Locus EIM
How did Locus succeed in deploying Internet-based products and services in the environmental data sector? After several years of building and testing its first web-based systems (EIM) in the late 1990s, Locus began to market its product to organizations seeking to replace their home-grown and silo systems with a more centralized, user-friendly approach. Such companies were typically looking for strategies that eliminated their need to deploy hated and costly version updates while at the same time improving data access and delivering significant savings.
Several companies immediately saw the benefit of EIM and became early adopters of Locus’s innovative technology. Most of these companies still use EIM and are close to their 20th anniversary as a Locus client. For many years after these early adoptions, Locus enjoyed steady but not explosive growth in EIM usage.
Triumph of the SaaS Model
E. M. Roger’s Diffusion of Innovation (DOI) Theory has much to offer in explaining the pattern of growth in EIM’s adoption. In the early years of innovative and disruptive technology, a few companies are what he labels innovators and early adopters. These are ones, small in number, that are willing to take a risk, that is aware of the need to make a change, and that are comfortable in adopting innovative ideas. The vast majority, according to Rogers, do not fall into one of these categories. Instead, they fall into one of the following groups: early majority, late majority, and laggards. As the adoption rate grows, there is a point at which innovation reaches critical mass. In his 1991 book “Crossing the Chasm,” Geoffrey Moore theorizes that this point lies at the boundary between the early adopters and the early majority. This tipping point between niche appeal and mass (self-sustained) adoption is simply known as “the chasm.”
Rogers identifies the following factors that influence the adoption of an innovation:
- Relative Advantage – The degree to which an innovation is seen as better than the idea, program, or product it replaces.
- Compatibility – How consistent the innovation is with the potential adopters’ values, experiences, and needs.
- Complexity – How difficult innovation is to understand and use.
- Trialability – The extent to which the innovation can be tested or experimented with before a commitment to adoption.
- Observability – The extent to which the innovation provides tangible results.
In its early years of marketing EIM, some of these factors probably considered whether EIM was accepted or not by potential clients. Our early adopters were fed up with their data stored in various incompatible silo systems to which only a few had access. They appreciated EIM’s organization, the lack of need to manage updates, and the ability to test the design on the web using a demonstration database that Locus had set up. When no sale could be made, other factors not listed by Rogers or Moore were often involved. In several cases, organizations looking to replace their environmental software had budgets for the initial purchase or licensing of a system but had insufficient monies allocated for recurring costs, as with Locus’s subscription model. One such client was so enamored with EIM that it asked if it could have the system for free after the first year. Another hurdle that Locus came up against was the unwillingness of clients at the user level to adopt an approach that could eliminate their co-workers’ jobs in their IT departments. But the most significant barriers that Locus came up against revolved around organizations’ security concerns regarding the placement of their data in the cloud.

One of the earliest versions of EIM
Oh, how so much has changed in the intervening years! The RFPs that Locus receives these days explicitly call out for a web-based system or, much less often, express no preference for a web-based or client-server system. We believe this change in attitudes toward SaaS applications has many root causes. Individuals now routinely do their banking over the web. They store their files in Dropbox and their photos on sites like Google Photos or Apple and Amazon Clouds. They freely allow vendors to store their credit card information in the cloud to avoid entering this information anew every time they visit a site. No one who keeps track of developments in the IT world can be oblivious to the explosive growth of Amazon Web Services (AWS), Salesforce, and Microsoft’s Azure. We believe most people now have more faith in the storage and backup of their files on the web than if they were to assume these tasks independently.
An early update to EIM software
Changes have also occurred in the attitudes of IT departments. The adoption of SaaS applications removes the need to perform system updates or the installation of new versions on local computers. Instead, for systems like EIM, updates only need to be completed by the vendor, and these take place at off-hours or at announced times. This saves money and eliminates headaches. A particularly nasty aspect of local, client-server systems is the often experienced nightmare when installing an updated version of one application causes failures in others that are called by this application. None of these problems typically occur with SaaS applications. In the case of EIM, all third-party applications used by it run in the cloud and are well tested by Locus before these updates go live.
Locus EIM continues to become more streamlined and user friendly over the years.
Yet another factor has driven potential clients in the direction of SaaS applications, namely, search. Initially, Locus was primarily focused on developing software tools for environmental cleanups, monitoring, and mitigation efforts. Such efforts typically involved (1) tracking vast amounts of data to demonstrate progress in the cleanup of dangerous substances at a site and (2) the increased automation of data checking and reporting to regulatory agencies.
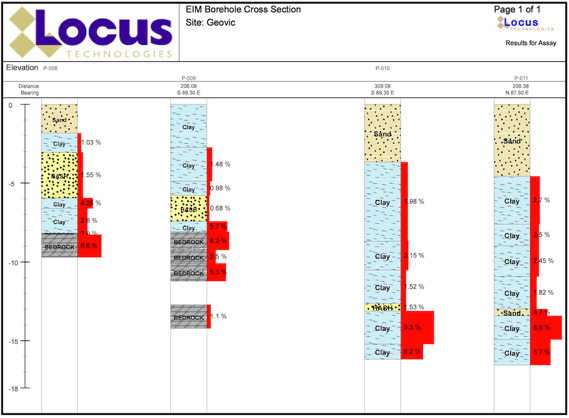
Locus EIM handles all types of environmental data.
Before systems like EIM were introduced, most data tracking relied on inefficient spreadsheets and other manual processes. Once a mitigation project was completed, the data collected by the investigative and remediation firms remained scattered and stored in their files, spreadsheets, or local databases. In essence, the data was buried away and was not used or available to assess the impacts of future mitigation efforts and activities or to reduce ongoing operational costs. Potential opportunities to avoid additional sampling and collection of similar data were likely hidden amongst these early data “storehouses,” yet few were aware of this. The result was that no data mining was taking place or possible.
Locus EIM in 2022
The early development of EIM took place while searches on Google were relatively infrequent (see years 1999-2003 below). Currently, Google processes 3.5 billion searches a day and 1.2 trillion searches per year. Before web-based searches became possible, companies that hired consulting firms to manage their environmental data had to submit a request such as “Tell me the historical concentrations of Benzene from 1990 to the most recent sampling date in Wells MW-1 through MW-10.” An employee at the firm would then have to locate and review a report or spreadsheet or perform a search for the requested data if the firm had its database. The results would then be transmitted to the company in some manner. Such a request need not necessarily come from the company but perhaps from another consulting firm with unique expertise. These search and retrieval activities translated into prohibitive costs and delays for the company that owned the site.
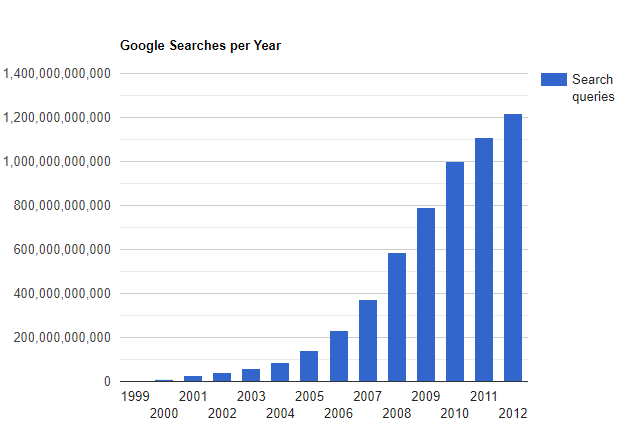
Google Searches by Year
Over the last few decades, everyone has become dependent on and addicted to web searching. Site managers expect to be able to perform their searches, but honestly, these are less frequent than we would have expected. What has changed are managers’ expectations. They hope to get responses to requests like those we have imagined above in a matter of minutes or hours, not days. They may not even expect a bill for such work. The bottom line is that the power of search on the web predisposes many companies to prefer to store their data in the cloud rather than on a spreadsheet or in their consultant’s local, inaccessible system.
The world has changed since EIM was first deployed, and as such, many more applications are now on the path, that Locus embarked on some 20 years ago. Today, Locus is the world leader in managing on-demand environmental information. Few potential customers question the merits of Locus’s approach and its built systems. In short, the software world has caught up with Locus. EIM and LP have revolutionized how environmental data is stored, accessed, managed, and reported. Locus’ SaaS applications have long been ahead of the curve in helping private, and public organizations manage their environmental data and turn their environmental data management into a competitive advantage in their operating models.
We refer to the competitive advantages of improved data quality and flow and lower operating costs. EIM’s Electronic Data Deliverable (EDD) module allows for the upload of thousands of laboratory results in a few minutes. Over 60 automated checks are performed on each reported result. Comprehensive studies conducted by two of our larger clients show savings in the millions gained from the adoption of EIM’s electronic data verification and validation modules and the ability of labs to load their EDDs directly into a staging area in the system. The use of such tools reduces much of the tedium of manual data checking and, at the same time, results both in the elimination of manually introduced errors and the reduction of throughput times (from sampling to data reporting and analysis). In short, the adoption of our systems has become a win-win for companies and their data managers alike.
This is the second post highlighting the evolution of Locus Technologies over the past 25 years. The first can be found here. This series continues with Locus at 25 Years: Locus Platform, Multitenant Architecture, the Secret of our Success.
![]()






 Mr. Hawthorne has been with Locus since 1999, working on development and implementation of services and solutions in the areas of environmental compliance, remediation, and sustainability. As President, he currently leads the overall product development and operations of the company. As a seasoned environmental and engineering executive, Hawthorne incorporates innovative analytical tools and methods to develop strategies for customers for portfolio analysis, project implementation, and management. His comprehensive knowledge of technical and environmental compliance best practices and laws enable him to create customized, cost-effective and customer-focused solutions for the specialized needs of each customer.
Mr. Hawthorne has been with Locus since 1999, working on development and implementation of services and solutions in the areas of environmental compliance, remediation, and sustainability. As President, he currently leads the overall product development and operations of the company. As a seasoned environmental and engineering executive, Hawthorne incorporates innovative analytical tools and methods to develop strategies for customers for portfolio analysis, project implementation, and management. His comprehensive knowledge of technical and environmental compliance best practices and laws enable him to create customized, cost-effective and customer-focused solutions for the specialized needs of each customer.