Shed Light On Your Air and GHG Calculations
Locus’ Air Quality app is designed to integrate with data sources to seamlessly calculate air emissions monthly or annually.
Locus’ Air Quality app is designed to integrate with data sources to seamlessly calculate air emissions monthly or annually.
2022 has given us a wealth of new features and growth! Both of our platforms have undergone improvements to enhance our client’s user experience. Let’s look at all the new features for 2022.
1. New Site Metrics dashboard allows immediate visibility into your data with clickable mapping. This is especially powerful for customers with multiple sites where they want to keep track of site activity and usage.
2. Finding data can sometimes be overwhelming especially when you have hundreds, if not thousands, of locations and numerous analytical parameters to review. Locus added advanced database search tools to support multiple search terms and ‘exact match’ searches, making it easy to find exactly what you want with a couple of key words and a click. Never has finding the right results from large complex datasets been so easy.
3. Locus has enhanced its API functionality to enable easier integration with external BI tools, including Tableau, PowerBI, and other apps. Now, customers that rely on external business analytical tools will have quick and easy access to data to combine with other internal data sources.
4. Locus document management has been taken to the next level by allowing customers to link documents from any external library directly into their sites, monitoring locations, samples, and more. This means with a simple click, users can go to lab reports, regulatory reports, and any other current or historical document associated with the site. If you are using SharePoint, for example, to manage documents – they can be accessed directly from Locus software. Document access and security will be preserved by existing document library access controls.
5. 2022 was the year of “help”. In addition to the advanced search, Locus added a new Help Browser to provide access to comprehensive documentation for every feature of the software. It is similar to the familiar “site map”, only the links take you to help content. With this new feature, users can view help in a single location vs having to access the information on each individual screen. For new users, or infrequent users, this will be their new favorite feature.
1. Locus’ Survey/Questionnaire tool enables you to securely & easily obtain data globally without the burdens of training or maintaining user lists. The survey system effortlessly supports data entry from external organizations (such as suppliers) or even occasional users internal to your organization, with a simple link click.
2. Locus released a new pivot table tool that enables you to perform full data analysis on any query in the system. Data may be grouped and organized by any value. Output options include bar charts, heatmaps, tables, area charts, scatter charts, and tree maps. In support of the output options, Locus has improved the ability for users to create dashboards more easily.
3. Complex inspection and audit forms require branching, sophisticated, scoring, and automated responses. Locus added new question types to its inspection/ audit module, including conditional questions based on responses to one or more previous questions. Locus augmented the scoring calculation mechanism and automated creation and tracking of corrective action.
4. In today’s world, users need access to environmental data on the go. Locus augmented its mobile offerings to include configurable layouts for mobile users, with compact forms specially designed for smartphone and tablet access.
5. Today’s managers want immediate access to the data they need. Locus’ new Landing Page feature makes it simple to configure the dashboards, bookmarks, and record lists. This enables the user to review just the areas they need to see and navigate efficiently to complete the work.
MOUNTAIN VIEW, Calif., 29 November 2022 — Locus Technologies (Locus) is pleased to announce that The Port of Seattle (Port) has selected Locus’ multitenant Software as a Service (SaaS) for its Environmental Permit Compliance Tracking software. The Port of Seattle is a government agency overseeing the seaport and airport of Seattle. Their portfolio ranges from parks and waterfront real estate to one of the largest airports and container terminals on the West Coast. With Locus’ software, the Port of Seattle’s Maritime Environment & Sustainability department will track and manage compliance with their many permits associated with ongoing Maritime operations. This win represents additional work under Locus’ existing 10-year contract with the Port.
Locus’ SaaS will replace existing systems, which no longer meet the Port’s requirements. The Port will use Locus’ configurable compliance features to track, notify, and manage thousands of regulatory commitments for the Port and its facilities. Locus software provides a unified system for environmental data management and compliance and allows the flexibility to adapt to regulatory changes over the course of the contract.
“We are very pleased that Port of Seattle after selecting Locus earlier this year, recognized the power and flexibility of Locus and extended the use of Locus to include Permit Compliance. The Port selected Locus software because it meets a wide set of robust permit tracking and notification requirements for their active Maritime operations. The Port will streamline tracking of environmental compliance obligations using Locus’ SaaS with a configuration suited to their business processes,” said Neno Duplan, CEO of Locus.
Today is GIS Day, a day started in 1999 to showcase the many uses of geographical information systems (GIS). Earlier Locus blog posts have explained how GIS and maps support visualization of objects in space and over time. This post covers a specific visualization method called data dashboards.
A data dashboard is a combination of charts, maps, text, and images that enables analysis of data and thereby promotes discovery of previously unknown relationships in the data. Companies and organizations use dashboards to develop insight into the overall status of a company or of a company division, process, or product line. Dashboards are also a common function in ‘business intelligence’ applications such as Microsoft Power BI and Tableau. A printed dashboard is static, but an online dashboard can be dynamic; in a dynamic dashboard, interacting with one item on the dashboard causes the other items to update. Taken together, the visualizations on a dynamic dashboard can help you find the story in your data.
One reason dashboards are so helpful is that they allow humans to partially ‘offload’ their thinking. Cognitive research has shown that human ‘working memory’ handles at most four items at a time. A good visualization, however, reduces the number of items to process in memory.
Consider a large table of carbon dioxide emissions by country for multiple years; it can be difficult to keep all the numbers in mind if you are trying to find trends.
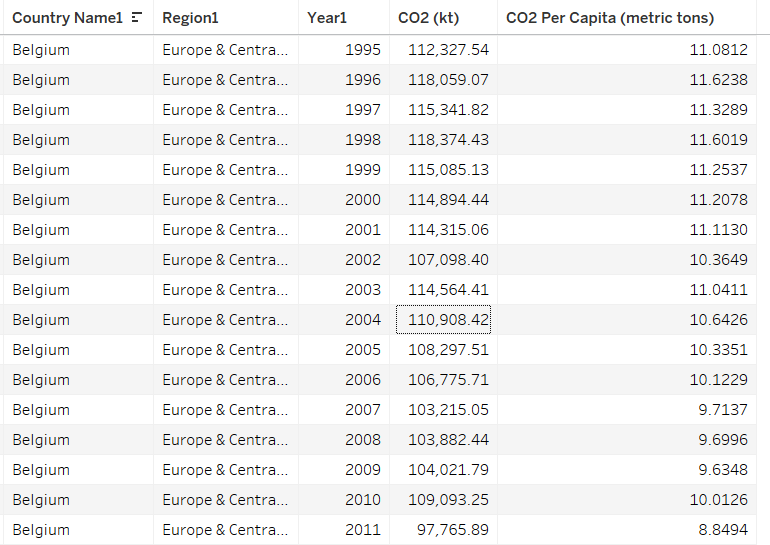
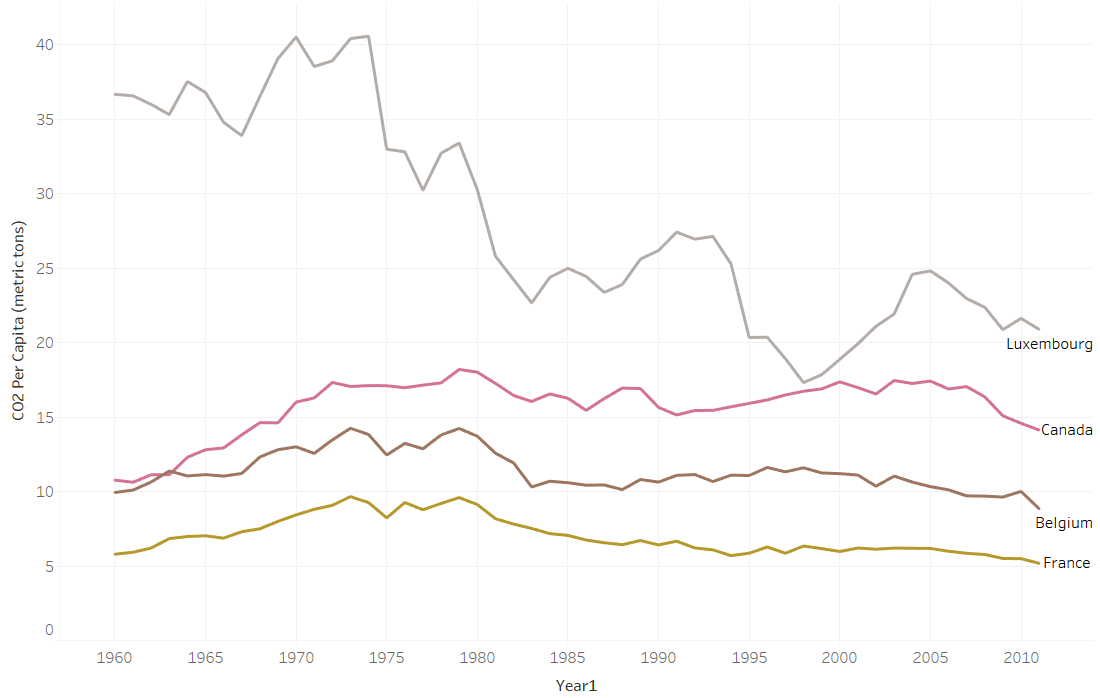
If you plot the data in a graph, however, each series of data in the chart becomes just one line on the graph. It is much easier to compare lines on the chart than to compare columns of numbers.
Now consider making a map with countries color coded by emissions. Again, for each country, the map reduces multiple numbers to a single color for that country on the map. You can compare country colors more easily than columns of numbers.
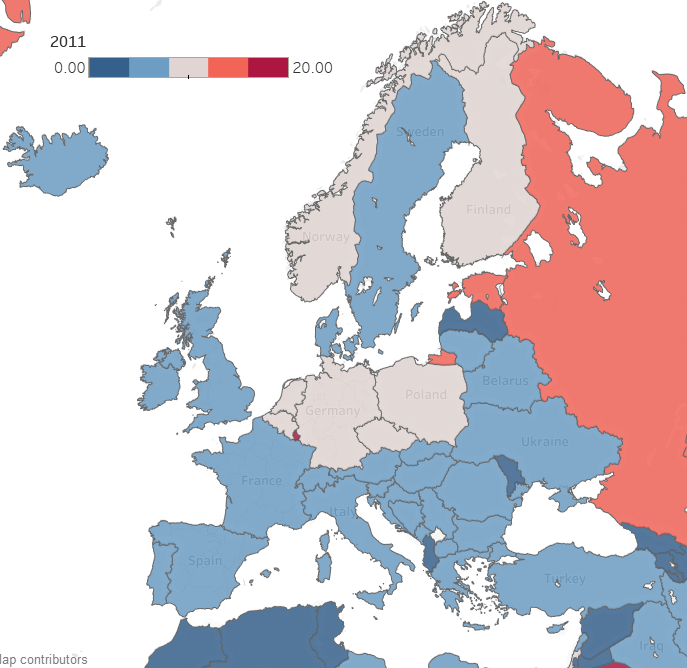
A dashboard that combines multiple visualizations further enhances data analysis. Imagine a dynamic dashboard showing you both the emissions chart and map described above. If you select a country on the map, the chart can highlight the line for that country, so you compare its emissions to other countries over time. Similarly, if you select a line on the chart for a specific country, the map can highlight the selected country to show how its emissions compare to nearby countries. This interactivity lets you drill into your data more effectively than using either the chart or the map by itself.
Here are three examples of effective dashboards that are available online:
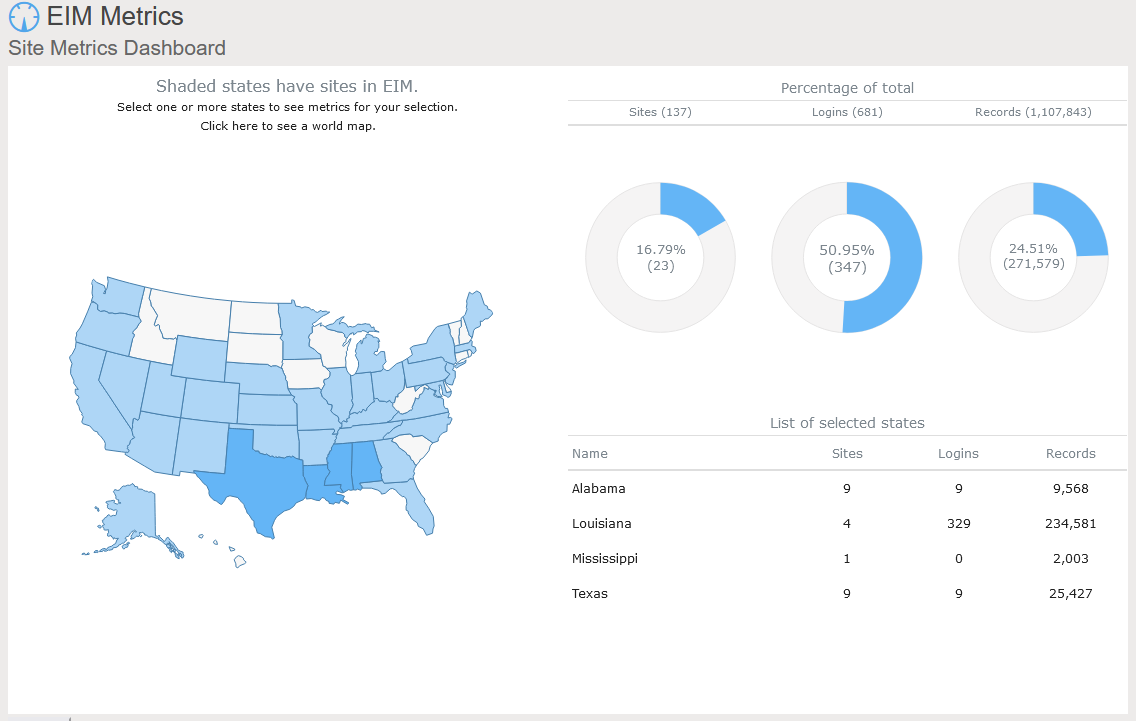
Locus includes data dashboards in our applications. One example is the Site Metrics dashboard in EIM, Locus’s cloud-based, software-as-a-service application for environmental data management. The Site Metrics dashboard lets you perform roll-up queries across your portfolio of sites. A map on the dashboard shows all states with active sites. If you select one or more states, the dashboard updates the charts and tables on the right to show total sites, user logins, and record counts. Other dashboards can support showing sample locations of certain chemicals or counts of regulatory limit exceedances.
A further example comes from the Locus Environmental Social and Governance (ESG) application. ESG metrics are becoming increasingly important measures for an organization’s performance. Data dashboards can help companies quickly visualize trends in their ESG metrics using intuitive mapping tools.
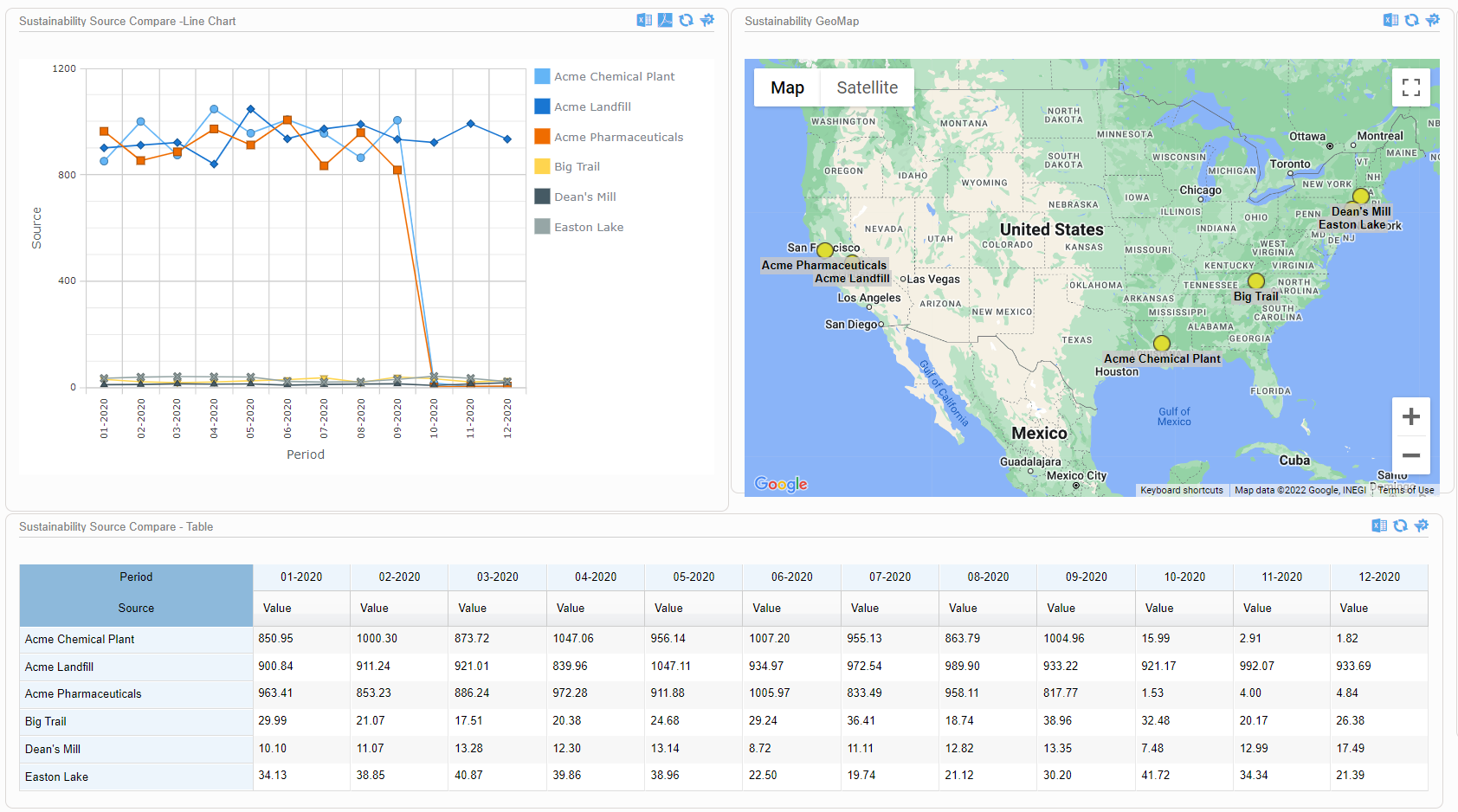
This dashboard illustrates both spatial and time trends and provides the raw data necessary for auditability and transparent decision making. Having these features on a single combined view provides users with instant access to the key inputs for ESG prioritization, planning, and project implementation.
As these examples from Locus show, data dashboards with integrated mapping are important tools for maximizing the value of your collected environmental and ESG data. For any dataset with a geographic component, it’s important to incorporate mapping elements in the outputs, to highlight trends and patterns that may not otherwise be visible in a chart or table. Modern software can combine these output formats in a way that tells the story shown by your data.
Locus GIS+ features all of the functionality you love in EIM’s classic Google Maps GIS for environmental management—integrated with the powerful cartography, interoperability, & smart-mapping features of Esri’s ArcGIS platform!
Learn more about Locus’ GIS solutions.
About the Author—Dr. Todd Pierce, Locus Technologies
Dr. Pierce manages a team of programmers tasked with development and implementation of Locus’ EIM application, which lets users manage their environmental data in the cloud using Software-as-a-Service technology. Dr. Pierce is also directly responsible for research and development of Locus’ GIS (geographic information systems) and visualization tools for mapping analytical and subsurface data. Dr. Pierce earned his GIS Professional (GISP) certification in 2010.
MOUNTAIN VIEW, Calif., 24 June 2022 — Locus Technologies (Locus) is pleased to announce that The Port of Seattle (Port) has selected Locus’s multitenant Software as a Service (SaaS) for its environmental data management and compliance software. The Port of Seattle is a government agency overseeing the seaport and airport of Seattle. Their portfolio ranges from parks and waterfront real estate to one of the largest airports and container terminals on the West Coast. With Locus’s software, The Port will streamline its environmental management across its properties. The term of this contract is ten (10) years with a contract value of over one million dollars.
The Port of Seattle competitively procured environmental software that will serve as the Port’s centralized system for managing environmental data and information, site investigations and permit compliance for Aviation and Maritime Port operations.
Locus’s cloud software will replace several existing systems, which no longer meet the Port’s requirements. Locus’s software combines the power of EIM’s environmental data analytical and reporting capabilities with Locus Platform’s configurable compliance features to track, notify, and manage regulatory commitments for the Port and its contractors. Locus software provides a unified system for environmental data management and compliance and allows the flexibility to adapt to regulatory changes over the course of the contract.
“We are very pleased that Port of Seattle recognized the power of our cloud software. The Port selected Locus software due to its robust environmental data management and compliance capabilities tested for nearly a quarter-century in the cloud. With Locus, the Port will have all data in a central data repository available on the web 24 hours a day, seven days a week. Port will reap the benefits of using Locus’ SaaS to manage and automate their environmental data, compliance, and reporting,” said Neno Duplan, CEO of Locus.
Many in our material-driven culture, particularly in Silicon Valley, assign more excellent value to companies based on how much venture capital or private equity money they have raised or how quickly their companies have grown after initial seeding, and less to founders who bootstrapped their companies from nothing and after that, positioned them for long and steady growth. Although the term means different things in different areas of knowledge, in entrepreneurship, bootstrapping is the process of starting a business with little or no external funding.
Locus has proven that how much funding a startup company has raised or how quickly it has grown are the wrong metrics to measure a company’s success, particularly in the arena of environmental compliance and data management. We bootstrapped Locus in 1997 and, without outside capital, created a new industry at the intersection of two significant trends before either was a trend: the growth in Internet usage and the growth in the acquisition, storage, and analysis of environmental information. Locus not only defined and pioneered this new space of environmental information management in the cloud but also became an industry leader leaving behind many well-funded startups with “borrowed ideas” and established ERP software companies. At every startup stage, some actions are “right” for the startup to maximize return on time, money, and effort. Fortunately, Locus took the necessary steps that allowed it to weather several recessions and market downfalls.
While bootstrapping techniques are not just limited to funding, they also apply to how companies are run. By bootstrapping Locus, we created a built-to-last, slow-burn startup that was focused on the singular goal of building a cloud-based environmental data information management system and avoided expending effort on expanding applications that the market did not need or those that we were too dependent on external help. Bootstrapping provided Locus with a strategic roadmap for achieving sustainability through customer funding (i.e., partnering with customers)—if it is essential for Locus, it must be necessary for the customer first. If it is vital for customers, they must pay for a portion of it and have “skin in the game. “We don’t build applications to attract customers. We attract customers with our ideas to build applications together” became Locus’s modus operandi: Locus was born and built with this simple philosophy.
Once Locus had built a solid customer base, Locus encouraged its paying customers to become consultants who defined the Locus product map. This strategy resulted in a rapid evolutionary expansion of Locus’ software in the marketplace. Crowdsourcing product development from customers with real-world problems has become the cornerstone of Locus’ success in the market.
Let us digress here to comment on what it takes to build an environmental database management system. In the 1990s, when Dr. Duplan was leading the development of a client-server database for his then-employer (there were no internet-based databases back then), he and others now at Locus attended a trade show where a product called Oracle Environmental or something like that was being marketed. Yes, this is the same Oracle that is now one of the largest software companies in the world, with a market cap in the hundreds of billions, revenues in the tens of billions, profits in the billions, and over 130,000 employees.
This small group of engineers and scientists wondered how they could compete against a growing behemoth like Oracle with all its programmers and financial resources. They listened to a marketing spiel and took the system for a test drive at Oracle’s booth. Their worries almost immediately vanished. What they saw was characterized by all as a system that was “a mile wide and an inch deep.” It was designed and developed by individuals with no field experience, little or no engineering or scientific expertise, and little understanding of environmental data and data flow. It claimed to touch on many different types of data (which it did) but owing to its lack of depth, it clearly could not work in the real world. Sure enough, the product was gone within a few years.
In contrast, EIM has been designed and developed by individuals with advanced degrees in civil and environmental engineering, water resources, geology, chemistry, and biology. All who are not solely computer programmers have spent serious time in the field, have overseen the drilling of boreholes and wells, planned and collected samples, verified and validated analytical data, and have created data reports for internal, external entities. These individuals are very cognizant of the vagaries of environmental data.
All these questions make sense to us, and we have an answer to them. Our deep domain expertise in such matters, coupled with our backgrounds in engineering and the sciences and our relevant work experience, has enabled us to work with our customers to build ground-breaking tools and modules for our products that work for all companies.
While other environmental software companies have come and gone—often after getting much press, only to fizzle out on broken promises and dried-up funding, Locus has never wavered from its path to provide environmental data management services to corporations and government agencies. Despite the absence of a flashy PR machine and VC or PE funding, Locus has continued to be a profitable, independent, and visionary organization, which is now considered one of the top environmental software companies in the world.
This is the fourth post highlighting the evolution of Locus Technologies over the past 25 years. The first three can be found here and here, and here. This series continues with Locus at 25 Years: Blockchain for Emissions Management.
How did Locus succeed in deploying Internet-based products and services in the environmental data sector? After several years of building and testing its first web-based systems (EIM) in the late 1990s, Locus began to market its product to organizations seeking to replace their home-grown and silo systems with a more centralized, user-friendly approach. Such companies were typically looking for strategies that eliminated their need to deploy hated and costly version updates while at the same time improving data access and delivering significant savings.
Several companies immediately saw the benefit of EIM and became early adopters of Locus’s innovative technology. Most of these companies still use EIM and are close to their 20th anniversary as a Locus client. For many years after these early adoptions, Locus enjoyed steady but not explosive growth in EIM usage.
E. M. Roger’s Diffusion of Innovation (DOI) Theory has much to offer in explaining the pattern of growth in EIM’s adoption. In the early years of innovative and disruptive technology, a few companies are what he labels innovators and early adopters. These are ones, small in number, that are willing to take a risk, that is aware of the need to make a change, and that are comfortable in adopting innovative ideas. The vast majority, according to Rogers, do not fall into one of these categories. Instead, they fall into one of the following groups: early majority, late majority, and laggards. As the adoption rate grows, there is a point at which innovation reaches critical mass. In his 1991 book “Crossing the Chasm,” Geoffrey Moore theorizes that this point lies at the boundary between the early adopters and the early majority. This tipping point between niche appeal and mass (self-sustained) adoption is simply known as “the chasm.”
Rogers identifies the following factors that influence the adoption of an innovation:
In its early years of marketing EIM, some of these factors probably considered whether EIM was accepted or not by potential clients. Our early adopters were fed up with their data stored in various incompatible silo systems to which only a few had access. They appreciated EIM’s organization, the lack of need to manage updates, and the ability to test the design on the web using a demonstration database that Locus had set up. When no sale could be made, other factors not listed by Rogers or Moore were often involved. In several cases, organizations looking to replace their environmental software had budgets for the initial purchase or licensing of a system but had insufficient monies allocated for recurring costs, as with Locus’s subscription model. One such client was so enamored with EIM that it asked if it could have the system for free after the first year. Another hurdle that Locus came up against was the unwillingness of clients at the user level to adopt an approach that could eliminate their co-workers’ jobs in their IT departments. But the most significant barriers that Locus came up against revolved around organizations’ security concerns regarding the placement of their data in the cloud.

One of the earliest versions of EIM
Oh, how so much has changed in the intervening years! The RFPs that Locus receives these days explicitly call out for a web-based system or, much less often, express no preference for a web-based or client-server system. We believe this change in attitudes toward SaaS applications has many root causes. Individuals now routinely do their banking over the web. They store their files in Dropbox and their photos on sites like Google Photos or Apple and Amazon Clouds. They freely allow vendors to store their credit card information in the cloud to avoid entering this information anew every time they visit a site. No one who keeps track of developments in the IT world can be oblivious to the explosive growth of Amazon Web Services (AWS), Salesforce, and Microsoft’s Azure. We believe most people now have more faith in the storage and backup of their files on the web than if they were to assume these tasks independently.
An early update to EIM software
Changes have also occurred in the attitudes of IT departments. The adoption of SaaS applications removes the need to perform system updates or the installation of new versions on local computers. Instead, for systems like EIM, updates only need to be completed by the vendor, and these take place at off-hours or at announced times. This saves money and eliminates headaches. A particularly nasty aspect of local, client-server systems is the often experienced nightmare when installing an updated version of one application causes failures in others that are called by this application. None of these problems typically occur with SaaS applications. In the case of EIM, all third-party applications used by it run in the cloud and are well tested by Locus before these updates go live.
Locus EIM continues to become more streamlined and user friendly over the years.
Yet another factor has driven potential clients in the direction of SaaS applications, namely, search. Initially, Locus was primarily focused on developing software tools for environmental cleanups, monitoring, and mitigation efforts. Such efforts typically involved (1) tracking vast amounts of data to demonstrate progress in the cleanup of dangerous substances at a site and (2) the increased automation of data checking and reporting to regulatory agencies.
Locus EIM handles all types of environmental data.
Before systems like EIM were introduced, most data tracking relied on inefficient spreadsheets and other manual processes. Once a mitigation project was completed, the data collected by the investigative and remediation firms remained scattered and stored in their files, spreadsheets, or local databases. In essence, the data was buried away and was not used or available to assess the impacts of future mitigation efforts and activities or to reduce ongoing operational costs. Potential opportunities to avoid additional sampling and collection of similar data were likely hidden amongst these early data “storehouses,” yet few were aware of this. The result was that no data mining was taking place or possible.
Locus EIM in 2022
The early development of EIM took place while searches on Google were relatively infrequent (see years 1999-2003 below). Currently, Google processes 3.5 billion searches a day and 1.2 trillion searches per year. Before web-based searches became possible, companies that hired consulting firms to manage their environmental data had to submit a request such as “Tell me the historical concentrations of Benzene from 1990 to the most recent sampling date in Wells MW-1 through MW-10.” An employee at the firm would then have to locate and review a report or spreadsheet or perform a search for the requested data if the firm had its database. The results would then be transmitted to the company in some manner. Such a request need not necessarily come from the company but perhaps from another consulting firm with unique expertise. These search and retrieval activities translated into prohibitive costs and delays for the company that owned the site.
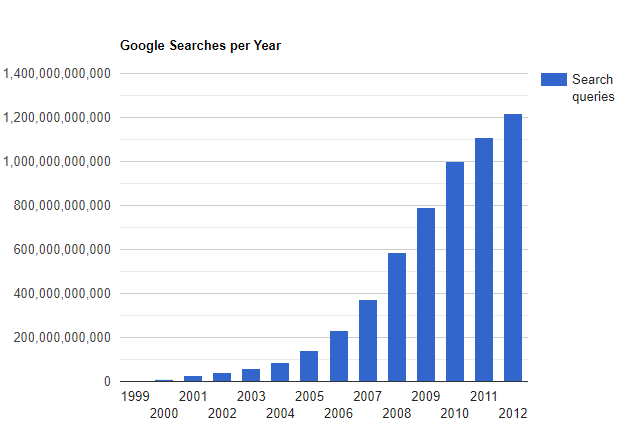
Google Searches by Year
Over the last few decades, everyone has become dependent on and addicted to web searching. Site managers expect to be able to perform their searches, but honestly, these are less frequent than we would have expected. What has changed are managers’ expectations. They hope to get responses to requests like those we have imagined above in a matter of minutes or hours, not days. They may not even expect a bill for such work. The bottom line is that the power of search on the web predisposes many companies to prefer to store their data in the cloud rather than on a spreadsheet or in their consultant’s local, inaccessible system.
The world has changed since EIM was first deployed, and as such, many more applications are now on the path, that Locus embarked on some 20 years ago. Today, Locus is the world leader in managing on-demand environmental information. Few potential customers question the merits of Locus’s approach and its built systems. In short, the software world has caught up with Locus. EIM and LP have revolutionized how environmental data is stored, accessed, managed, and reported. Locus’ SaaS applications have long been ahead of the curve in helping private, and public organizations manage their environmental data and turn their environmental data management into a competitive advantage in their operating models.
We refer to the competitive advantages of improved data quality and flow and lower operating costs. EIM’s Electronic Data Deliverable (EDD) module allows for the upload of thousands of laboratory results in a few minutes. Over 60 automated checks are performed on each reported result. Comprehensive studies conducted by two of our larger clients show savings in the millions gained from the adoption of EIM’s electronic data verification and validation modules and the ability of labs to load their EDDs directly into a staging area in the system. The use of such tools reduces much of the tedium of manual data checking and, at the same time, results both in the elimination of manually introduced errors and the reduction of throughput times (from sampling to data reporting and analysis). In short, the adoption of our systems has become a win-win for companies and their data managers alike.
This is the second post highlighting the evolution of Locus Technologies over the past 25 years. The first can be found here. This series continues with Locus at 25 Years: Locus Platform, Multitenant Architecture, the Secret of our Success.
To celebrate a milestone 25 years of success in EHS and ESG software development, we sat down with Locus President, Wes Hawthorne for a brief discussion. In this post, we ask him a series of questions highlighting the past, present and future of EHS and ESG.
One of the persistent challenges we’ve seen for the past 25 years is that the responsibilities of environmental professionals are continually expanding. Previously, almost all environmental work was localized, with facility-level permits for air, water, waste, etc. That has expanded over the years to include new regulations and reporting requirements for sustainability, social metrics, and other new compliance areas, while the old facility-level programs still continue. This has led to more pressure on environmental managers to keep up with these programs, and increased reliance on tools to manage that information. That’s where Locus has always focused our effort, to make that ever-expanding workload more manageable with modern solutions.
The current flood of interest in ESG is certainly notable as far as bringing corporate attention to the environmental field, as well as having requirements originate from the SEC here in the US. We have become accustomed to managing oversight from multiple regulatory bodies at the local, state, and federal level, but SEC would be a newcomer in our line of work. Their involvement will be accompanied by a range of new requirements that are common for the financial world, but would be unfamiliar to environmental staff.
Across other EHS fields, we are seeing increased demand for transparency in EHS functions. Overall, this is a positive move, as it brings more attention to EHS issues and develops a better EHS culture within organizations. But this also drives the need for better tools to make EHS information readily available across all levels of the organization.
As far as technologies, the ones most likely to have significant impact in the environmental field are ones that don’t require a significant capital investment. Although there are definitely some practical advantages to installing smart monitoring devices and other new technologies, procuring the funding for those purchases is often difficult for environmental professionals. Fortunately, there are still many technologies that have already been implemented successfully in other fields, but only need to be adapted for environmental purposes. Even simple changes like using web-based software in place of spreadsheets can have a huge impact on efficiency. And we haven’t yet seen the full impact of the proliferation of mobile devices on EHS functions. We are still working on new ways to take advantage of mobile devices for data collection, analysis, and communication purposes.
We’ve seen a number of innovation milestones in the past 25 years, and while we didn’t invent SaaS, we’ve been largely responsible for adapting it and perfecting it for environmental purposes. One of the major innovations we’ve integrated into our products include online GIS tools where users can easily visualize their environmental data on maps without expensive desktop software. Another one was our fully configurable software platform with built-in form, workflow, and report builders tailored for environmental purposes, which allows anyone to build and deploy environmental software applications that exactly match their needs. There have been many other innovations we’ve incorporated into our software, but these two stand out as the most impactful.
More and more, we are seeing all types of reporting being converted into pure data exchanges. Reports that used to include regulatory forms and text interpretations are being replaced with text or XML file submittals. This transition is being driven largely by availability of technology for EHS professionals to generate and read these files, but it is also promoted by regulatory agencies and other stakeholders receiving these reports. Stakeholders have less time to read volumes of interpretive text, and are becoming more skeptical of potential bias in how facts are presented in text. These are driving the need for more pure data exchanges, with increasing emphasis on quantifiable metrics. These types of reports are also more readily compared against regulatory or industry standards. For reporters, lengthy corporate reports with volumes of text and graphics are becoming less common, and the success of an organization’s programs will be increasingly reliant on robust data sets, since ultimately only the data will be reported.
There are actually a few that immediately come to mind. One reason is the nature of our continually evolving products. By providing our solutions as SaaS, our software adapts with new environmental requirements, and with new technologies. If our software was still the same as it was 25 years ago, it simply wouldn’t be sufficient for today’s requirements. Since our software is updated multiple times each year, it is difficult to notice the incremental changes, but they can be readily seen if you compare today’s software with the original in 1997. And we’re committed to continuing the development of our products as environmental needs change.
The other primary reason for our success is our excellent staff and the environmental expertise we bring to our customers. We simply could not provide the same level of support without our team of environmental engineers, scientists, geologists, chemists, and an array of others. Having that real-world understanding of environmental topics is how we’ve maintained customer relationships for multiple decades. And our software only has value because it is maintained and operated by staff who appreciate the complexity and importance of environmental work.
 Mr. Hawthorne has been with Locus since 1999, working on development and implementation of services and solutions in the areas of environmental compliance, remediation, and sustainability. As President, he currently leads the overall product development and operations of the company. As a seasoned environmental and engineering executive, Hawthorne incorporates innovative analytical tools and methods to develop strategies for customers for portfolio analysis, project implementation, and management. His comprehensive knowledge of technical and environmental compliance best practices and laws enable him to create customized, cost-effective and customer-focused solutions for the specialized needs of each customer.
Mr. Hawthorne has been with Locus since 1999, working on development and implementation of services and solutions in the areas of environmental compliance, remediation, and sustainability. As President, he currently leads the overall product development and operations of the company. As a seasoned environmental and engineering executive, Hawthorne incorporates innovative analytical tools and methods to develop strategies for customers for portfolio analysis, project implementation, and management. His comprehensive knowledge of technical and environmental compliance best practices and laws enable him to create customized, cost-effective and customer-focused solutions for the specialized needs of each customer.
Mr. Hawthorne holds an M.S. in Environmental Engineering from Stanford University and B.S. degrees in Geology and Geological Engineering from Purdue University. He is registered both as a Professional Engineer and Professional Geologist, and is also accredited as Lead Verifier for the Greenhouse Gas Emissions and Low Carbon Fuel Standard programs by the California Air Resources Board.
MOUNTAIN VIEW, CA and LOS ALAMOS, N.M., 21 April 2022 —
A significant software improvement is driving enhanced decision-making on N3B Los Alamos’ environmental cleanup at Los Alamos National Laboratory (LANL).
Samples collected of soil, sediment, water and other parts of the environment potentially contaminated by historical LANL operations now receive faster and more comprehensive validation due to software tool improvements made by N3B and leading environmental software provider Locus Technologies.
The improved software functionality is part of a database containing all data associated with environmental cleanup at LANL. N3B implements the legacy portion of that cleanup on behalf of the U.S. Department of Energy’s Environmental Management Los Alamos Field Office. Legacy cleanup involves the remediation of contamination from Manhattan Project and Cold War era weapons development and government-sponsored nuclear research.
The software improvement ensures more thorough validation of results from third-party analytical laboratories that analyze collected samples for various contaminants, which may include metals, radionuclides, high explosives, and human-made chemicals used in industrial solvents, known as volatile organic compounds.
The types of contaminants potentially found in these samples, along with levels of contamination, guide N3B’s cleanup.
“Decisions on legacy environmental cleanup are based on the validity and quality of this analytical data, including the nature and extent of contamination, how much we clean up, and how well the interim remediation measure is working to mitigate migration of the hexavalent chromium groundwater plume,” said Sean Sandborgh, sample and data management director at N3B. “If you have lapses in the quality of analytical data, that could have negative effects on our program’s decision-making capacity.”
Once N3B personnel collect samples from potentially contaminated sites, they send them to a third-party laboratory for analysis. When N3B receives the results of those samples, they perform a validation process to demonstrate data is sufficient in quality and supports defensible decision-making.
“Validation consists of determining the data quality and the extent to which external analytical laboratories accurately and completely reported all sample and quality control results,” Sandborgh said.
The process can catch data quality issues that may result from incorrect calibration of equipment in a laboratory or issues inherent in the samples, such as improper preservation or temperature control, that mask detection of contaminants.
With the improved functionality, more of the validation process is automated, instead of manually conducted, which means a lower likelihood of errors.
Another crucial improvement is the ability to evaluate sample results containing radioactive material at lower activity concentrations, which provides quick information on the potential for low levels of radionuclide activity.
The improved functionality is also being used by LANL’s management and operating contractor, Triad, and will soon be used by the New Mexico Environment Department Oversight Bureau.
The software improvement saved N3B 265 hours of labor and more than $25,000 in taxpayer dollars since its launch nearly one year ago.
“As we’ve done for the past 25 years, Locus is committed to continually improving our solutions for the often costly and complex data review process,” said Locus Technologies President Wes Hawthorne. “We are proud to enable a data-forward approach with a focus on accuracy that results in confident and correct decisions.”
“The quality and defensibility of environmental data generated from sampling activities is a key component of an effective remediation process,” said Sandborgh. “When the automated data review is used in conjunction with manual examination of sample data packages, we meet and exceed our data quality requirements.”
ABOUT N3B Los Alamos
N3B manages the 10-year, $1.4 billion Los Alamos Legacy Cleanup Contract for the U.S. Department of Energy Environmental Management’s Los Alamos Field Office. N3B is responsible for cleaning up contamination that resulted from LANL operations before 1999. N3B personnel also package and ship radioactive and hazardous waste off-site for permanent disposal.
There are two promising technologies that are about to change how we aggregate and manage EHS+S data: artificial intelligence (AI) and blockchain. When it comes to technology, history has consistently shown that the cost will always decrease, and its impact will increase over time. We still lack access to enough global information to allow AI to make a significant dent in global greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions by merely providing better tools for emissions management. For example, the vast majority of energy consumption is wasted on water treatment and movement. AI can help optimize both. Along the way, water quality management becomes an add-on app.
AI is a collective term for technologies that can sense their environment, think, learn, and act in response to what they’re detecting and their objectives. Possible applications include (1) Automation of routine tasks like sampling and analyses of water samples, (2) Segregation of waste disposal streams based on the waste containers content, (3) Augmentation of human decision-making, and (4) Automation of water treatment systems. AI systems can greatly aid the process of discovery – processing and analyzing vast amounts of data for the purposes of spotting and acting on patterns, skills that are difficult for humans to match. AI can be harnessed in a wide range of EHS compliance activities and situations to contribute to managing environmental impacts and climate change. Some examples of applications include permit interpretation and response to regulatory agencies, precision sampling, predicting natural attenuation of chemicals in water or air, managing sustainable supply chains, automating environmental monitoring and enforcement, and enhanced sampling and analysis based on real-time weather forecasts. Applying AI in water resource prediction, management, and monitoring can help to ameliorate the global water crisis by reducing or eliminating waste, as well as lowering costs and lessening environmental impacts. A similar analogy holds for air emissions management.
The onset of blockchain technology will have an even bigger impact. It will first liberate data and, second, it will decentralize monitoring while simultaneously centralizing emissions management. It may sound contradictory, but we need to decentralize in order to centralize management and aggregate relevant data across corporations and governmental organizations without jeopardizing anyone’s privacy. That is the power of blockchain technology. Blockchain technology will eliminate the need for costly synchronization among stakeholders: corporations, regulators, consultants, labs, and the public. What we need is secure and easy access to any data with infinite scalability. It is inevitable that blockchain technology will become more accessible with reduced infrastructure over the next few decades. My use of reduced architecture here refers to a replacement of massive centralized databases controlled by one of the big four internet companies using the hub-and-spoke model concept with a device-to-device communication with no intermediaries.
This post was originally published in Environmental Business Journal in June of 2020.
299 Fairchild Drive
Mountain View, CA 94043
P: +1 (650) 960-1640
F: +1 (415) 360-5889
Locus Technologies provides cloud-based environmental software and mobile solutions for EHS, sustainability management, GHG reporting, water quality management, risk management, and analytical, geologic, and ecologic environmental data management.
