal government under one agency. A new Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) was born. For most of its existence, the EPA fulfilled its mission to deal with environmental problems in a manner beyond the previous capability of government pollution control programs.
The EPA is best positioned to lead the development of reporting standards for climate change that financial institutions can incorporate in their reporting. The SEC regulates the securities markets and facilitates capital formation, helping entrepreneurs start businesses and companies grow. The EPA should do the same to activities that have harmful effects on the climate. The current trend of using voluntary reporting programs gets it all wrong, letting financial institutions determine how best to assess a firm’s environmental impacts. What does the financial sector know about the setting limits for the concentration of toxic chemicals in discharge water or the potential effects of specific air emissions?
Unfortunately, in the last several years, the U.S. EPA has drifted away from regulating climate change. Just last week (January 12, 2021), the agency set higher barriers for controlling the emissions that contribute to climate change, setting new rules that effectively block the federal government from imposing new restrictions on several heavy industries. The regulations establish new criteria for entities that are significant contributors to greenhouse gas emissions. The agency claimed that the law requires determination of who these entities are. With unmatched chutzpah and antipathy toward environmental controls, the agency declared that oil and gas producers, refiners, steelmakers, and other heavy industries don’t meet the criteria. As such, the hamstrung EPA is ostensibly prohibited from regulating these industries’ emissions under the Clean Air Act.
This abrogation of EPA’s role in protecting the environment has never been seen in any other administration. Programs and agencies elsewhere in the federal government have had their missions bent to serve polluters’ sole interests or had their scientific research halted, and their reporting suppressed. Please make no mistake about it. The Trump administration has been quite successful in some of its efforts. Fortunately, though there are anomalies, as is the case with Trump, the overall direction of our attitudes toward the environment in the last 60 years is one in which reduced emissions and sustainability have taken on ever greater importance. In future years, the EPA will hopefully once again assume its leadership role in promoting best practices and the promulgation of meaningful ESG reporting.
As of the writing of this paper, there is already some good news: A federal appeals court today, the last full day of Trump presidency, vacated the Trump administration’s rules that eased restrictions on greenhouse-gas emissions from power plants, potentially making it easier for the incoming Biden administration to reset the nation’s signature rules addressing climate change.
Until the EPA reenters the climate change business, expect that the SEC will follow the European lead and impose enhanced ESG disclosure requirements on public companies.
Software to Organize and Report ESG
To compare companies relative to their impacts on the climate, one must take a holistic approach that includes many factors. Among those to consider when assigning a score to a company are:
- The magnitude of its overall and coupled emissions to natural media
- The efficiency of its operations in water and energy usage
- Its carbon footprint
- Waste treatment operations
- The transparency and impacts of members of its supply chains
This holistic approach requires new, integrated, and interactive software tools. Such ESG software, equivalent to the ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) software that made its appearance in the early nineties, would provide complex tracking of all kinds of emissions linked to assets in real-time. We need an equivalent of the balance sheet, income statement, and cash flow (emissions flow) across all aspects of companies’ assets and activities.
Ironically, although the term ERP includes “Resource,” it has little to do with real natural resources being affected by its operation. Instead, ERP refers to companies’ software that is used to manage and integrate the critical parts of their businesses but mainly focuses on financial, human resources, and physical asset management to satisfy financial reporting, not asset emissions. ERP software applications integrate the processes needed to run a company with a single system: planning, purchasing inventory, sales, marketing, finance, and human resources. However, they do not typically integrate any technical information or activity related to emissions, waste, climate, environmental compliance, etc. Never mind that much of the ERP software in the market today is obsolete, running on the outdated technology of the seventies and eighties, and hard to integrate with anything.

Figure 5: Traditional ERP software is siloed and applications are pigeon-holed. ESG requires an all-new approach.
The traditional approach of bolting-on another application to an existing software infrastructure will not work to integrate emissions tracking, sustainability, and other environmental and sustainability-related verticals. Many ERP systems are caving in under their weight and are hugely and unnecessarily complicated. New, cloud-based Software as a Service (SaaS) technologies such as the Locus Platform are promising as they allow for the fast deployment and sharing of input, storage, and reporting tools among all key players: companies, investors, and regulators in a single system of record. One new software technology, Blockchain, is up-and-coming.
Blockchain for ESG
Though created as the digital ledger underpinning bitcoin, Blockchain has since been adopted by various industries for applications outside the realm of finance and cryptocurrency. But the potential for this technology far eclipses its current uses. Alongside the growing expectation for better ESG reporting, blockchain technology has the opportunity to enable ESG reporting to become more transparent, secure, consistent, standardized, and useful.
At first glance, the convergence of Blockchain with ESG reporting might seem to be contradictory, but a more in-depth analysis of trends shows its value. Blockchain has rapidly transformed into a financial reporting and attestation tool that has caught the attention of many key decision-makers and technology drivers. At the same time, the importance of ESG has never been more pronounced. Combining the two could be the key to making ESG reporting more straightforward and more meaningful. The broader trends of both are alike: each has been steadily making inroads into organizational management and the reporting landscape. The difference is that now, with accelerated digital transformation and automation, both broader trends have moved into a much sharper focus.
Blockchain technology is ideally suited for the complexities of tracking a global supply chain. Improving the traceability of supply chains is old news in terms of goods, but supply chains are much bigger than that. Securing the information that drives business decision making is where Blockchain can deliver significant value. Blockchain for ESG purposes is gaining traction already, with many pilot platforms being launched and tested in the last year. For example, two hospitals in the U.K. are actively using blockchain technology to help maintain the temperature of coronavirus vaccines before administering them to patients. Several off-the-shelf blockchain ledgers can provide authentication and corporate oversight systems. You can read more here: Blockchain Technology for Emissions Management.
Blockchain technology will allow companies to track resources from the first appearance in their supply chain, certifying their products’ compliance with regulations and their quality. Blockchain technology would enable government agencies to effectively aggregate emissions quantities and origins across geographies, industries, and other criteria. More importantly, all parties would need only one software system of record to avoid constant synchronization, submittals, and reporting requirements. The open question remains: Who will run it, and who will pay for it?
Though their data may be more transparent, corporations stand to benefit considerably from adopting a technology in which all their emissions and other data reside in a single system of record. Star performers, as well as laggards in their factories and supply chains, could more easily be identified.
Along the way, companies would undoubtedly lower their operating cost and, at the same time, reduce the dizzying number of unconnected, heavily supported, siloed software applications they currently operate to keep in compliance with existing environmental regulations.